Question: CS 351 c++ project I need help with answering this question .. Build a class dynListType based on dynamic array. Its declaration is provided below:
CS 351 c++ project
I need help with answering this question ..
Build a class dynListType based on dynamic array. Its declaration is provided below:
| // no more MAX
class dynListType { public:
private: int* dataPtr; int size; int maxSize; }; |
Follow example in Unit 6 PPT 1 (ch12-ch13 Classes with Dynamic Data), add:
a (default) constructor with an int param (default value 5) and
a destructor.
Add those 10 functions from HW9 into dynListType. Be sure to change each occurrence of dataArr (HW9) into dataPtr. Make additional necessary changes.
getSize()
getMaxSize()
isEmpty()
search()
at()
two inserts
remove()
operator +
operator
At this point your program should be able to compile, but may crash during execution. Thats because copy constructor and overloaded assignment are required to handle dynamic data members.
Now add:
Copy constructor
Overloaded assignment operator =
Your program should work perfectly now. dynListType provides the same functionality listType (HW9) does, except that dynListType doesnt have any capacity cap (i.e. there is no MAX for maxSize).
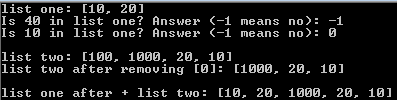
Test your class thoroughly before proceeding to Part 2.
Part 2
Modify your dynListType program from Part 1.
Overload == operator (comparison operator, as in if (obj1 == obj2) ): return true if two list objects contain the same data items in a same order. Values of maxSize dont matter. For example, given obj1 {maxSize 10, } and obj2 {maxSize 5, }, the comparison should return true. Given obj3 {maxSize 5, }, (obj1 == obj3) should be false.
Modify the two insert functions so a list will never be full, like how Java ArrayList and the STL vector class work. Whenever an insertion reaches the maxSize cap, double maxSize, and reallocate storage space. Here is the suggested pseudo code:
| If size before insertion is equal to maxSize // current maxSize reached maxSize allocate a new dynamic array with maxSize slots copy data pointed by dataPtr over to new array delete the dynamic array currently pointed by dataPtr let dataPtr point to the newly allocated dynamic array End if
Insert as normal |
Modify your driver accordingly to test the new/modified functions. Here is the output of my sample driver. I hard-coded data in the driver and generate some data using loops. You may do it differently, as long as it tests EACH new/modified function.
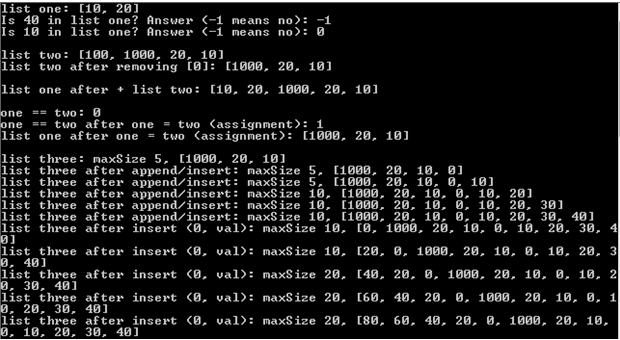
Additional requirements for Part 1 and Part 2
Organize your program into header file (interface), implementation file, and driver file. Use #include guard with the header file.
Pre- and Post- condition comments for each new/updated function. Pre- condition may be skipped if the pre-condition is just xx is initialized (not requiring any specific values) for value or const reference parameters. Such a prerequisite will be enforced by compiler.
Hw9 CODE
//LISTTYPE.H
#ifndef LISTTYPE_H
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100; // max capacity for all listType objects
class listType
{
public:
listType(int max = 5); // constructor
// Post: maxSize MAX, MAX will be used
// size
int getSize() const { return size; } // return # of elements actually stored
int getMaxSize() const { return maxSize; } // return capacity
bool isEmpty() const { return size == 0; }
bool isFull() const { return size == maxSize; }
int search(int element) const; // look for an item. return index of first occurrence
int at(int index) const; // return element at a specific location
void print() const; // print content of list on screen in format of [a, b, c] (like what ArrayList in Java does)
bool insert(int element); // append/insert an element at the end
bool insert(int index, int element);
// insert an element into location index.
// Shifts the element currently at that index (if any) and any subsequent elements to the right
bool remove(int index); // remove element at the specified location
friend ostream& operator
listType operator+(listType& obj);
private:
int dataArr[MAX]; // static array storing data items
int size; // actual # of elements stored. size
int maxSize; // The capacity of this listType obj. 0
}; #endif // LISTTYPE_H
//LISTTYPE.cpp
#include"listType.h"
listType::listType(int max) // constructor
// Post: maxSize MAX, MAX will be used
// size
{
maxSize = max;
size = 0;
}
int listType::search(int element) const
{ // initialize for item for (int i = 0; i
{ if (dataArr[i] == element)
return i;
} // item no found return -1;
}
int listType::at(int index) const
{ // return index value of item return dataArr[index];
}
void listType::print() const {
cout
{
if (i
else cout
}
cout
}
bool listType::insert(int element)
{ if (size
{
dataArr[size++] = element; //return element in array return true;
}
else return false;
}
bool listType::insert(int index, int element)
{
int tmp;
//push elements at given index to right
if (index
{ // Shifts the element currently at that index (if any) and any subsequent elements to the right for (int i = size; i > index; i--)
{
dataArr[i] = dataArr[i - 1];
} // insert an element into location index. dataArr[index] = element;
++size;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
// Shifts the element currently at that index (if any) and any subsequent elements to the right
bool listType::remove(int index) // remove element at the specified location
{ //check for if index is less than size and move elements given index //to the left if (index
{
//move elements after given index to left
for (int i = index; i
{
dataArr[i] = dataArr[i + 1];
}
--size;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
ostream& operator
{
cout
{
if(i cout else //else add number at the end of array cout } cout cout } listType listType::operator+(listType& obj)//overload binary operator return objects that contain all elements { //initialize value and append to arraylist for (int i = 0; i { dataArr[size++] = dataArr[i]; } //initialize value and append to object arraylst for (int i = size; i { dataArr[size++] = obj.dataArr[i]; } //return arraylist with all values return *this; } // main.cpp #include"listType.h" // start main function int main() { listType list1(20), list2(10); // add numbers to array list1.insert(10); list1.insert(20); cout list1.print(); // add numbers to array list2.insert(100); list2.insert(1000); list2.insert(20); list2.insert(10); //print out result cout cout cout cout list one: [10, 20] Is 40 in list one? Answer -1 means no: -1 Is 10 in list one? Answer -1 means no: 0 list two: 100, 1000. 20. 101 list two after removing 01: [1000. 20. 101 list one after list two: 10. 20. 1000. 20. 101
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


