Question
Create the fullAdder function that implements a full adder (that is made up of two half adders). Of course, you will also need to implement
Create the fullAdder function that implements a full adder (that is made up of two half adders). Of course, you will also need to implement the program in the template to test appropriately. Make sure to use bitwise operators in your implementation of the full adder! A template is provided that will be added to to make a full adder program:
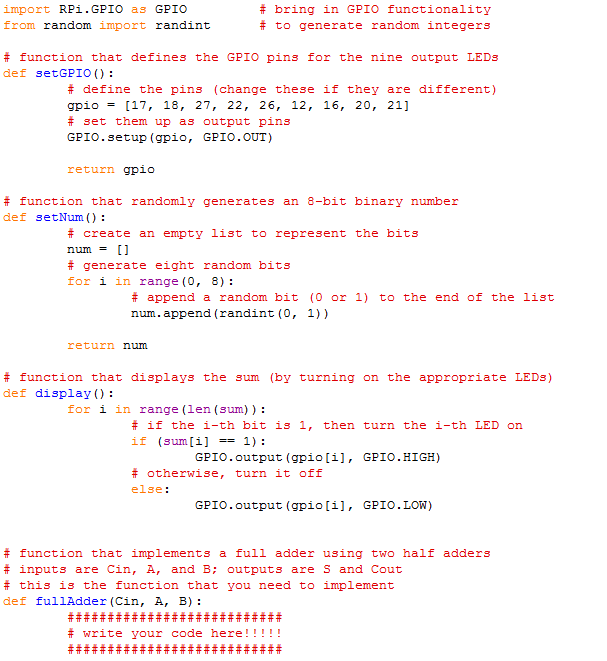


Copyable Code:
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO # bring in GPIO functionality
from random import randint # to generate random integers
# function that defines the GPIO pins for the nine output LEDs
def setGPIO():
# define the pins (change these if they are different)
gpio = [17, 18, 27, 22, 26, 12, 16, 20, 21]
# set them up as output pins
GPIO.setup(gpio, GPIO.OUT)
return gpio
# function that randomly generates an 8-bit binary number
def setNum():
# create an empty list to represent the bits
num = []
# generate eight random bits
for i in range(0, 8):
# append a random bit (0 or 1) to the end of the list
num.append(randint(0, 1))
return num
# function that displays the sum (by turning on the appropriate LEDs)
def display():
for i in range(len(sum)):
# if the i-th bit is 1, then turn the i-th LED on
if (sum[i] == 1):
GPIO.output(gpio[i], GPIO.HIGH)
# otherwise, turn it off
else:
GPIO.output(gpio[i], GPIO.LOW)
# function that implements a full adder using two half adders
# inputs are Cin, A, and B; outputs are S and Cout
# this is the function that you need to implement
def fullAdder(Cin, A, B):
###########################
# write your code here!!!!!
###########################
return S, Cout # yes, we can return more than one value!
# controls the addition of each 8-bit number to produce a sum
def calculate(num1, num2):
Cout = 0 # the initial Cout is 0
sum = [] # initialize the sum
n = len(num1) - 1 # the position of the right-most bit of num1
# step through each bit, from right-to-left
while (n >= 0):
# isolate A and B (the current bits of num1 and num2)
A = num1[n]
B = num2[n]
# set the Cin (as the previous half adder's Cout)
Cin = Cout
# call the fullAdder function that takes Cin, A, and B...
# ...and returns S and Cout
S, Cout = fullAdder(Cin, A, B)
# insert the sum bit, S, at the beginning (index 0) of sum
sum.insert(0, S)
# go to the next bit position (to the left)
n -= 1
# insert the final carry out at the beginning of the sum
sum.insert(0, Cout)
return sum
# use the Broadcom pin scheme
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# setup the GPIO pins
gpio = setGPIO()
# get a random num1 and display it to the console
num1 = setNum()
print " ", num1
# get a random num2 and display it to the console
num2 = setNum()
print "+ ", num2
# calculate the sum of num1 + num2 and display it to the console
sum = calculate(num1, num2)
print "= ", sum
# turn on the appropriate LEDs to "display" the sum
display()
# wait for user input before cleaning up and resetting the GPIO pins
raw_input("Press ENTER to terminate")
GPIO.cleanup()
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO from random import randint # bring in GPIO functionality # to generate random integers # function that defines the GPIO pins for the nine output LEDs def setGPIO ): # define the pins (change these if they are different) gp10= [17, 18, 27, 22, 26, 12, 16, 20, 21] # set them up as output pins GPIO.setup (gpio, GPIO. OUT) return gpio # function that randomly generates an 8-bit binary number def setNum # create an empty list to represent the bits num - # generate eight random bits for i in range (0, 8) # append a random bit (0 or 1) to the end of the list num.append (randint (0, 1)) return num # function that displays the sum (by turning on the appropriate LEDs) def display): for i in range (len (sum)) # if the i-th bit 13 1, then turn the i-th LED on if (sum[i]1): GPIO.output (gpio[i],GPIO.HIGH) otherwise, turn it off else: GPIO.output (gpio[i], GPIO.LOW) # function that implements a full adder using tw half adders # inputs are Cin, A, and B; outputs are S and Cout # this is the function that you need to implement def fullAdder (Cin, A, B) # write your code hereStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


