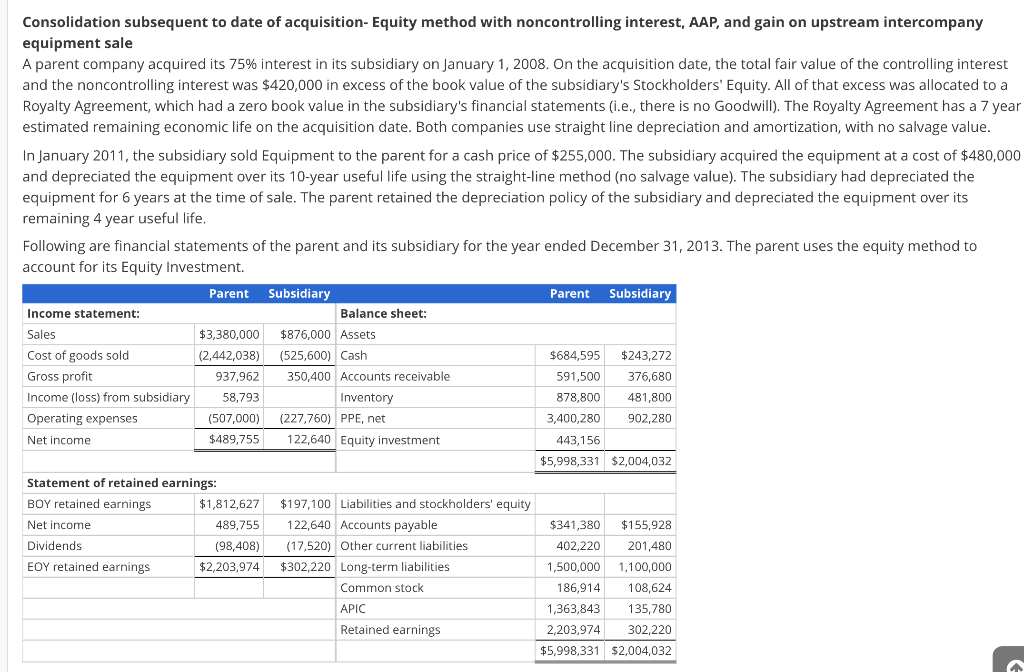
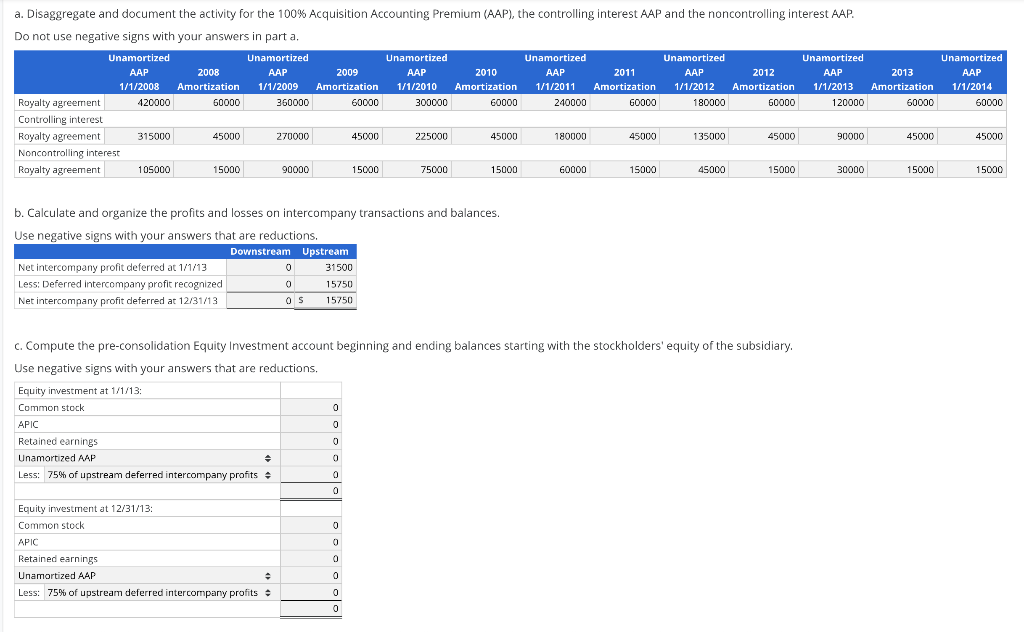
Consolidation subsequent to date of acquisition-Equity method with noncontrolling interest, AAP, and gain on upstream intercompany equipment sale A parent company acquired its 75% interest in its subsidiary on January 1, 2008. On the acquisition date, the total fair value of the controlling interest and the noncontrolling interest was $420,000 in excess of the book value of the subsidiary's Stockholders' Equity. All of that excess was allocated to a Royalty Agreement, which had a zero book value in the subsidiary's financial statements (i.e., there is no Goodwill). The Royalty Agreement has a 7 year estimated remaining economic life on the acquisition date. Both companies use straight line depreciation and amortization, with no salvage value. In January 2011, the subsidiary sold Equipment to the parent for a cash price of $255,000. The subsidiary acquired the equipment at a cost of $480,000 and depreciated the equipment over its 10-year useful life using the straight-line method (no salvage value). The subsidiary had depreciated the equipment for 6 years at the time of sale. The parent retained the depreciation policy of the subsidiary and depreciated the equipment over its remaining 4 year useful life. Following are financial statements of the parent and its subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2013. The parent uses the equity method to account for its Equity Investment. Parent Subsidiary Parent Subsidiary Income statement: Balance sheet: Sales $3,380,000 $876,000 Assets Cost of goods sold (2,442,038) (525,600) Cash $684,595 $243,272 Gross profit 937.962 350,400 Accounts receivable 591,500 376,680 Income (loss) from subsidiary 58,793 Inventory 878,800 481,800 Operating expenses (507,000) (227,760) PPE, net 3,400,280 902,280 Net income $489,755 122,640 Equity investment 443,156 $5,998,331 $2,004,032 Statement of retained earnings: BOY retained earnings $1,812,627 $197,100 Liabilities and stockholders' equity Net income 489,755 122,640 Accounts payable $341,380 $155,928 Dividends (98,408) (17,520) Other current liabilities 402,220 201,480 EOY retained earnings $2,203,974 $302,220 Long-term liabilities 1,500,000 1,100,000 Common stock 186,914 108,624 APIC 1,363,843 135,780 Retained earnings 2,203,974 302,220 $5,998,331 $2,004,032 a. Disaggregate and document the activity for the 100% Acquisition Accounting Premium (AAP), the controlling interest AAP and the noncontrolling interest AAP. Do not use negative signs with your answers in part a, Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 1/1/2008 