
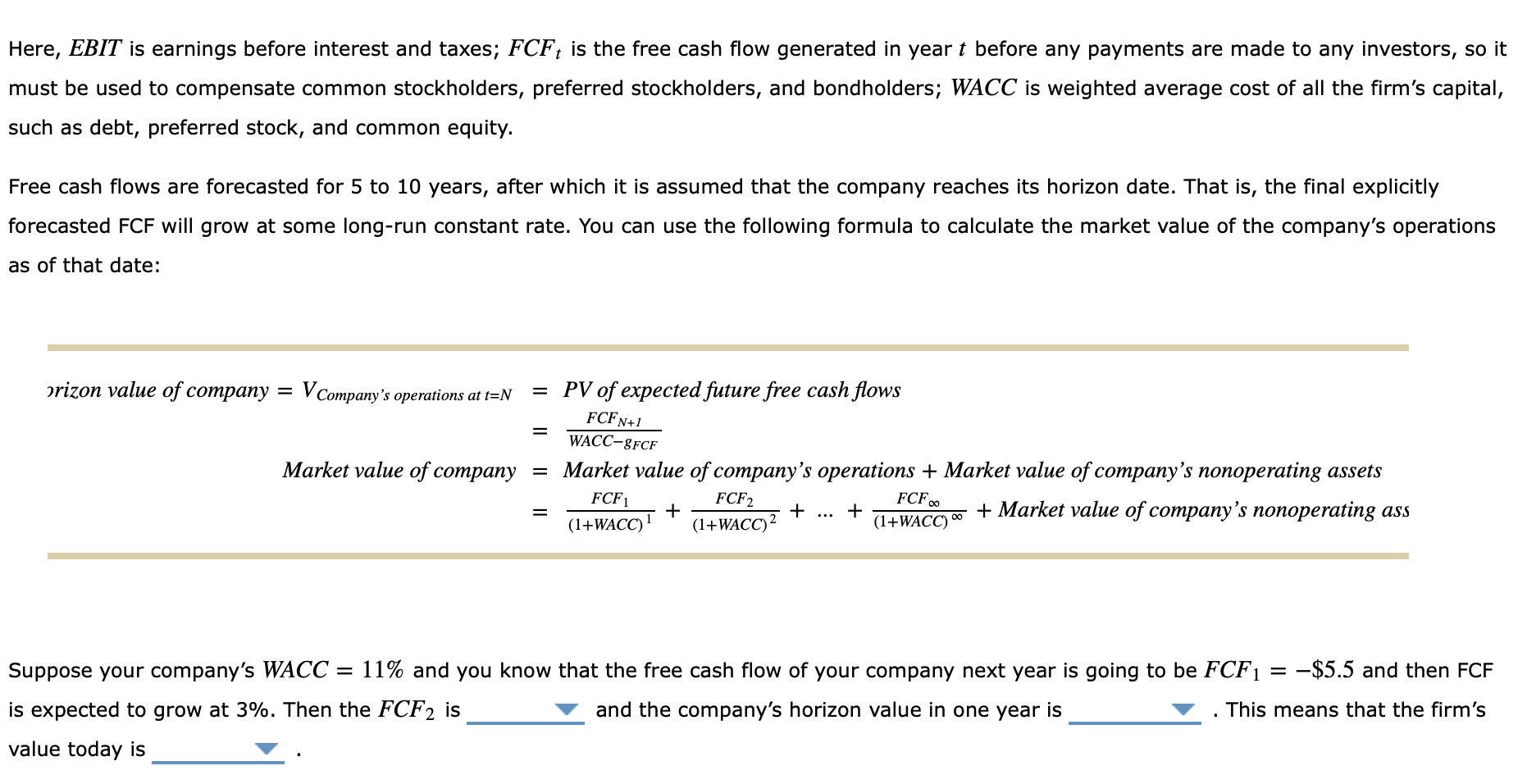
Corporate Valuation is a fundamental concept in finance. A corporate valuation model is used to determine value of a firm with no history of dividends, or divisions of a larger firm. A firm's value is determined by its ability to generate cash flow both now and in the future. The corporate model first calculates the firm's free cash flows, then finds their present values to determine the firm's value: FCF = [EBIT(1-1) + Depreciation and amortization) + (Capital expenditures + 4Net operating working V Company's operations PV of expected future free cash flows FCF FCF FCF + ... (1+WACC) (1+WACC (1+WACC) Here, EBIT is earnings before interest and taxes; FCF, is the free cash flow generated in year t before any payments are made to any investors, so it must be used to compensate common stockholders, preferred stockholders, and bondholders; WACC is weighted average cost of all the firm's capital, such as debt, preferred stock, and common equity. Free cash flows are forecasted for 5 to 10 years, after which it is assumed that the company reaches its horizon date. That is, the final explicitly forecasted FCF will grow at some long-run constant rate. You can use the following formula to calculate the market value of the company's operations as of that date: = prizon value of company = V Company's operations at t=N = PV of expected future free cash flows FCFN+1 WACC-8FCF Market value of company = Market value of company's operations + Market value of company's nonoperating assets FCF FCF2 FCF ... + (1+WACC) (1+WACC)2 (I+WACC + Market value of company's nonoperating ass = + + Here, EBIT is earnings before interest and taxes; FCF is the free cash flow generated in year t before any payments are made to any investors, so it must be used to compensate common stockholders, preferred stockholders, and bondholders; WACC is weighted average cost of all the firm's capital, such as debt, preferred stock, and common equity. Free cash flows are forecasted for 5 to 10 years, after which it is assumed that the company reaches its horizon date. That is, the final explicitly forecasted FCF will grow at some long-run constant rate. You can use the following formula to calculate the market value of the company's operations as of that date: prizon value of company = V Company's operations at t=N = PV of expected future free cash flows FCFN+1 WACC-8FCF Market value of company = Market value of company's operations + Market value of company's nonoperating assets FCF1 FCF2 + + ... + + Market value of company's nonoperating ass (1+WACC) 1 (1+WACC) (1+WACC) FCF = Suppose your company's WACC = 11% and you know that the free cash flow of your company next year is going to be FCF1 = -$5.5 and then FCF is expected to grow at 3%. Then the FCF2 is and the company's horizon value in one year is This means that the firm's value today is








