Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
CS1120 Python Lab Assignment - The Coordinate Distance Calculator Link to the PDF file: https://gofile.io/d/AaJBKl CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator
CS1120 Python Lab Assignment - The Coordinate Distance Calculator





Link to the PDF file: https://gofile.io/d/AaJBKl
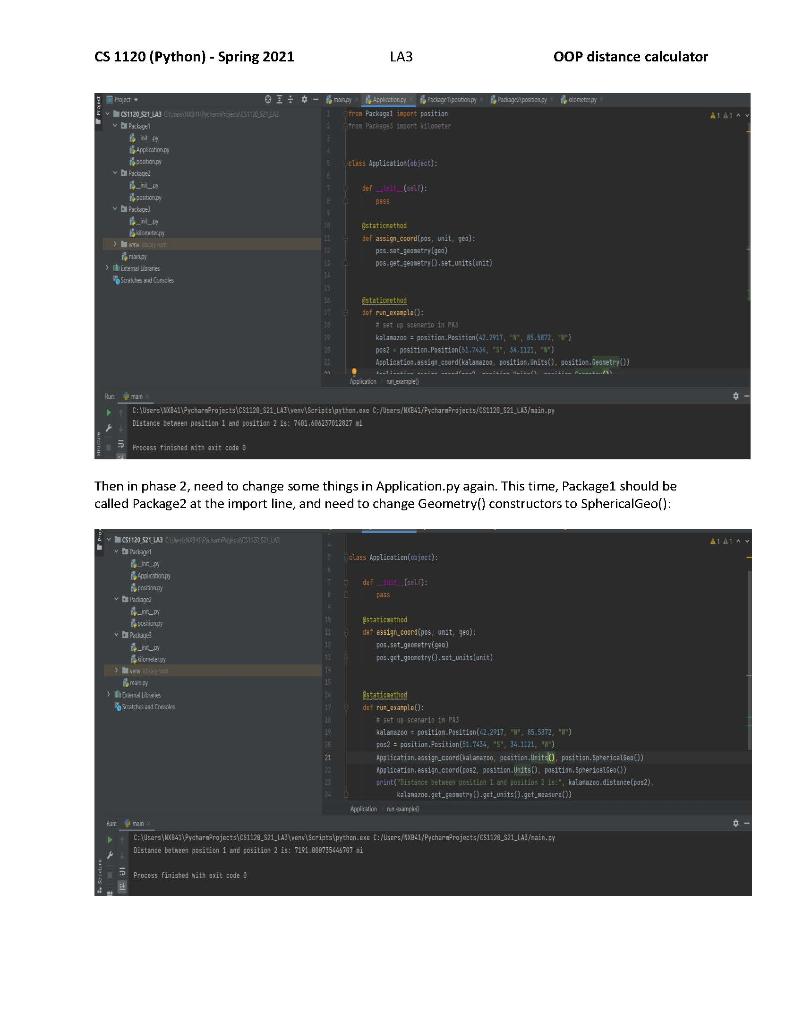
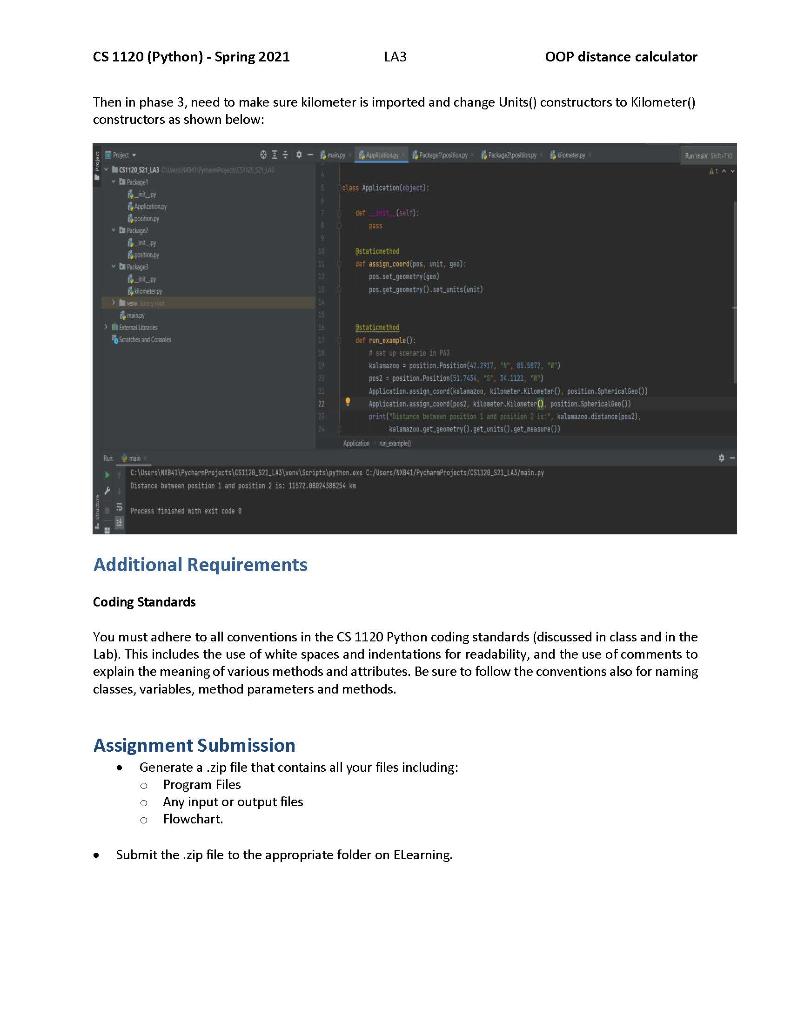
CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator Lab Assignment 3 The Coordinate Distance Calculator Due Date (a two-week LA) Sections(540,543,544,545) 3/3/21 @ 11:59:59pm Concepts Review of Object-Oriented Programming and Polymorphism (OOP) Using pseudocode in algorithm development Design the program flowchart Problem Specification Develop an application in Python to determine the distance between two real world objects in different measures of distance. You are to write a Python program that will compute distance and between two coordinates based on longitude and latitude angles in three contexts geometric and unit of distance contexts. Three versions will be given in three different packages: Package1, Package2 and Package3. In the first version, i.e., Package1, two files exist: Application.py and position.py. The Application file will contain a method to call a method in Position object to compute distance between coordinates in the three contexts. The position.py file gives the classes necessary to compute coordinate distance in the first context as follows: Given two coordinates, given by latitude and longitude, and the radius of the Earth, determine distance between the coordinates in statute miles and planar geometry (equirectangular flat- Earth approximation). The formula to compute this distance is shown here: d=R-Vx2 + y2 where R is the radius of the Earth, * is the term given by the formula x = (longitude2 - longitude1) - cos((latitudel + latitude2)/2) and y is given by the formula y = (latitude2 latitudel). It should be noted that latitude and longitude for position 1 and position 2, (latitude1, longitudel) and (latitude, longitude2) respectively, must be converted into radians in the computation of d. The Position Class has the latitude and longitude attributes that converted from an input (latitude, N/S, longitude, W/E) such as such as (42.917, N, 85.5872, E) to (42.917, S, 85.5872 W). Namely, the valid value for latitude is (-90,90] where the negative represents a position south of the equator and the positive a position north of the equator. The range for longitude is [-180, 180] where the negative represents a position west of the meridian line while the positive a position east of the meridian line. Last, the Unit Class has the radius attribute for the Earth in miles, whose value is 3959 miles (mean volumetric radius). CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator Next, to test the information hiding of the calculation to the Application file/class, you are asked to change the Position class, with the new one in Package2, has a file postion.py, where the distance computed between two coordinates is in statue miles and through spherical coordinates and so the haversine calculation is based on the theta and phi, which are: d =R*C, where Ris Earth's radius, c is given by the formula c= 2 atan2( Va, v1-a), and a is given by the formula a = (ratitude 2-latitude) })2 + cos(latitude 1)* cos(latitude 2) - (singlongitude2-longitude:))) Here, the latitudes and longitudes must be converted to radians as well. In fact, latitude converted to radians is the angle phi and longitude converted to radians is the angle theta. (sin Last, you are asked to consider the distance output in kilometers instead of status miles without modifying the current implementation, i.e., increasing the reusability. Package3 has a file kilometer.py which expands into the third context, in which the distance between two coordinates must be determined in kilometers and in spherical geometry. Here, you must consider the Earth's mean volumetric radius as 6371 kilometers. Design Requirements Basic Structure Your program should have several classes in different modules as follows: 1. The main class (which contains the main method); this class should be called LA3Main. It executes the run_example() method in Application class defined below. The main class module needs to import the Application class from Package1/Application.py. 2. The Application class (in Application.py of Packagell; this class has a constructor, which should not do anything, a static method (named "assign_coord") that takes three parameters: position, units, and geometry and sets the associations between position-units and position-geometry, and a stative method (named "run_example") which takes no parameters and creates instances of GPS positions, distance units and coordinate geometries to compute distance, based on each given scenario. This package will need to import position.py from Package 1, then later replace with position.py from Package 2, and import Kilometer from Package 3. 