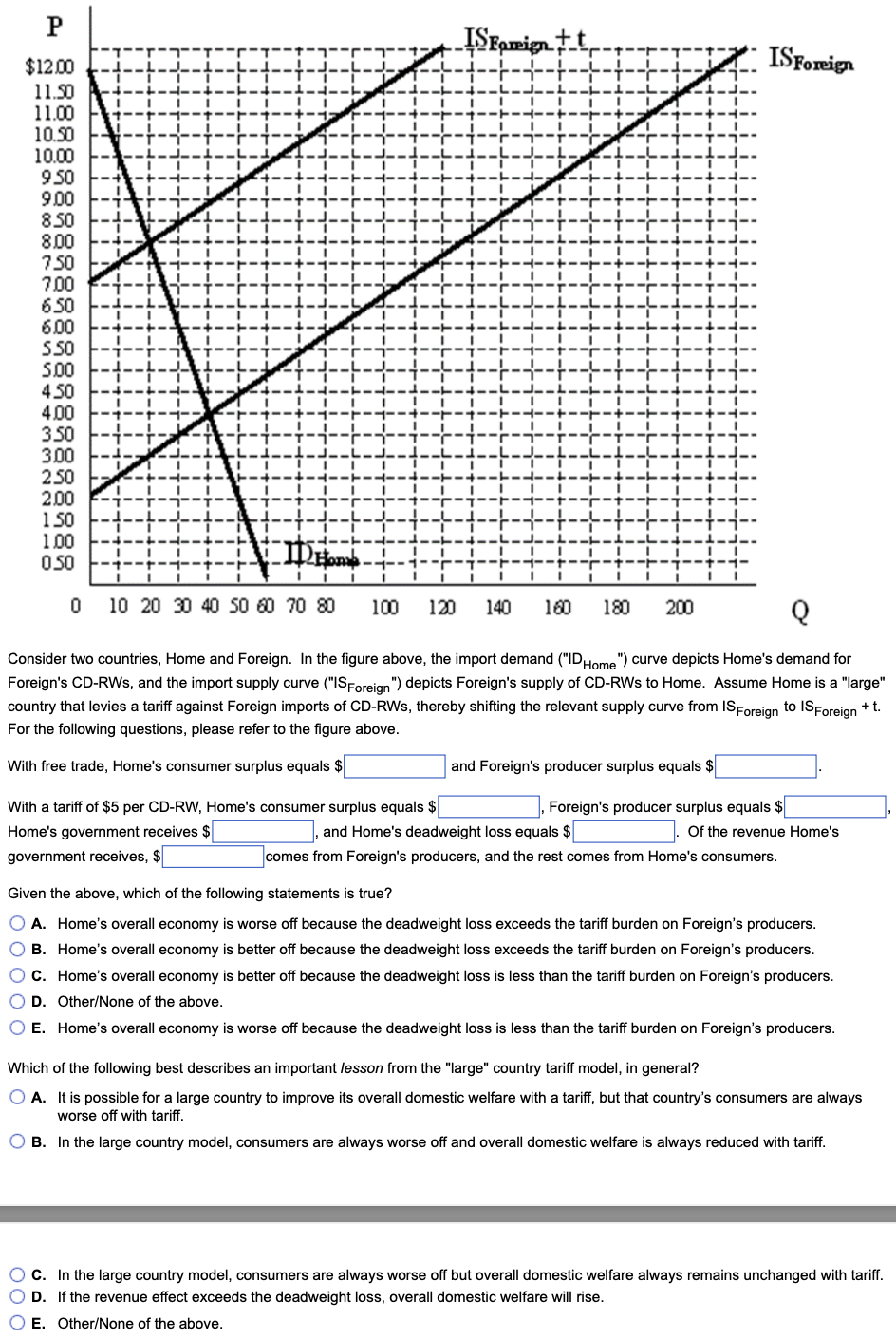
Consider two countries, Home and Foreign. In the figure above, the import demand ("ID Home ")curvedepictsHomesdemandfor Foreign's CD-RWs, and the import supply curve ("IS Foreign") depicts Foreign's supply of CD-RWs to Home. Assume Home is a "large" country that levies a tariff against Foreign imports of CD-RWs, thereby shifting the relevant supply curve from IS Foreign to IS Foreign +t. For the following questions, please refer to the figure above. With free trade, Home's consumer surplus equals $ and Foreign's producer surplus equals $ With a tariff of $5 per CD-RW, Home's consumer surplus equals $ , Foreign's producer surplus equals $ Home's government receives \$ , and Home's deadweight loss equals $ Of the revenue Home's government receives, $ zomes from Foreign's producers, and the rest comes from Home's consumers. Given the above, which of the following statements is true? A. Home's overall economy is worse off because the deadweight loss exceeds the tariff burden on Foreign's producers. B. Home's overall economy is better off because the deadweight loss exceeds the tariff burden on Foreign's producers. C. Home's overall economy is better off because the deadweight loss is less than the tariff burden on Foreign's producers. D. Other/None of the above. E. Home's overall economy is worse off because the deadweight loss is less than the tariff burden on Foreign's producers. Which of the following best describes an important lesson from the "large" country tariff model, in general? A. It is possible for a large country to improve its overall domestic welfare with a tariff, but that country's consumers are always worse off with tariff. B. In the large country model, consumers are always worse off and overall domestic welfare is always reduced with tariff. C. In the large country model, consumers are always worse off but overall domestic welfare always remains unchanged with tariff. D. If the revenue effect exceeds the deadweight loss, overall domestic welfare will rise. E. Other/None of the above. Consider two countries, Home and Foreign. In the figure above, the import demand ("ID Home ")curvedepictsHomesdemandfor Foreign's CD-RWs, and the import supply curve ("IS Foreign") depicts Foreign's supply of CD-RWs to Home. Assume Home is a "large" country that levies a tariff against Foreign imports of CD-RWs, thereby shifting the relevant supply curve from IS Foreign to IS Foreign +t. For the following questions, please refer to the figure above. With free trade, Home's consumer surplus equals $ and Foreign's producer surplus equals $ With a tariff of $5 per CD-RW, Home's consumer surplus equals $ , Foreign's producer surplus equals $ Home's government receives \$ , and Home's deadweight loss equals $ Of the revenue Home's government receives, $ zomes from Foreign's producers, and the rest comes from Home's consumers. Given the above, which of the following statements is true? A. Home's overall economy is worse off because the deadweight loss exceeds the tariff burden on Foreign's producers. B. Home's overall economy is better off because the deadweight loss exceeds the tariff burden on Foreign's producers. C. Home's overall economy is better off because the deadweight loss is less than the tariff burden on Foreign's producers. D. Other/None of the above. E. Home's overall economy is worse off because the deadweight loss is less than the tariff burden on Foreign's producers. Which of the following best describes an important lesson from the "large" country tariff model, in general? A. It is possible for a large country to improve its overall domestic welfare with a tariff, but that country's consumers are always worse off with tariff. B. In the large country model, consumers are always worse off and overall domestic welfare is always reduced with tariff. C. In the large country model, consumers are always worse off but overall domestic welfare always remains unchanged with tariff. D. If the revenue effect exceeds the deadweight loss, overall domestic welfare will rise. E. Other/None of the above







