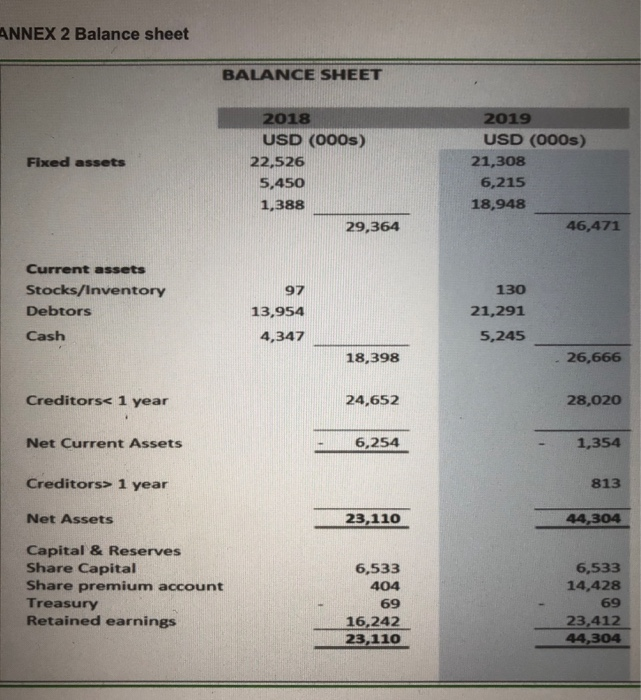
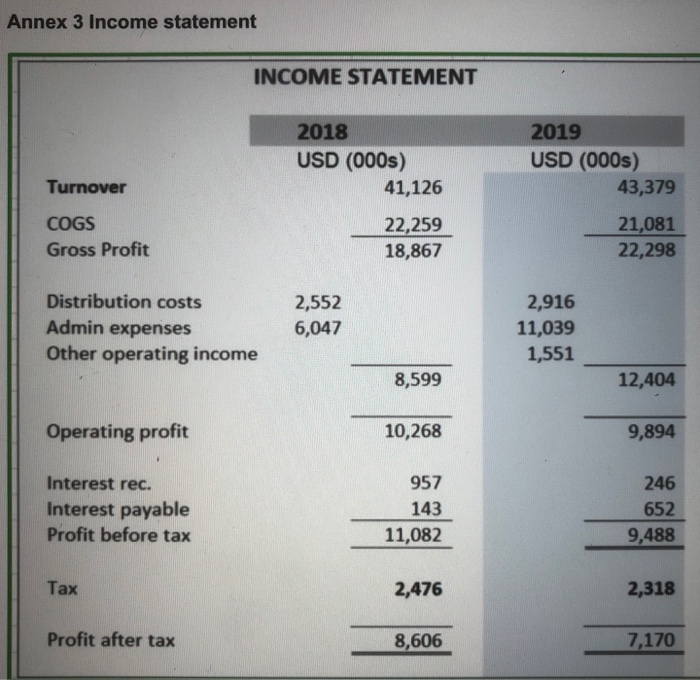
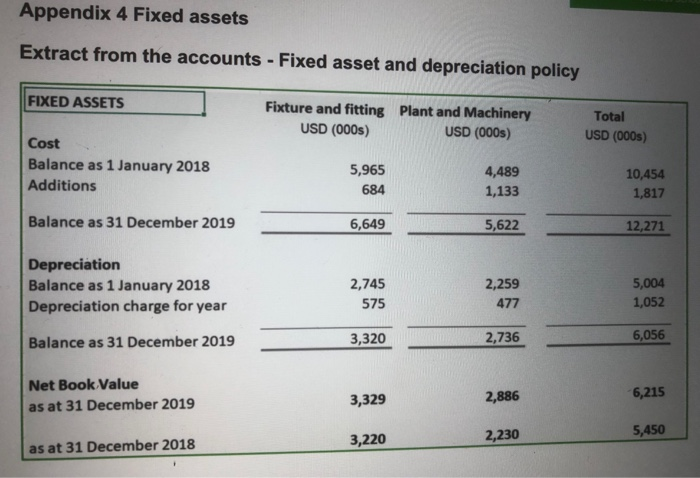
CONTEXT Felix Pharmaceuticals Inc. is a diagnostic company. They are a small start-up and have some promising developments for covid- 19 diagnostic tools. They have just completed their accounts for December 2019 but they did not finish the audit, as unfortunately most of their key staff in the finance team are ill due to the pandemic. You have been recruited as a consultant by the CEO as recent graduate from EU Busi- ness School to assist in this difficult situation. The CEO is a very bright scientist but gets very afraid of accounts. Your job is to get him through this difficult period with your deep insights about finance and accounting. ANNEX 1 - The CEO's questions. The CFO before she became ill prepared a budget but you need to prepare the journals and explain each one. The CEO is also worried about the financial situation of the com- pany once these transactions are processed. The following journals are required to be prepared and explanations required. 1. 1 Feb. They plan to borrow $1,300,000 from Valley Bank, signing a 90-days, 1,5% Note Payable on 1 February 2020. (Use 360 day rule) II. I March. The wants to sell some old plant and machinery for $500,000, receiving $100,000 cash and a five-year, 12 percent note receivable for the remaining bal- ance in one year. (Use 360 day rule) III. 1 May. The paid Valley Bank the Note Payable plus the accrued interest. IV. 1 June. They plan to issue 100,000 ordinary shares of par value $0.01 at $20 each V. 1 Oct they plan to purchase fixture and fitting for $1,500,000 with residual value of $200,000 at the end of its economic life. VI. 1 December - they plan to buy 20,000 ordinary shares at $15. VII. 31 December a. Calculate the depreciation charge at 31 December for item bought on 1 Oc- tober. b. The interest receivable for item sold on 1 March Instructions - Your client has asked you to prepare the following for the report: 1. Is the company healthy?: Using ratio analysis examine the financial statements for 2018 and 2019 of the company and provide insights on profitability, solvency, ROE and leverage (25%) 2. Transactions planned: Prepare the required journals for transaction and put these in the annex to your report. However, put a small explanation for each jour- nals in the report and how these may affect earlier ratios analysed. (40%) 3. Understanding Finance (30%): The CEO needs you to explain the following concepts which deeply trouble him: a. What is advantage and disadvantages between raising money from debt and equity? b. What is purpose of Treasury shares? C. Explain the benefits and downside of different depreciation policies such as straight line and declining method? d. Explain what is financial leverage and its advantage and disadvantage. The remaining marks, 5% are for overall professional presentation of the report. ANNEX 2 Balance sheet BALANCE SHEET Fixed assets 2018 USD (000s) 22,526 5,450 1,388 29,364 2019 USD (000s) 21,308 6,215 18,948 46,471 Current assets Stocks/Inventory Debtors 97 13,954 130 21,291 5,245 Cash 4,347 18,398 26,666 