
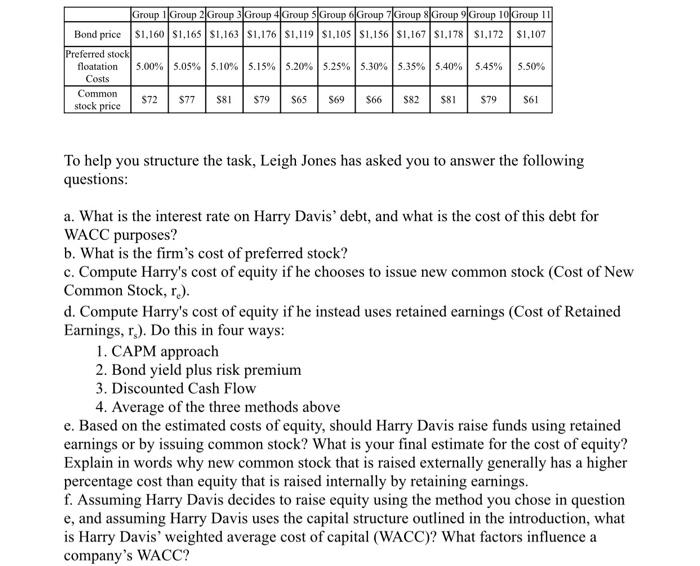
Cost of Capital Section: Harry Davis is raising capital for a major expansion program. What is his WACC? During the last few years, Harry Davis Industries has been too constrained by the high cost of capital to make many capital investments, Recently, though, capital costs have been declining, and the company has decided to look seriously at a major expansion program proposed by the marketing department. Assume that you are an assistant to Leigh Jones, the financial vice president. Your first task is to estimate Harry Davis' cost of capital. Jones has provided you with the following data, which she believes may be relevant to your task: The firm's tax rate is 35%. The price of Harry Davis' $1000 par value, 8.5% coupon, semiannual payment, noncallable bonds with 15 years remaining to maturity is $1000. New bonds would be privately placed with no flotation cost. The current price of the firm's $100 par value, quarterly dividend, perpetual preferred stock is $116 per share. The next perpetual preferred stock dividend is scheduled to be $8.00 per share. The company expects dividends on this preferred stock to grow at a rate of 4.5% per year. Harry Davis would incur flotation costs if they issue new preferred stock. The flotation costs are given below. Harry Davis' is also considering financing the project using equity. He can choose to equity finance through retained earnings or through issuance of new common stock. If he issues new common stock, he will have to incur flotation costs of 6%. The common stock is currently selling as shown in the table per share. Its last dividend (DO) was 2.5% of price, and dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 10.0% in the foreseeable future. Harry Davis' beta is 1.1, the yield on 3-mo T-bills is 2.0%, and the market risk premium is estimated to be 10.0%. For the own-bond-yield-plus-risk-premium approach, the firm uses a 4.0% risk premium. Harry Davis' target capital structure is 30% long-term debt, 10% preferred stock, and 60% equity. Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group Group 7 Group 8 Group Group 10 Group 11 Bond price $1,160 $1,165 $1,163 $1,176 $1,119 $1,105 $1,156 S1,167 1,178 $1,172 $1,107 Preferred stock floatation 5.00% 5.05% 5.10% 5.15%5.20% 5.25% 5.30% 5.35% 5.40% 5.45% 5.50% Costs Common $79 $65 $69 $66 $82 stock price $81 $79 S61 $72 $77 $81 To help you structure the task, Leigh Jones has asked you to answer the following questions: a. What is the interest rate on Harry Davis' debt, and what is the cost of this debt for WACC purposes? b. What is the firm's cost of preferred stock? c. Compute Harry's cost of equity if he chooses to issue new common stock (Cost of New Common Stock, r.). d. Compute Harry's cost of equity if he instead uses retained earnings (Cost of Retained Earnings, r.). Do this in four ways: 1. CAPM approach 2. Bond yield plus risk premium 3. Discounted Cash Flow 4. Average of the three methods above e. Based on the estimated costs of equity, should Harry Davis raise funds using retained earnings or by issuing common stock? What is your final estimate for the cost of equity? Explain in words why new common stock that is raised externally generally has a higher percentage cost than equity that is raised internally by retaining earnings. f. Assuming Harry Davis decides to raise equity using the method you chose in question e, and assuming Harry Davis uses the capital structure outlined in the introduction, what is Harry Davis' weighted average cost of capital (WACC)? What factors influence a company's WACC? Cost of Capital Section: Harry Davis is raising capital for a major expansion program. What is his WACC? During the last few years, Harry Davis Industries has been too constrained by the high cost of capital to make many capital investments, Recently, though, capital costs have been declining, and the company has decided to look seriously at a major expansion program proposed by the marketing department. Assume that you are an assistant to Leigh Jones, the financial vice president. Your first task is to estimate Harry Davis' cost of capital. Jones has provided you with the following data, which she believes may be relevant to your task: The firm's tax rate is 35%. The price of Harry Davis' $1000 par value, 8.5% coupon, semiannual payment, noncallable bonds with 15 years remaining to maturity is $1000. New bonds would be privately placed with no flotation cost. The current price of the firm's $100 par value, quarterly dividend, perpetual preferred stock is $116 per share. The next perpetual preferred stock dividend is scheduled to be $8.00 per share. The company expects dividends on this preferred stock to grow at a rate of 4.5% per year. Harry Davis would incur flotation costs if they issue new preferred stock. The flotation costs are given below. Harry Davis' is also considering financing the project using equity. He can choose to equity finance through retained earnings or through issuance of new common stock. If he issues new common stock, he will have to incur flotation costs of 6%. The common stock is currently selling as shown in the table per share. Its last dividend (DO) was 2.5% of price, and dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 10.0% in the foreseeable future. Harry Davis' beta is 1.1, the yield on 3-mo T-bills is 2.0%, and the market risk premium is estimated to be 10.0%. For the own-bond-yield-plus-risk-premium approach, the firm uses a 4.0% risk premium. Harry Davis' target capital structure is 30% long-term debt, 10% preferred stock, and 60% equity. Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group Group 7 Group 8 Group Group 10 Group 11 Bond price $1,160 $1,165 $1,163 $1,176 $1,119 $1,105 $1,156 S1,167 1,178 $1,172 $1,107 Preferred stock floatation 5.00% 5.05% 5.10% 5.15%5.20% 5.25% 5.30% 5.35% 5.40% 5.45% 5.50% Costs Common $79 $65 $69 $66 $82 stock price $81 $79 S61 $72 $77 $81 To help you structure the task, Leigh Jones has asked you to answer the following questions: a. What is the interest rate on Harry Davis' debt, and what is the cost of this debt for WACC purposes? b. What is the firm's cost of preferred stock? c. Compute Harry's cost of equity if he chooses to issue new common stock (Cost of New Common Stock, r.). d. Compute Harry's cost of equity if he instead uses retained earnings (Cost of Retained Earnings, r.). Do this in four ways: 1. CAPM approach 2. Bond yield plus risk premium 3. Discounted Cash Flow 4. Average of the three methods above e. Based on the estimated costs of equity, should Harry Davis raise funds using retained earnings or by issuing common stock? What is your final estimate for the cost of equity? Explain in words why new common stock that is raised externally generally has a higher percentage cost than equity that is raised internally by retaining earnings. f. Assuming Harry Davis decides to raise equity using the method you chose in question e, and assuming Harry Davis uses the capital structure outlined in the introduction, what is Harry Davis' weighted average cost of capital (WACC)? What factors influence a company's WACC








