Question
Costco nearly $2.5 billion in profit that come from over 700 stores (up from 600 in 2011). Costco focuses on low prices and high volume
Costco nearly $2.5 billion in profit that come from over 700 stores (up from 600 in 2011). Costco focuses on low prices and high volume with a target market of small businesses and large families. The low prices in part comes from an operational strategy that leads to a cost advantage. The assortment is limited; there is usually only one brand for any category, which gives Costco significant market power and logistic efficiencies. Where a typical Walmart Supercenter carries over 140,000 products, Costco carries fewer than 4,000. The items are generally bulk-packaged, which means customers buy more of the item on their Costco trips and the brand involved can justify having Costco sell the brand at a sharply lower price. It has a well-regarded house brand, Kirkland, that is sold at a very low profit margin?around 15 percent mark-up?and generates about 12 percent of the sales. Most products are delivered to the warehouse on shipping pallets and these pallets are used to display products for sale on the warehouse floor. Costco does not have a large advertising budget. Costco has a membership model, which generates a close customer relationship and commitment plus significant revenue since the memberships represent about 15 percent of the value of the firm. The in-store experience is unique with many tasting opportunities, some upscale brands, and a lot of energy. The meat and produce selections have an outstanding quality reputation and include many organic options. Costco was behind in e-commerce in 2016, generating only about 3 percent of sales. The firm had a slow start and a rather poor web presence compared to Amazon and even to its other competitors.
FOR DISCUSSION
1. Why is Costco immune from the Amazon threat? Will that continue going forward? What are the strengths and weaknesses?
2. How should Costco react to the Amazon threat? Besides create more competitive website, is there anything that Costco could do to leapfrog competitors on the e-commerce side?
3. How does Amazon's recent purchase of Whole Foods threaten Costco? What should Costco do in response?
B.
2. Your stockbroker has called has called you about Netflix, Inc. (NFLX). She tells you that Netflix is selling for $370.00 per share and that she expects the price in one year to be $395.00. The expected return on NFLX has a standard deviation of 20 percent. The market risk premium for the S & P 500 has averaged 6.0 percent. The beta for NFLX is 1.14. The ten-year Treasury bond rate is 3 percent. NFLX does not pay a cash dividend.
Required: a) Determine the probability that you would earn a positive return on an investment in NFLX.
b) Determine the probability that you would earn more than your required rate of return on an investment in NFLX.
c) Explain why you would or would not buy NFLX.
3. Suppose that Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) common stock is selling for $2,025.00. Analysts believe that the growth rate for AMZN will be 25% for the next two years, 20% for the following 5 years, and thereafter the growth rate will be 7% indefinitely. Due to its growth, AMZN will not pay a cash dividend until three years from now. At that time, the dividend per share will be $15.00. Thereafter the dividend will grow by the same rate as the company. Stockholders require a return of 15 percent on Amazon's stock.
Required: a) Based on the above assumptions, determine the price of Amazon's common stock.
b) Explain whether an investor should buy the stock.
4. Jasper Inc.'s preferred stock is selling for $125 per share in the market. This preferred stock has a par value of $100 and a dividend rate of 9 percent.
Required: a) What is the current yield on the stock?
b) If an investor has a required rate of return of 7 percent, what is the value of the stock for that investor?
c) Should the investor acquire the stock? Explain.
d) Explain why preferred stock is referred to as a hybrid security.
5. On September 1, 2008, Casper, Inc. sold a $500 million bond issue to finance the purchase of a new manufacturing facility. These bonds were issued in $1,000 denominations with a maturity date of September 1, 2038. The bonds have a coupon rate of 10.00% with interest paid semiannually.
Required: a) Determine the value today, September 1, 2018 of one of these bonds to an investor who requires a 4 percent return on these bonds. Why is the value today different from the par value?
b) Assume that the bonds are selling for $1,215. Determine the current yield and the yield-to-maturity. Explain what these terms mean.
c) Explain what layers or textures of risk play a role in the determination of the required rate of return on Casper's bonds.
C.
Solve the following questions.
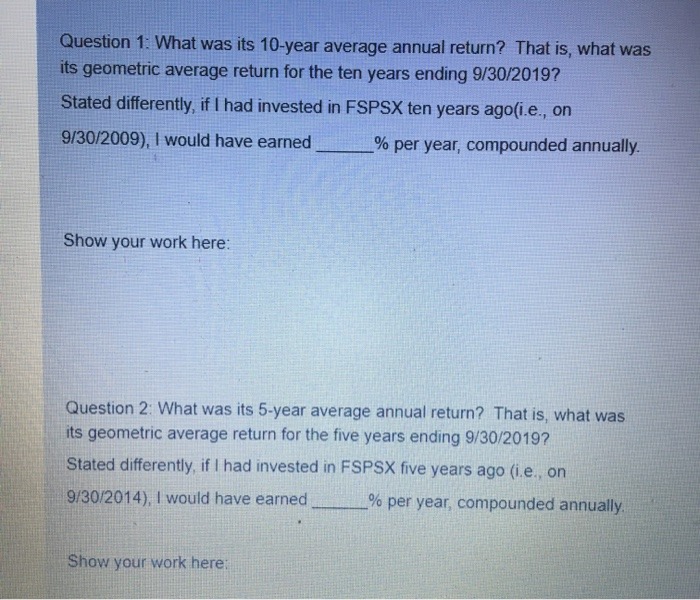
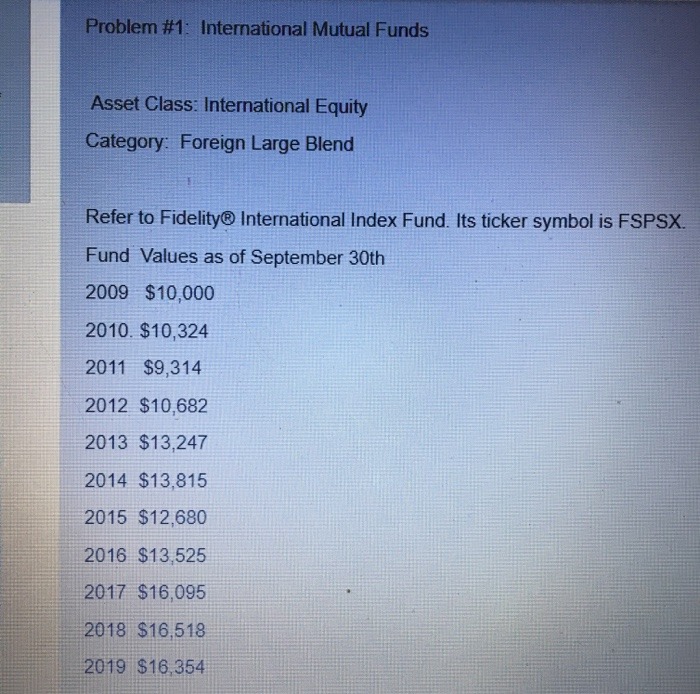

Question 1: What was its 10-year average annual return? That is, what was its geometric average return for the ten years ending 9/30/2019? Stated differently, if I had invested in FSPSX ten years ago(i.e., on 9/30/2009), I would have earned % per year, compounded annually. Show your work here: Question 2: What was its 5-year average annual return? That is, what was its geometric average return for the five years ending 9/30/2019? Stated differently, if I had invested in FSPSX five years ago (i.e., on 9/30/2014), I would have earned % per year, compounded annually. Show your work here:
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Here are the responses to the questions 1 For the international mutual fund question the annualized ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


