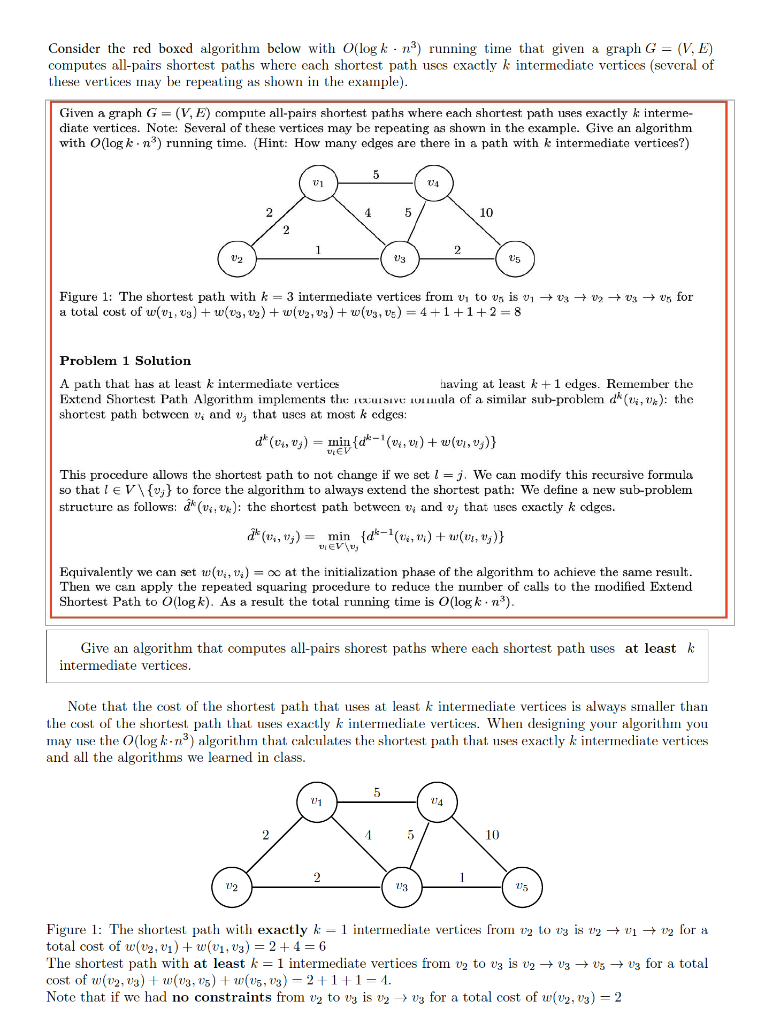
Consider the red boxed algorithm below with O(log kn) running time that given a graph G = (V, E) computes all-pairs shortest paths where cach shortest path uses cxactly k intermediate vertices (several of these vertices may be repeating as shown in the example). Given a graph G = (V, E) compute all-pairs shortest paths where each shortest path uses exactly k interme- diate vertices. Note: Several of these vertices may be repeating as shown in the example. Give an algorithm with O(log kn) running time. (Hint: How many edges are there in a path with k intermediate vertices?) 5 2 5 10 2 1 2 212 Us Us Figure 1: The shortest path with k = 3 intermediate vertices from vi to v; is v1 + 0 + 0 + 03 + vfor a total cost of (01, 23) + w(03, 12) + W(V2, V3) + (U3, vs) = 4+1+1+2 = 8 Problem 1 Solution A path that has at least k intermediate vertices having at least k +1 edges. Remember the Extend Shortest Path Algorithm implements the Sive cumala of a similar sub-problem d(04, 0x): the shortest path between vi and U, that uses at most k cdges: d*(04,0y) = min{c-(040) + (v1,v3)} This procedure allows the shortest path to not change if we set 1 = j. We can modify this recursive formula so that I eV {v} to force the algorithm to always extend the shortest path: We define a new sub-problem structure as follows: dk (V4.uk): the shortest path betwocn v; and v; that uses cxactly k cdges. * (1, 1) = min {d6-(,0) + (11,3)} DEV Equivalently we can set w(, ) = c at the initialization phase of the algorithm to achieve the same result. Then we can apply the repeated squaring procedure to reduce the number of calls to the modified Extend Shortest Path to O(log k). As a result the total running time is O(log kn). Give an algorithm that computes all-pairs shorest paths where each shortest path uses at least k intermediate vertices. Note that the cost of the shortest path that uses at least k intermediate vertices is always smaller than the cost of the shortest path that uses exactly k intermediate vertices. When designing your algorithm you may use the O(logk.n) algorithm that calculates the shortest path that uses exactly k intermediate vertices and all the algorithms we learned in class. 24 2 1 3 10 13 25 Figure 1: The shortest path with exactly h 1 intermediate vertices from v2 to vy is vu +01+ v2 for a total cost of w(v2,) + w(V1, V3) = 2+4= 6 The shortest path with at least k = 1 intermediate vertices from Uz to vz is v2 + 03 Vs + 03 for a total cost of w(02, 03) + w(03, 05) + (05, 03) - 2+1+1=1. Note that if we had no constraints from Uz to vy is vy 23 for a total cost of w(v2,v3) = 2







