Question
Consider the search tree given below. The letter next to a node is the name of the (state represented by that) node. The number in
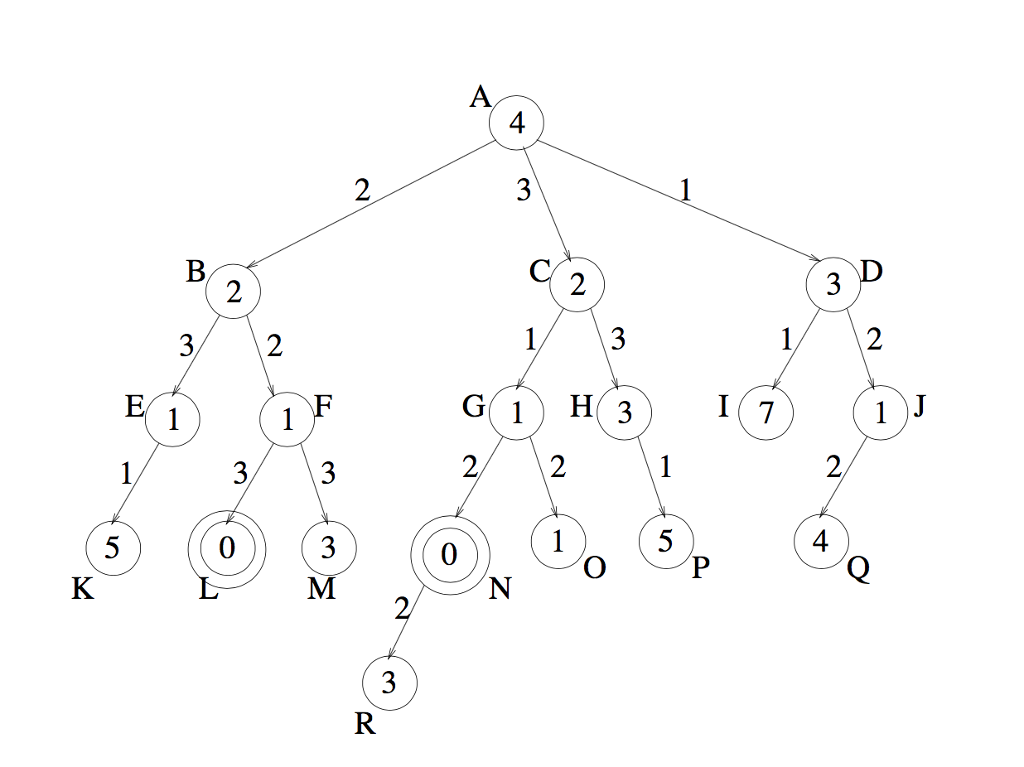
Consider the search tree given below. The letter next to a node is the name of the (state represented by that) node. The number in each node n is the heuristic estimate, h(n), of the cost of getting from n to the least-cost goal. The number on each edge (n1, n2) is the step cost of going from state n1 to state n2. The actual cost of going from a node n1 to a node n2 along a connecting path p is the sum of the step costs along p. The initial node is A. Goal nodes are represented by double circles.
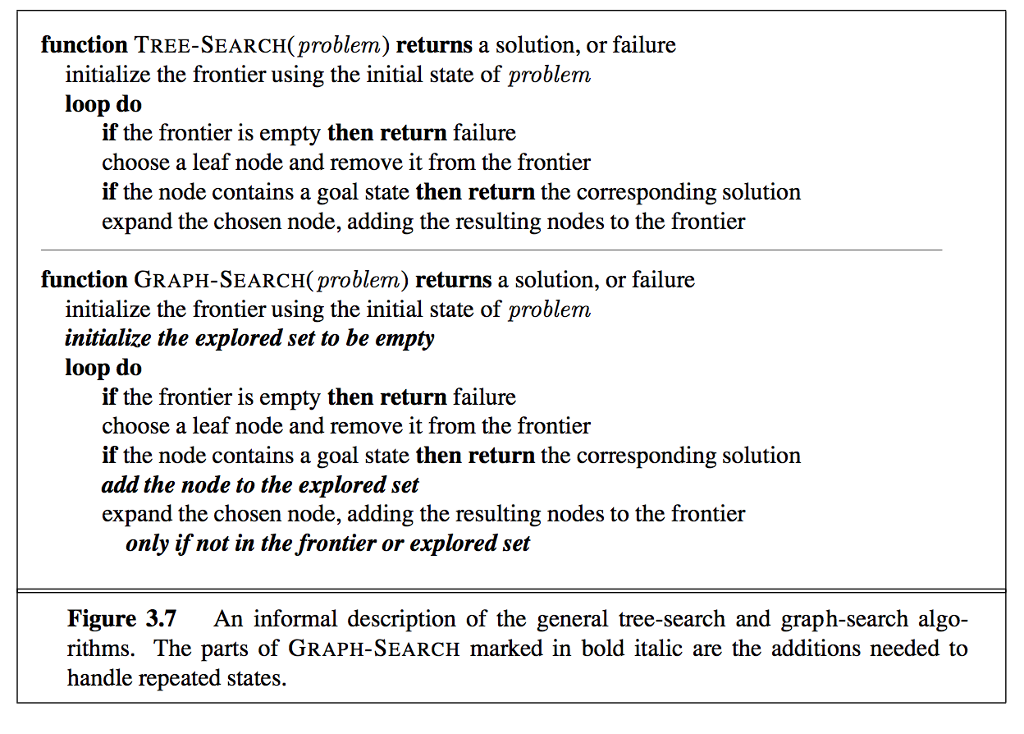
1. Using the general tree-search algorithm in Figure 3.7 of the textbook, perform a search of the tree according to each of the following search strategies.
(a) Breadth-first
(b) Uniform cost
(c) Greedy best-first
(d) A*
(e) Hill-climbing (For this tree, smaller values are better)
(f) Local beam search with number of nodes k = 2 and initial nodes A and H (Again, smaller values are better)
Treat the frontier as a priority queue ordered by an appropriate evaluation function. For each strategy:
Specify what evaluation function and additional restrictions on the queue are needed for the general algorithm in Figure 3.7 to implement that strategy.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