3. The Units class (in position.py of Packagel); It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An _init_0 method, which takes no arguments and initializes the attributes measure and e_radius. The measure attribute is the string name of the distance units applied in a distance computation should be set to the initials, "mi", referring to statute miles. e_radius is the numerical value of Earth's radius in those distance units. This should be set to the Earth's radius in statute miles, upon initialization. b. A method (named "set_radius") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter and sets the attribute e_radius. A method (named "get_radius") that takes no parameter and gets the value of e_radius. c CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator d. A method (named "set_measure") that takes a string as a parameter and sets the attribute measure. e. A method (named "get_measure") that takes no parameter and gets the value of measure. 4. The Kilometer class (in kilometer.py of Package 3, an inherits from Units in position.py of Packagel); It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An _init__() method, which takes no arguments and initializes the super class' attributes measure and e_rodius. The measure attribute is the string name of the distance units applied in a distance computation. It should be set to the initials, "km", referring to kilometers. e radius is the numerical value of Earth's radius in those distance units. This should be set to the Earth's radius in kilometers, upon initialization. b. A method (named "set_radius") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter and sets the super class' attribute e_radius. c. A method (named "get_radius") that takes no parameter and gets the super class' value of e_radius. d. A method (named "set_measure") that takes a string as a parameter and sets the super class' attribute measure. A method (named "get_measure") that takes no parameter and gets the super class' value of measure. e 5. The Geometry class (in position.py of Packagel); It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An __init_() method, which takes no arguments and initializes the attributes units and geometry. The geometry attribute is the string name of the coordinate system applied to compute position distance (i.e., spherical, planar, cylindrical). units is a reference to an instance of units to be applied to the distance calculations. b. A method (named "set_units") that takes a Units instance as a parameter and sets the attribute units. C. A method (named "get_units") that takes no parameter and gets the reference of a Units object associated to the Geometry object. d. A method (named "set geometry') that takes a string as a parameter and sets the attribute geometry. e. A method (named "get_geometry") that takes no parameter and gets the value of geometry. f. A method (named "curry_distance") that takes two positions as parameters and computes the distance between them based on equirectangular (flat-Earth approximation) coordinate system and the Earth's radius in units. 6. The SphericalGeo class (in new position.py of Package2. inherits from Geometry in position.py of Package1): It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An __init_() method, which takes no arguments and initializes the super class' attributes units and geometry. The geometry attribute is the string name of the coordinate system applied to compute position distance (i.e., spherical, planar, cylindrical). units is a reference to an instance of units to be applied to the distance calculations. b. A method (named "set_units) that takes a Units instance as a parameter and sets the attribute units. CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator C. A method (named "get_units") that takes no parameter and gets the reference of a Units object associated to the Geometry object. d. A method (named "set geometry") that takes a string as a parameter and sets the attribute geometry. e. A method (named "get_geometry") that takes no parameter and gets