Question
Convert the following C program's functions from pointers to array operations: #include #include #pragma warning(disable : 4996) // Read before you start: // Do not
Convert the following C program's functions from pointers to array operations:
#include
#include
#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
// Read before you start:
// Do not modify any part of this program that you are given. Doing so may cause you to fail automated test cases.
// You are given a partially complete program. Your job is to complete the functions in order for this program to work successfully.
// You should complete this homework assignment using Microsoft Visual Studios 2013 (or a later version).
// All instructions are given above the required functions, please read them and follow them carefully.
// If you modify the function return types or parameters, you will fail the automated test cases.
// You can assume that all inputs are valid. Ex: If prompted for a char, the input will be a char.
// Global Macro Values
#define NUM_STRINGS 5
#define STRING_LENGTH 32
// Forward Declarations
void initializeStrings(char[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH]);
void encryptStrings(char[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH], int);
void decryptStrings(char[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH], int);
void swapStrings(char[STRING_LENGTH], char[STRING_LENGTH]);
void sortStrings(char[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH]);
void printStrings(char[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH]);
// Problem 0: initializeStrings (5 points)
// Traverse the 2D array of characters variable 'strings' (in the main program) and set all 32 characters in each of
// the 5 char arrays to a null terminator so that there is a 5 row and 32 column 2D array full of null terminators.
// The null terminator is represented by the character value '\0' and is used to denote the end of a string.
// This will come in use later in the program when you will need to print the 2D array of characters.
void initializeStrings(char strings[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH])
{
int i;
int j;
for(i = 0; i
{
for (j = 0; j
{
strings[i][j] ='\0';
}
}
}
// Problem 1: encryptStrings (5 points)
// Rewrite this function to perform the same task as in hw03, using only pointer operations.
// You must use pointer operations only. If you use array operations, you will recieve no credit for this part.
// You may use the code you submitted for hw03 or you may use the solution code for hw03.
//
// Traverse the 2D array of characters variable 'strings' and encrypt each string using the integer value 'key'.
// In order to encrypt the 2D array of characters, we will shift those ASCII characters forward by the integer value of 'key'.
// If the string is "hello" and key = 2, we will shift those characters forward in ASCII by 2 and the result will be "jgnnq".
// The case above is an example of a string that has alphabetical letters in the encrypted and decrypted string.
// Once the value of 'key' gets larger, you will extend past alphabetical characters and reach non-alphabetical characters.
// NOTE: DO NOT encrypt the null terminator characters. Use the null terminators to find the end of each array of characters.
void encryptStrings(char strings[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH], int key)
{
int i;
int j;
for (i = 0; i
{
for (j = 0; j
{
*(*(strings + i) + j) += key;
}
}
}
// Problem 2: decryptStrings (5 points)
// Rewrite this function to perform the same task as in hw03, using only pointer operations.
// You must use pointer operations only. If you use array operations, you will recieve no credit for this part.
// You may use the code you submitted for hw03 or you may use the solution code for hw03.
//
// Traverse the 2D array of characters variable 'strings' and decrypt each string using the integer value 'key'.
// In order to decrypt the 2D array of characters, we will shift those ASCII characters backwards by the integer value of 'key'.
// If the string is "jgnnq" and key = 2, we will shift those characters backward in ASCII by 2 and the result will be "hello".
// NOTE: DO NOT decrypt the null terminator characters. Use the null terminators to find the end of each array of characters.
// HINT: This should be very similiar to the encryption function defined above in Problem 2.
void decryptStrings(char strings[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH], int key)
{
int i;
int j;
for (i = 0; i
{
for (j = 0; j
{
*(*(strings + i) + j) -= key;
}
}
}
void swapStrings(char string1[STRING_LENGTH], char string2[STRING_LENGTH])
{
char temp[STRING_LENGTH];
strcpy(temp, string1);
strcpy(string1, string2);
strcpy(string2, temp);
}
// Problem 3: sortStrings (10 points)
// Rewrite this function to perform the same task as in hw03, using only pointer operations.
// You must use pointer operations only. If you use array operations, you will recieve no credit for this part.
// You can use the swapStrings() function if you'd like, but are not required to do so.
// You may use the code you submitted for hw03 or you may use the solution code for hw03.
//
// Sort the 5 strings contained in the 2D character array parameter labeled "strings".
// Sort the strings based on their ASCII character value (use strcmp to compare strings).
// NOTE: You MUST incorporate your "swapStrings" function to recieve full points for this part.
// See the output provided in the word document for example input and output.
void sortStrings(char strings[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH])
{
int min;
int i;
int j;
for (i = 0; i
{
min = i; // set initial min index
for (j = i + 1; j
{
if (strcasecmp(*(strings + min), *(strings + j)) > 0)
{
min = j; // set new min index
}
}
swapStrings(*(strings + min), *(strings + i)); // swap strings
}
}
void printStrings(char strings[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH])
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i
{
printf("%s ", strings[i]);
}
}
// You should study and understand how this main function works.
