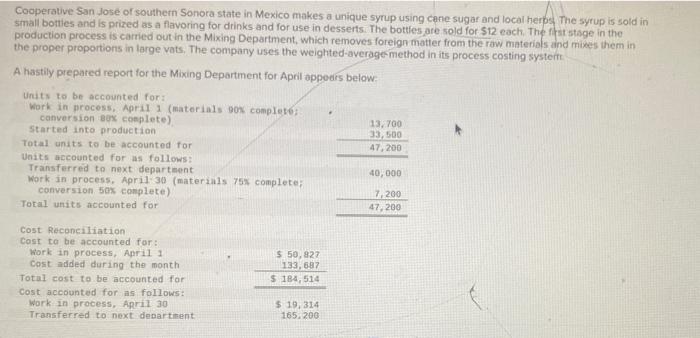
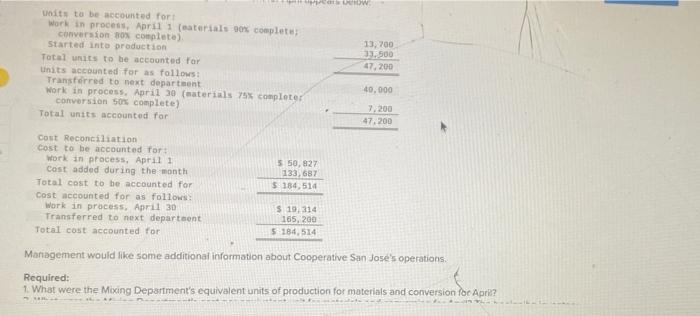
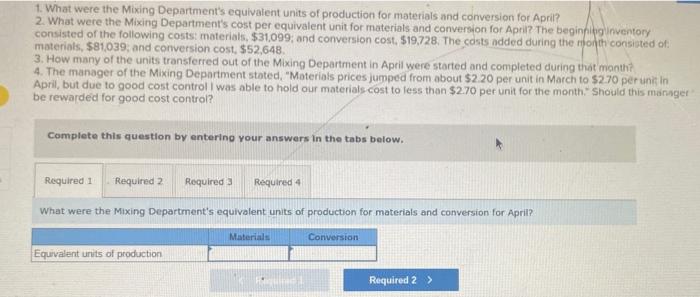
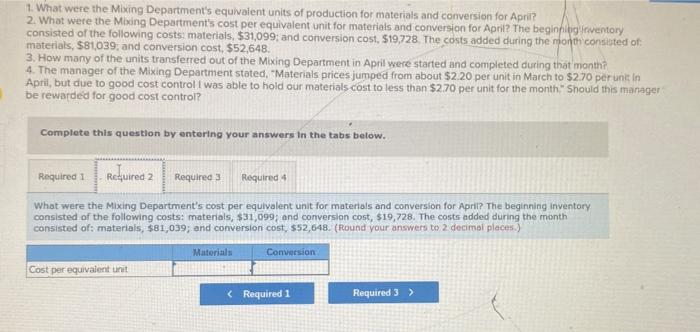
Cooperative San Jose of southern Sonora state in Mexico makes a unique syrup using cane sugar and local herps The syrup is sold in small boties and is prized as a flavoring for drinks and for use in desserts. The botties are sold for 512 each. The ff ststsge in the production process is carried out in the Mixing Department, which removes foreign matter from the raw materials and mikes them in the proper proportions in large vats. The company uses the weighted-average-method in its process costing systeit: A hastily prepared report for the Mixing Department for April appedrs beiow: Maragement would like some additionai information about Cooperative San Jose's operations. Required: 1. What were the Mixing Department's equivalent units of production for materials and conversion foo Apris? 1. What were the Mixing Department's equivalent units of production for materials and conversion for April? 2. What were the Mixing Department's cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion for April? The beginfilig inventory consisted of the following costs: materials, $31,099; and conversion cost, $19,728. The costs added during the rion th consisted of: materials, $81,039, and conversion cost, $52,648. 3. How many of the units transierred out of the Mixing Department in April were started and completed during that manth? 4. The manager of the Mixing Department stoted, "Moterials prices jumped from about $2.20 per unit in March to $270 pr unis in April, but due to good cost control I was able to hold our materials cost to less than $2.70 per unit for the month. \$hould this managet be rewarded for good cost control? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. What were the Mixing Department's equivalent units of production for materials and conversion for April? 1. What were the Mixing Department's equivaient units of production for materials and corversion for Apri? 2. What were the Mixing Department's cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion for April? The beginfingifiventory consisted of the following costs materials, $31,099; and conversion cost, $19,728. The costs added during the month consisted of: materials, $81,039; and conversion cost, $52,648. 3. How many of the units transferred out of the Maxing Department in April were started and completed during that month? 4. The manager of the Mixing Department stated, 7 Materials prices jumped from about $2.20 per unit in March to $270 per un in Aprii, but due to good cost controll was able to hoid our materials cost to less than $2.70 per unit for the month." 5 hould this manager? be rewarded for good cost control? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. What were the Mixing Department's cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion for April? The beginning inventory consisted of the following costs: materials, $31,099; and conversion cost, $19,728. The costs added during the month consisted of: materials, $81,039; and conversion cost, $52,648. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) 1. What were the Mixing Department's equivalent units of production for materials and conversion for April? 2. What were the Mbang Department's cost per equlvalent unit for materials and convers on for April? The beginnipgiinventory consisted of the following costs: materials, $31,099, and conversion cost, $19728. The costs added during the rifon th consicted of materials, \$81,039, and comversion cost, \$52,648, 3. How many of the units transferred out of the Mixing Department in April were started and compieted during that month? 4. The manager of the Mixing Department stated, "Materiais prices jumped from about $2.20 per unit in March to $2.70 per unit in April, but due to good cost control I was able to hoid our materials cost to less than $2.70 per unit for the month. 5 hould this manager be rewarded for good cost control? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. How many of the units transferred out of the Mixing Department in April were started and completed during that manth