the value of geometry. A method (named "curry_distance") that takes two positions as parameters and computes the distance between them based on a spherical coordinate system and the Earth's radius in units. fi 7. The Position class (in position.py of Packagel). It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An _init_() method, which takes four arguments: latitude, latitude cardinal direction string, longitude, and longitude cardinal direction string, then initializes the attributes tatitude, longitude, and geometry. The latitude and longitude attributes designate latitude and longitude angle values of the position. You must determine if they are positive or negative, given the cardinal direction strings (.e., S and W relate to negative latitude and longitude angles, respectively). The geometry attribute is a reference to an instance of a Geometry type or subtype object. b. A method (named "set_latitude") that takes a floating point number as a parameter and sets the attribute latitude. This method must make sure the latitude value is in the range (-90,90] c. A method (named "get_latitude") that takes no parameter and gets the value of latitude. d. A method (named "set_longitude") that takes a floating point number as a parameter and sets the attribute longitude. This method must make sure the longitude is in the range [-180, 180) e. A method (named "get_longitude") that takes no parameter and gets the value of longitude. A method (named "set_geometry'') that takes a Geometry based reference as a parameter and sets the attribute geometry. g. A method (named "get_geometry") that takes no parameter and gets the value of geometry. h. A method (named "distance") that takes a position as a parameter, delegates the calculation to the Geometry class, i.e., the curry_distance() method, and finally returns the value obtained from a curry_distance() call from the this position's geometry. f. 8. The Position class (in new_position.py of Package2). It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An init method, which takes four arguments: latitude, latitude cardinal direction string, longitude, and longitude cardinal direction string, then initializes the attributes phi, theta, and geometry. The fatitude and longitude attributes designate latitude and longitude angle values of the position. You must determine if they are positive or negative, given the cardinal direction strings (ie., S and W relate negative latitude and longitude angles, respectively). The geometry attribute is a reference to an instance of a Geometry type or subtype object. b. A method (named "set_latitude") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter, converts it from degrees into radians and passes the result to method set_phi() to set the phi. C. A method (named "get_latitude") that takes no parameter and gets the latitude converted back from phi, from radians to degrees. CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator d. A method (named "set_longitude") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter, converts it from degrees into radians and passes the result to method set_phi() to set the theta. e. A method (named "get_longitude") that takes no parameter and gets the latitude converted back from theta, from radians to degrees. f. A method (named "set_phi") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter and sets the value phi. This method must make sure phi is set to a value between (-1/2, 1/2]. g. A method (named "get_phi") that takes no parameter and gets the value of phi. h. A method (named "set_theta") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter and sets the value of theto. This method must make sure theto is set to a value between (-11, ). i. A method (named "get_theta") that takes no parameter and gets the value of theta. j A method (named "set geometry") that takes a Geometry based reference as a parameter and sets the attribute geometry. k. A method (named "get geometry") that takes no parameter and gets the value of geometry. 