Amortization 1/1/2009 Amortization 1/1/2010 Amortization 1/1/2011 Amortization 1/1/2012 Amortization 1/1/2013 Royalty agreement 420000 60000 360000 60000 300000 60000 240000 60000 180000 60000 120000 Controlling interest Royalty agreement 315000 270000 45000 225000 45000 180000 45000 135000 45000 90000 Noncontrolling interest Royalty agreement 105000 15000 90000 15000 75000 15000 60000 15000 45000 15000 30000 2013 Amortization 60000 Unamortized 1/1/2014 60000 45000 45000 45000 15000 15000 b. Calculate and organize the profits and losses on intercompany transactions and balances. Use negative signs with your answers that are reductions, Downstream Upstream Net intercompany profit deferred at 1/1/13 0 0 31500 Less: Deferred intercompany profit recognized 0 15750 Net intercompany profit deferred at 12/31/13 os 15750 C. Compute the pre-consolidation Equity Investment account beginning and ending balances starting with the stockholders' equity of the subsidiary. Use negative signs with your answers that are reductions, Equity investment at 1/1/13: Common stock APIC 0 Retained earnings Unamortized AAP Less: 75% of upstream deferred intercompany profits 0 0 0 0 Equity investment at 12/31/13: Common stock APIC 0 0 0 0 Retained earnings Unamortized AAP . Less: 75% of upstream deferred intercompany profits 0 0 Consolidation subsequent to date of acquisition-Equity method with noncontrolling interest, AAP, and gain on upstream intercompany equipment sale A parent company acquired its 75% interest in its subsidiary on January 1, 2008. On the acquisition date, the total fair value of the controlling interest and the noncontrolling interest was $420,000 in excess of the book value of the subsidiary's Stockholders' Equity. All of that excess was allocated to a Royalty Agreement, which had a zero book value in the subsidiary's financial statements (i.e., there is no Goodwill). The Royalty Agreement has a 7 year estimated remaining economic life on the acquisition date. Both companies use straight line depreciation and amortization, with no salvage value. In January 2011, the subsidiary sold Equipment to the parent for a cash price of $255,000. The subsidiary acquired the equipment at a cost of $480,000 and depreciated the equipment over its 10-year useful life using the straight-line method (no salvage value). The subsidiary had depreciated the equipment for 6 years at the time of sale. The parent retained the depreciation policy of the subsidiary and depreciated the equipment over its remaining 4 year useful life. Following are financial statements of the parent and its subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2013. The