Creditors 1 year 813 Net Assets 23,110 44,304 Capital & Reserves Share Capital Share premium account Treasury Retained earnings 6,533 404 69 16,242 23,110 6,533 14,428 69 23,412 44,304 Annex 3 Income statement INCOME STATEMENT 2018 USD (000s) 41,126 Turnover 2019 USD (000s) 43,379 21,081 22,298 COGS Gross Profit 22,259 18,867 Distribution costs Admin expenses Other operating income 2,552 6,047 2,916 11,039 1,551 8,599 12,404 Operating profit 10,268 9,894 Interest rec. Interest payable Profit before tax 957 143 11,082 246 652 9,488 Tax 2,476 2,318 Profit after tax 8,606 7,170 Appendix 4 Fixed assets Extract from the accounts - Fixed asset and depreciation policy FIXED ASSETS Fixture and fitting Plant and Machinery USD (000s) USD (000s) Total USD (000s) Cost Balance as 1 January 2018 Additions 5,965 684 4,489 1,133 10,454 1,817 Balance as 31 December 2019 6,649 5,622 12,271 Depreciation Balance as 1 January 2018 Depreciation charge for year 2,745 575 2,259 477 5,004 1,052 3,320 Balance as 31 December 2019 2,736 6,056 Net Book Value as at 31 December 2019 3,329 2,886 6,215 2,230 5,450 3,220 as at 31 December 2018 1.6. Tangible fixed assets Tangible fixed assets are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses Leases in which the Company assumes substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership of the leased asset are classified as finance leases. All other leases are classified as operating leases. Leased assets acquired by way of finance lease are stated on initial recognition at an amount equal to the lower of their fair value and the present value of the minimum lease payments at inception of the lease, including any incremental costs directly attributable to negotiating and arranging the lease. At initial recognition a finance lease liability is recognised equal to the fair value of the leased asset or, if lower, the present value of the minimum lease payments. The present value of the minimum lease payments is calculated using the interest rate implicit in the lease. Lease payments are accounted for as described at 1.13 below. The company assesses at each reporting date whether tangible fixed assets (including those leased under a finance lease) are impaired. Depreciation is charged to the profit and loss account on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of each part of an item of tangible fixed assets. Leased assets are depreciated over the shorter of the lease term and their useful lives. Land is not depreciated. The estimated useful lives are as follows: Fixtures and fittings - 8 years Plant and machinery - 8 years Office equipment 8 years Included within office equipment - Hardware - 4 years, Software - 3 years Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed if there is an indication of a significant change since last annual reporting date in the pattern by which the company expects to consume an asset's future economic benefits. Appendix 5 Share capital CAPITAL AND RESERVES Share capital In issuance at 1 January 2019 Issuance for cash Ordinary shares- Numbe 653,292,526 1 In issue at 31December 2019 653,292,527 2018 USD (000s) 2019 USD (000s Allotted called up and