1. A method (named "distance") that takes a position as a parameter and returns the value obtained from a curry_distance() call from the this position's geometry. The output and interface should be neat and well-described. See the example provided in the Testing Phase section. Flowchart You must design a flowchart that illustrates the algorithm you design to solve the problem. Implementation Phase Using the pseudocode developed, write the Python code for your assignment. This is a two-week assignment. Choose example coordinates for all three distances to computer their distances. Testing Phase . Your program should include code to validate user input and ensure that all input meets the specifications. If input is not valid, your program should keep looping to force the user to provide valid input. Each time your program loops, it should provide information to the user to indicate what is considered valid input. Build your program incrementally, carefully testing each method as you go. . Example: When testing each version of the proble your Application.py, need to comment out/change relevant import statements. For instance, in phase 1, need to import position1 from Packagel as shown below: CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator Pages festay schody tra Packagalingont position fra Potere ter ATATAN 091120_21_43 Por $ is app Lass Application abject): il ciel 1995 stem Doctor LA Santa staticnathos del assign_coordipas, unite] passat_geantrylge) prostem.situnitslant) Sticles stetice that of run_exacla: 1997 SEO i PRI kalamazoo = aration Position (42-2017, 14.407 ps2 p16111m.Positan.7436, 12, Application as a coordekatana 200 posities, ani). positios. Grant) AL - - - - - -- : Rosanotte Para Clusers 411Pycharnerajects (51120_821_L45werk.Seristalpythos, and Cr/Users/14841fycharmeraject(CS1120_21_413/main.pl Distance better position and position 2 29: 760.000257012827 Process finished with antt code Then in phase 2, need to change some things in Application.py again. This time, Package1 should be called Package2 at the import line, and need to change Geometry() constructors to SphericalGeo(): e 0511292 23 babae class doplication cajast): des Tass Peso bakau 1 staticated dessin corpos unst 960) posset.getrv(990) pos.get_gametry().set_witsluit) creley forany tech dut rur_examplo): scrario Balanszoo = position. Pasitis(12:2011. T. 85.5372 ) pos2 = position, sitian 1.7454 S 34.12.) 21 Aplicatian.sign.cordialaatto, gestion tits). position.Sorerica) fortsatian, Essign.ctord10:2 priedon Units). position, Speicale) intestatct to the line to 24", kata distantelp:2) kalamazoo.gtamtry).gat_units).get()) Action taman -Brera/E43\pycharrojects101122_521_LA! v'crists phenet:/Users/XL/Pycharmerojects/6517_21_LA2/main.cy Distance betreet position i and sositio: 2 is: 710.0987:5448707 i Process finistes hits axit sede CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator Then in phase 3, need to make sure kilometer is imported and change Units() constructors to Kilometer() constructors as shown below: BI: - Brings In C51120.8.1.143 ALAY s potication cajet] cy bre staticheted Et assign.coordipos, init, gas) poet_cott(e) pes.get_goty). nits(int) des Diruttaramana static.tacd defen_example): 1881 in 2 Ralamazoo = position. Position (42.2914, 31.07.09 ps2 position. Position 1.7456 3.1.1121 ) Application saiat cseed (kutanazcu, states kiloetar:C). position Speedcat.600) Application. 219.012, kitomter Kilometer). position. Sherica 00) print "tanca bi postiosoit last.distance 2). Atanazou.get, geometry().et mits().getar) 22 C:\Users\M1847yerererujarts\C51128_521_445.Strapsyenot c-/Users/x/841/tycarrojects CS117_521_143/main.TV Distance between position and stis: 11993.822243254 Precast time nith exit tode? Additional Requirements Coding Standards You must adhere to all conventions in the CS 1120 Python coding standards (discussed in class and in the Lab). This includes the use of white spaces and indentations for readability, and the use of comments to explain the meaning of various methods and attributes. Be sure to follow the conventions also for naming classes, variables, method parameters and methods. Assignment Submission Generate a .zip file that contains all your files including: o Program Files Any input or output files a Flowchart. . Submit the .zip file to the appropriate folder on ELearning. CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator Lab Assignment 3 The Coordinate Distance Calculator Due Date (a two-week LA) Sections(540,543,544,545) 3/3/21 @ 11:59:59pm Concepts Review of Object-Oriented Programming and Polymorphism (OOP) Using pseudocode in algorithm development Design the program flowchart Problem Specification Develop an application in Python to determine the distance between two real world objects in different measures of distance. You are to write a Python program that will compute distance and between two coordinates based on longitude and latitude angles in three contexts geometric and unit of distance contexts. Three versions will be given in three different packages: Package1, Package2 and