Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Create code for polymath and show graphs A two-component fluid is tested in a transient hot wire (THW) device. The wire has radius R and
Create code for polymath and show graphs 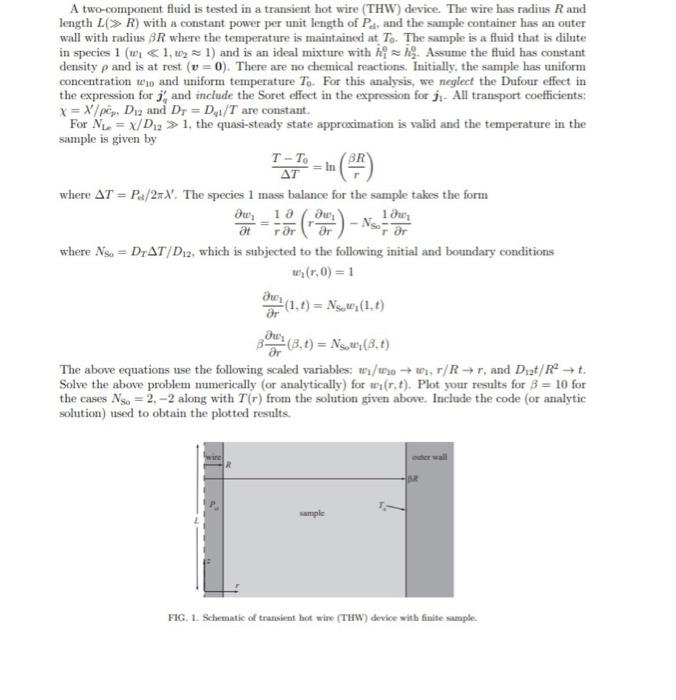
A two-component fluid is tested in a transient hot wire (THW) device. The wire has radius R and length L(R) with a constant power per unit length of Pell, and the sample container has an outer wall with radius R where the temperature is maintaincd at T0. The sumple is a fluid that is dilute in species 1(w1&1,w21) and is an ideal mixture with h10h^20. Assume the fluid has constant density and is at rest (v=0). There are no chemical reactions. Initially, the sample has uniform concentration w10 and uniform temperature T0. For this analysis, we neglect the Dufour effect in the expression for j4 and include the Soret effect in the expression for j1. All transport coefficients: =/c^p,D12 and DT=Dq1/T are constant. For NLe=/D121, the quasi-steady state approximation is valid and the temperature in the sample is given by TTT0=ln(rR) where T=Pd/2. The species 1 mass balance for the sample takes the form tw1=r1r(rrw1)NSO0r1rw1 where Nso=DTT/D12, which is subjected to the following initial and botudary conditions w1(r,0)=1rw1(1,t)=NSow1(1,t)ru1(,t)=NSow1(,t) The above equations use the following scaled variables: w1/w10w1,r/Rr, and D12t/R2t. Solve the above problem numerically (or analytically) for w1(r,t). Plot your results for =10 for the cases NSo=2,2 along with T(r) from the solution given above. Include the code (or analytic solution) used to obtain the plotted results. FIG. 1. Schematic of transient hot wire (THW) device with finite sample. A two-component fluid is tested in a transient hot wire (THW) device. The wire has radius R and length L(R) with a constant power per unit length of Pell, and the sample container has an outer wall with radius R where the temperature is maintaincd at T0. The sumple is a fluid that is dilute in species 1(w1&1,w21) and is an ideal mixture with h10h^20. Assume the fluid has constant density and is at rest (v=0). There are no chemical reactions. Initially, the sample has uniform concentration w10 and uniform temperature T0. For this analysis, we neglect the Dufour effect in the expression for j4 and include the Soret effect in the expression for j1. All transport coefficients: =/c^p,D12 and DT=Dq1/T are constant. For NLe=/D121, the quasi-steady state approximation is valid and the temperature in the sample is given by TTT0=ln(rR) where T=Pd/2. The species 1 mass balance for the sample takes the form tw1=r1r(rrw1)NSO0r1rw1 where Nso=DTT/D12, which is subjected to the following initial and botudary conditions w1(r,0)=1rw1(1,t)=NSow1(1,t)ru1(,t)=NSow1(,t) The above equations use the following scaled variables: w1/w10w1,r/Rr, and D12t/R2t. Solve the above problem numerically (or analytically) for w1(r,t). Plot your results for =10 for the cases NSo=2,2 along with T(r) from the solution given above. Include the code (or analytic solution) used to obtain the plotted results. FIG. 1. Schematic of transient hot wire (THW) device with finite sample 
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