fully paid 653,292,527 Ordinary shares of $0.01 each 6,533 6,533 CONTEXT Felix Pharmaceuticals Inc. is a diagnostic company. They are a small start-up and have some promising developments for covid- 19 diagnostic tools. They have just completed their accounts for December 2019 but they did not finish the audit, as unfortunately most of their key staff in the finance team are ill due to the pandemic. You have been recruited as a consultant by the CEO as recent graduate from EU Busi- ness School to assist in this difficult situation. The CEO is a very bright scientist but gets very afraid of accounts. Your job is to get him through this difficult period with your deep insights about finance and accounting. ANNEX 1 - The CEO's questions. The CFO before she became ill prepared a budget but you need to prepare the journals and explain each one. The CEO is also worried about the financial situation of the com- pany once these transactions are processed. The following journals are required to be prepared and explanations required. 1. 1 Feb. They plan to borrow $1,300,000 from Valley Bank, signing a 90-days, 1,5% Note Payable on 1 February 2020. (Use 360 day rule) II. I March. The wants to sell some old plant and machinery for $500,000, receiving $100,000 cash and a five-year, 12 percent note receivable for the remaining bal- ance in one year. (Use 360 day rule) III. 1 May. The paid Valley Bank the Note Payable plus the accrued interest. IV. 1 June. They plan to issue 100,000 ordinary shares of par value $0.01 at $20 each V. 1 Oct they plan to purchase fixture and fitting for $1,500,000 with residual value of $200,000 at the end of its economic life. VI. 1 December - they plan to buy 20,000 ordinary shares at $15. VII. 31 December a. Calculate the depreciation charge at 31 December for item bought on 1 Oc- tober. b. The interest receivable for item sold on 1 March Instructions - Your client has asked you to prepare the following for the report: 1. Is the company healthy?: Using ratio analysis examine the financial statements for 2018 and 2019 of the company and provide insights on profitability, solvency, ROE and leverage (25%) 2. Transactions planned: Prepare the required journals for transaction and put these in the annex to your report. However, put a small explanation for each jour- nals in the report and how these may affect earlier ratios analysed. (40%) 3. Understanding Finance (30%): The CEO needs you to explain the following concepts which deeply trouble him: a. What is advantage and disadvantages between raising money from debt and equity? b. What is purpose of Treasury shares? C. Explain the benefits and downside of different depreciation policies such as straight line and declining method? d. Explain what is financial leverage and its advantage and disadvantage. The remaining marks, 5% are for overall professional presentation of the report. ANNEX 2 Balance sheet BALANCE SHEET Fixed assets 2018 USD (000s) 22,526 5,450 1,388 29,364 2019 USD (000s) 21,308 6,215 18,948 46,471 Current assets Stocks/Inventory Debtors 97 13,954 130 21,291 5,245 Cash 4,347 18,398 26,666 Creditors 1 year 813 Net Assets 23,110 44,304 Capital & Reserves Share Capital Share premium account Treasury Retained earnings 6,533 404 69 16,242 23,110 6,533 14,428 69 23,412 44,304 Annex 3 Income statement INCOME STATEMENT 2018 USD (000s) 41,126 Turnover 2019 USD (000s) 43,379 21,081 22,298 COGS Gross Profit 22,259 18,867 Distribution costs Admin expenses Other operating income 2,552 6,047 2,916 11,039 1,551 8,599 12,404 Operating profit 10,268 9,894 Interest rec. Interest payable Profit before tax 957 143 11,082 246 652 9,488 Tax 2,476 2,318 Profit after tax 8,606 7,170 Appendix 4 Fixed assets Extract from the accounts - Fixed asset and depreciation policy FIXED ASSETS Fixture and fitting Plant and Machinery USD (000s) USD (000s) Total USD (000s) Cost Balance as 1 January 2018 Additions 5,965 684 4,489 1,133 10,454 1,817 Balance as 31 December 2019 6,649 5,622 12,271 Depreciation Balance as 1 January 2018 Depreciation charge for year 2,745 575 2,259 477 5,004 1,052 3,320 Balance as 31 December 2019 2,736 6,056 Net Book Value as at 31 December 2019 3,329 2,886 6,215 2,230 5,450 3,220 as at 31 December 2018 1.6. Tangible fixed assets Tangible fixed assets are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses Leases in which the Company assumes substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership of the leased asset are classified as finance leases. All other leases are classified as operating leases. Leased assets acquired by way of finance lease are stated on initial recognition at an amount equal to the lower of their fair value and the present value of the minimum lease payments at inception of the lease, including any incremental costs directly attributable to negotiating and arranging the lease. At initial recognition a finance lease liability is recognised equal to the fair value of the leased asset or, if lower, the present value of the minimum lease payments. The present value of the minimum lease payments is calculated using the interest rate implicit in the lease. Lease payments are accounted for as described at 1.13 below. The company assesses at each reporting date whether tangible fixed assets (including those leased under a finance lease) are impaired. Depreciation is charged to the profit and loss account on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of each part of an item of tangible fixed assets. Leased assets are depreciated over the shorter of the lease term and their useful lives. Land is not depreciated. The estimated useful lives are as follows: Fixtures and fittings - 8 years Plant and machinery - 8 years Office equipment 8 years Included within office equipment - Hardware - 4 years, Software - 3 years Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed if there is an indication of a significant change since last annual reporting date in the pattern by which the company expects to consume an asset's future economic benefits. Appendix 5 Share capital CAPITAL AND RESERVES Share capital In issuance at 1 January 2019 Issuance for cash Ordinary shares- Numbe 653,292,526 1 In issue at 31December 2019 653,292,527 2018 USD (000s) 2019 USD (000s Allotted called up and fully paid 653,292,527 Ordinary shares of $0.01 each 6,533 6,533