Package3. In the first version, i.e., Package1, two files exist: Application.py and position.py. The Application file will contain a method to call a method in Position object to compute distance between coordinates in the three contexts. The position.py file gives the classes necessary to compute coordinate distance in the first context as follows: Given two coordinates, given by latitude and longitude, and the radius of the Earth, determine distance between the coordinates in statute miles and planar geometry (equirectangular flat- Earth approximation). The formula to compute this distance is shown here: d=R-Vx2 + y2 where R is the radius of the Earth, * is the term given by the formula x = (longitude2 - longitude1) - cos((latitudel + latitude2)/2) and y is given by the formula y = (latitude2 latitudel). It should be noted that latitude and longitude for position 1 and position 2, (latitude1, longitudel) and (latitude, longitude2) respectively, must be converted into radians in the computation of d. The Position Class has the latitude and longitude attributes that converted from an input (latitude, N/S, longitude, W/E) such as such as (42.917, N, 85.5872, E) to (42.917, S, 85.5872 W). Namely, the valid value for latitude is (-90,90] where the negative represents a position south of the equator and the positive a position north of the equator. The range for longitude is [-180, 180] where the negative represents a position west of the meridian line while the positive a position east of the meridian line. Last, the Unit Class has the radius attribute for the Earth in miles, whose value is 3959 miles (mean volumetric radius). CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator Next, to test the information hiding of the calculation to the Application file/class, you are asked to change the Position class, with the new one in Package2, has a file postion.py, where the distance computed between two coordinates is in statue miles and through spherical coordinates and so the haversine calculation is based on the theta and phi, which are: d =R*C, where Ris Earth's radius, c is given by the formula c= 2 atan2( Va, v1-a), and a is given by the formula a = (ratitude 2-latitude) })2 + cos(latitude 1)* cos(latitude 2) - (singlongitude2-longitude:))) Here, the latitudes and longitudes must be converted to radians as well. In fact, latitude converted to radians is the angle phi and longitude converted to radians is the angle theta. (sin Last, you are asked to consider the distance output in kilometers instead of status miles without modifying the current implementation, i.e., increasing the reusability. Package3 has a file kilometer.py which expands into the third context, in which the distance between two coordinates must be determined in kilometers and in spherical geometry. Here, you must consider the Earth's mean volumetric radius as 6371 kilometers. Design Requirements Basic Structure Your program should have several classes in different modules as follows: 1. The main class (which contains the main method); this class should be called LA3Main. It executes the run_example() method in Application class defined below. The main class module needs to import the Application class from Package1/Application.py. 2. The Application class (in Application.py of Packagell; this class has a constructor, which should not do anything, a static method (named "assign_coord") that takes three parameters: position, units, and geometry and sets the associations between position-units and position-geometry, and a stative method (named "run_example") which takes no parameters and creates instances of GPS positions, distance units and coordinate geometries to compute distance, based on each given scenario. This package will need to import position.py from Package 1, then later replace with position.py from Package 2, and import Kilometer from Package 3. 3. The Units class (in position.py of Packagel); It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An _init_0 method, which takes no arguments and initializes the attributes measure and e_radius. The measure attribute is the string name of the distance units applied in a distance computation should be set to the initials, "mi", referring to statute miles. e_radius is the numerical value of Earth's radius in those distance units. This should be set to the Earth's radius in statute miles, upon initialization. b. A method (named "set_radius") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter and sets the attribute e_radius. A method (named "get_radius") that takes no parameter and gets the value of e_radius. c CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator d. A method (named "set_measure") that takes a string as a parameter and sets the attribute measure. e. A method (named "get_measure") that takes no parameter and gets the value of measure. 