Question
Consider the simplified process shown in the figure below, which is designed to treat a gasphase mixture of trichloroethylene (TCE) in air by degrading the
Consider the simplified process shown in the figure below, which is designed to treat a gasphase mixture of trichloroethylene (TCE) in air by degrading the TCE within a porous catalyst layer of 0.50 cm thickness lining one side of a wellmixed chamber. The inlet composition of TCE is 5.0 mole%, but the treated gas exiting the process must contain no more than 2.0 mole% TCE. The process is carried out at 300 C and 1.0 atm total system pressure. At these conditions, the degradation of TCE within the porous catalyst layer is approximated as a homogeneous firstorder reaction process with rate constant (k) of 1.5 s1. The effective diffusion coefficient of TCE in air within the porous layer is 0.080 cm2/s. The gas mixing within the chamber is sufficiently high so that the gas space over the catalyst layer is well mixed and convective (boundary layer) resistances are minimized, resulting in
cAo = cA = cAs .
A) What is the mole fraction of TCE in the porous catalyst layer at z = L, the point where the porous catalyst layer is attached to its nonporous support surface?
B) If the process must be designed to remove 0.20 gmole TCE/s from the gas stream, what is the required external surface area (S) of the catalyst layer? 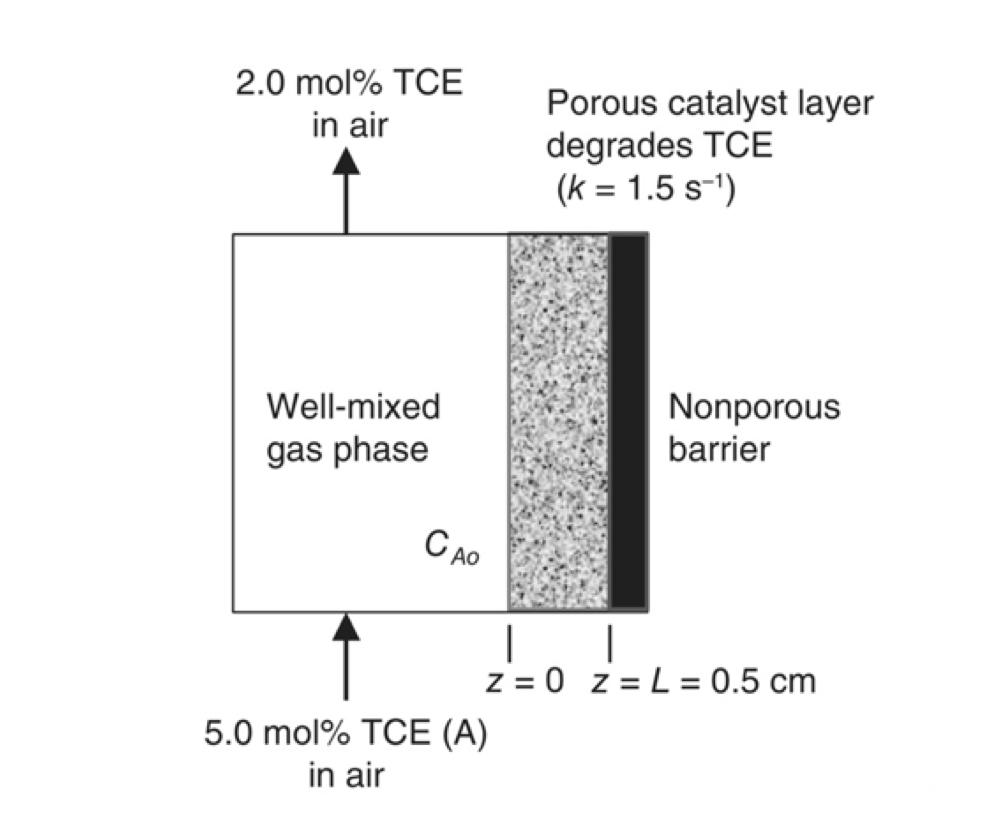
5.0 mol\% TCE (A) in air
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