parent uses the equity method to account for its Equity Investment. Parent Subsidiary Parent Subsidiary Income statement: Balance sheet: Sales $3,380,000 $876,000 Assets Cost of goods sold (2,442,038) (525,600) Cash $684,595 $243,272 Gross profit 937.962 350,400 Accounts receivable 591,500 376,680 Income (loss) from subsidiary 58,793 Inventory 878,800 481,800 Operating expenses (507,000) (227,760) PPE, net 3,400,280 902,280 Net income $489,755 122,640 Equity investment 443,156 $5,998,331 $2,004,032 Statement of retained earnings: BOY retained earnings $1,812,627 $197,100 Liabilities and stockholders' equity Net income 489,755 122,640 Accounts payable $341,380 $155,928 Dividends (98,408) (17,520) Other current liabilities 402,220 201,480 EOY retained earnings $2,203,974 $302,220 Long-term liabilities 1,500,000 1,100,000 Common stock 186,914 108,624 APIC 1,363,843 135,780 Retained earnings 2,203,974 302,220 $5,998,331 $2,004,032 a. Disaggregate and document the activity for the 100% Acquisition Accounting Premium (AAP), the controlling interest AAP and the noncontrolling interest AAP. Do not use negative signs with your answers in part a, Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized Unamortized 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 1/1/2008 Amortization 1/1/2009 Amortization 1/1/2010 Amortization 1/1/2011 Amortization 1/1/2012 Amortization 1/1/2013 Royalty agreement 420000 60000 360000 60000 300000 60000 240000 60000 180000 60000 120000 Controlling interest Royalty agreement 315000 270000 45000 225000 45000 180000 45000 135000 45000 90000 Noncontrolling interest Royalty agreement 105000 15000 90000 15000 75000 15000 60000 15000 45000 15000 30000 2013 Amortization 60000 Unamortized 1/1/2014 60000 45000 45000 45000 15000 15000 b. Calculate and organize the profits and losses on intercompany transactions and balances. Use negative signs with your answers that are reductions, Downstream Upstream Net intercompany profit deferred at 1/1/13 0 0 31500 Less: Deferred intercompany profit recognized 0 15750 Net intercompany profit deferred at 12/31/13 os 15750 C. Compute the pre-consolidation Equity Investment account beginning and ending balances starting with the stockholders' equity of the subsidiary. Use negative signs with your answers that are reductions, Equity investment at 1/1/13: Common stock APIC 0 Retained earnings Unamortized AAP Less: 75% of upstream deferred intercompany profits 0 0 0 0 Equity investment at 12/31/13: Common stock APIC 0 0 0 0 Retained earnings Unamortized AAP . Less: 75% of upstream deferred intercompany profits 0 0