// Do not modify it in any way, there is no implementation needed here.
void main()
{
char strings[NUM_STRINGS][STRING_LENGTH]; // will store 5 strings each with a max length of 32
int key, i;
char input[STRING_LENGTH];
initializeStrings(strings);
printf("Assignment 3: 2D Character Arrays ");
for (i = 0; i
{
printf("Enter the next String: "); // prompt for string
fgets(input, sizeof(input), stdin); // store input string
input[strlen(input) - 1] = '\0'; // convert trailing ' ' char to '\0' (null terminator)
strcpy(strings[i], input); // copy input to 2D strings array
}
printf("Enter a key value for encryption: "); // prompt for integer
scanf("%d", &key); // store integer
encryptStrings(strings, key);
printf(" Encrypted Strings: ");
printStrings(strings);
sortStrings(strings);
decryptStrings(strings, key);
printf(" Sorted Strings: ");
printStrings(strings);
i = getchar(); // remove the character ' '
i = getchar(); // keep console open
}
Sample Outputs:
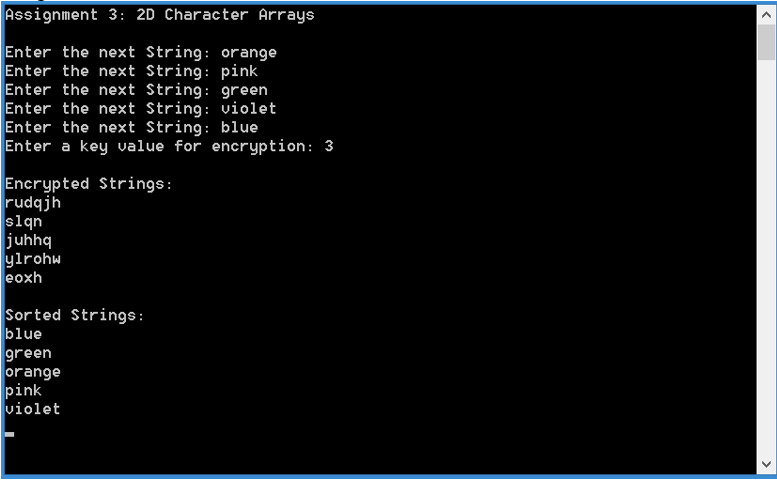
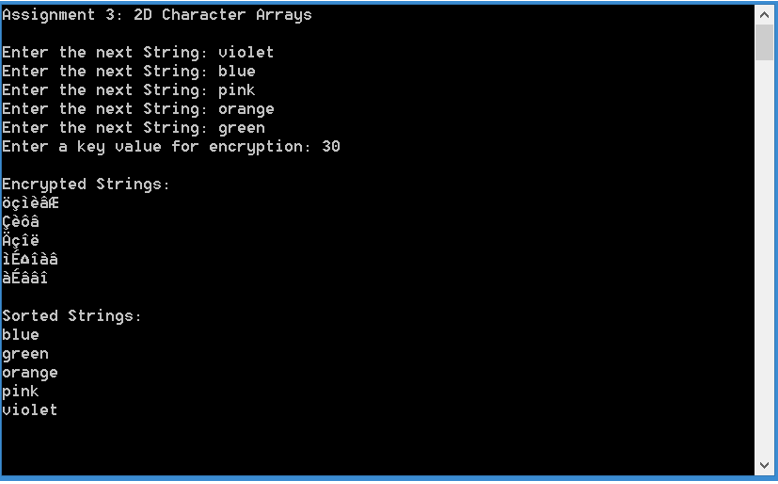
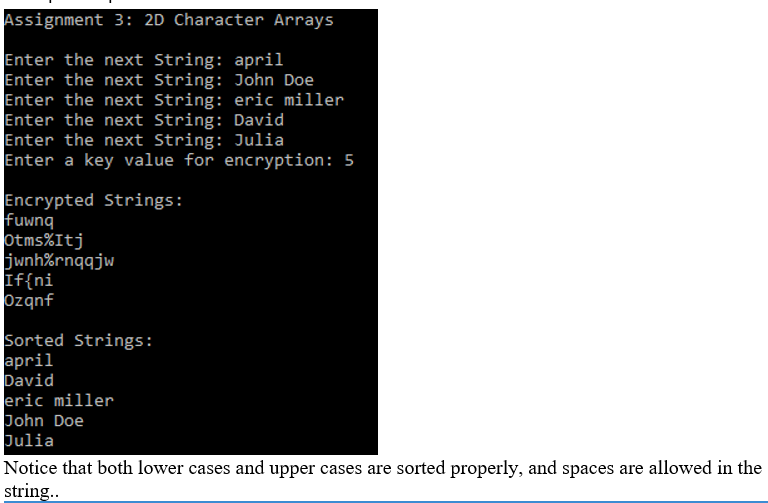
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


