Question
Could someone give me a quick over view of the Card class? Specifically how to implement and use bool errorFlag and bool equals(Card card). Also
Could someone give me a quick over view of the Card class? Specifically how to implement and use bool errorFlag and bool equals(Card card).
Also I need help with the Hand class portion as well. Thank you.
Assignment 1 - Game Basics: Cards and Hands
There is only one option this week. Make sure you have read and understood
both modules A and B this week, and
module 2R - Lab Homework Requirements
before submitting this assignment.
Understand the Class and Problem
We endeavor to set up some classes that can be used in future programs that involve playing card games with a human or simulating card games entirely by a computer. There are two basic classes we'll need this week:
Card: A class like the one presented in the modules, but with a few changes.
Hand: A class that represents the cards held by a single player.
Here are eight cards, each of which contains both a value ('A', '2', '3', ... 'T', 'J', 'Q',' K') and a suit (spades , hearts , diamonds , clubs ) 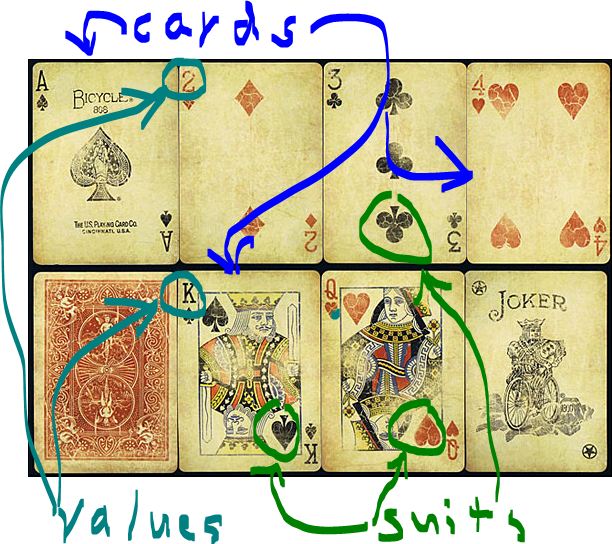
Notice that I am using the char 'T' to describe the value 10. (Ignore the Joker, which we will not need.)
The dealer uses a Deck object (not implemented this week) to deal Hand objects to the players. The dealer may or may not be a player who gets a hand of his own (poker dealers in casinos don't receive a hand, but most other games involve the dealer getting a hand).
Card: The Card class has two members: value (a char) and suit (an enum). But we add a new bool, errorFlag, which can inform a client that a card is in an illegal state. We'll want the usual constructors, mutators, accessors and toString() methods for the class. We only allow standard cards, like ('A', clubs), ('9', hearts) and ('T', diamonds), no jokers or other special cards.
Hand: As you can see, a Hand object usually contains several cards, so we'll need an array of Card objects (myCards) as the principal member of the Hand class. Since each game deals a different number of cards into its players hands, and even within a game the number of cards in a hand will increase or decrease, we must keep track of this with an int value (numCards). We'll need constructors, mutators, etc., of course. We'll also want a way for the hand to receive a card (from the deck or somewhere else), and play a card (to the table or to another player). These two methods will be called takeCard() and playCard(), respectively. Since this class has no information about the game being played, it always puts new cards received by takeCard() into the next available location of the array (index position numCards) and plays a card via playCard() from the highest occupied location (index position numCards - 1). The client game application would somehow prepare this highest position with the correct card to be played before calling Hand's playCard() method. This detail is not our concern.
Phase 1: The Card Class
A Public enum Type
Define the Suit enum, { clubs, diamonds, hearts, spades }, inside the Card class prototype.
Private Member Data
Include three members:
char value; Suit suit; bool errorFlag;
Public Methods
Card(char value = 'A', Suit suit = spades) - The constructor should call the proper mutator(s). Because we have the errorFlag member, the constructor (via the mutator), can set this flag to true when it gets bad data; it does not have to assign default values upon receipt of bad data. This is a new technique for us. The default card (no parameters passed) is the ('A', spades).
string toString() - a stringizer that the client can use prior to displaying the card. It provides a clean representation of the card. If errorFlag == true, it should return correspondingly reasonable reflection of this fact (something like "[ invalid ]" rather than a suit and value).
bool set(char value, Suit suit) - a mutator that accepts the legal values established in the earlier section. When bad values are passed, errorFlag is set to true and other values can be left in any state (even partially set). If good values are passed, they are stored and errorFlag is set to false. Make use of the private helper, listed below.
No mutator for errorFlag - that would not make sense.
Accessors for suit, value and errorFlag.
bool equals(Card card) - returns true if all the fields (members) are equal and false, otherwise.
Private Methods
static bool isValid(char value, Suit suit) - a static helper method that returns true or false, depending on the legality of the parameters. Note that, although it may be impossible for suit to be illegal (due to its enum-ness), we pass it, anyway, in anticipation of possible changes to the type from enum to, say, char or int, someday. We only need to test value, at this time.
Note: we don't need individual mutators for value or suit since they would not be useful for this particular class.
Recommended test of Card class
Instantiate at least three cards, one of them, passing illegal values. Display all three. Then make good card bad using set() with an illegal value, and turn the bad card "good" by setting a legal value, and re-display. This is a simple test, but you can test more thoroughly if you wish.
Example Test Run of Card Class
/* --------------------------------------------------------- A of Spades [ illegal ] J of Clubs [ illegal ] Q of Spades J of Clubs Press any key to continue . . . ----------------------------------------------------------- */
Phase 2: The Hand Class
Static Class Constants
Define a const public int value like MAX_CARDS and set it to something like 30 or 50 so a runaway program can't try to create a monster array.
Private Member Data
Card myCards[...]; int numCards;
Public Methods
Hand() - a default constructor.
void resetHand() - remove all cards from the hand (in the simplest way).
bool takeCard(Card card) - adds card to the next available position in the myCards array if the parameter is an error-free Card object and if there is room in the Hand object for another card (according to MAX_CARDS). It returns false if the Hand was full and true otherwise, even if card was an invalid (error-containing) Card. So, if card is invalid but there would have been room for it, the method will return true, even though it did not add card to the hand.
Card playCard() - returns and removes (effectively, not physically) the card in the top occupied position of the array.
string toString() - a stringizer that the client can use prior to displaying the entire hand.
Accessor for numCards.
Card inspectCard(int k) - Accessor for an individual card. Returns a card with errorFlag = true if k is bad.
Recommended test of Hand class
Create between two and five explicit Card objects and one Hand object. Use takeCard() on these few cards (resulting in many, unavoidable "duplicates" in the hand) in a loop to populate the hand until the maximum allowable cards is met (use this criterion to end the loop). Display the hand using toString(). Next, play each card in a loop, until the hand is empty. Display the card played as it is played, and finally, display the (now empty) hand, verifying that no cards remain. At some point in your program, test inspectCard() with both legal and illegal int arguments.
Example Test Run of Hand Class
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------------- Hand full After deal Hand = ( 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hear ts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clu bs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clu bs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hea rts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs, 9 of Hearts, 3 of Clubs, T of Clubs ) Testing inspectCard() 9 of Hearts ** illegal ** Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs Playing 9 of Hearts Playing T of Clubs Playing 3 of Clubs After playing all cards Hand = ( ) Press any key to continue . . . ----------------------------------------------------------------------- */c ar BICYCLE USAnsaduoCo JOKER 3 & N A
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