4. The Kilometer class (in kilometer.py of Package 3, an inherits from Units in position.py of Packagel); It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An _init__() method, which takes no arguments and initializes the super class' attributes measure and e_rodius. The measure attribute is the string name of the distance units applied in a distance computation. It should be set to the initials, "km", referring to kilometers. e radius is the numerical value of Earth's radius in those distance units. This should be set to the Earth's radius in kilometers, upon initialization. b. A method (named "set_radius") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter and sets the super class' attribute e_radius. c. A method (named "get_radius") that takes no parameter and gets the super class' value of e_radius. d. A method (named "set_measure") that takes a string as a parameter and sets the super class' attribute measure. A method (named "get_measure") that takes no parameter and gets the super class' value of measure. e 5. The Geometry class (in position.py of Packagel); It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An __init_() method, which takes no arguments and initializes the attributes units and geometry. The geometry attribute is the string name of the coordinate system applied to compute position distance (i.e., spherical, planar, cylindrical). units is a reference to an instance of units to be applied to the distance calculations. b. A method (named "set_units") that takes a Units instance as a parameter and sets the attribute units. C. A method (named "get_units") that takes no parameter and gets the reference of a Units object associated to the Geometry object. d. A method (named "set geometry') that takes a string as a parameter and sets the attribute geometry. e. A method (named "get_geometry") that takes no parameter and gets the value of geometry. f. A method (named "curry_distance") that takes two positions as parameters and computes the distance between them based on equirectangular (flat-Earth approximation) coordinate system and the Earth's radius in units. 6. The SphericalGeo class (in new position.py of Package2. inherits from Geometry in position.py of Package1): It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An __init_() method, which takes no arguments and initializes the super class' attributes units and geometry. The geometry attribute is the string name of the coordinate system applied to compute position distance (i.e., spherical, planar, cylindrical). units is a reference to an instance of units to be applied to the distance calculations. b. A method (named "set_units) that takes a Units instance as a parameter and sets the attribute units. CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator C. A method (named "get_units") that takes no parameter and gets the reference of a Units object associated to the Geometry object. d. A method (named "set geometry") that takes a string as a parameter and sets the attribute geometry. e. A method (named "get_geometry") that takes no parameter and gets the value of geometry. A method (named "curry_distance") that takes two positions as parameters and computes the distance between them based on a spherical coordinate system and the Earth's radius in units. fi 7. The Position class (in position.py of Packagel). It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An _init_() method, which takes four arguments: latitude, latitude cardinal direction string, longitude, and longitude cardinal direction string, then initializes the attributes tatitude, longitude, and geometry. The latitude and longitude attributes designate latitude and longitude angle values of the position. You must determine if they are positive or negative, given the cardinal direction strings (.e., S and W relate to negative latitude and longitude angles, respectively). The geometry attribute is a reference to an instance of a Geometry type or subtype object. b. A method (named "set_latitude") that takes a floating point number as a parameter and sets the attribute latitude. This method must make sure the latitude value is in the range (-90,90] c. A method (named "get_latitude") that takes no parameter and gets the value of latitude. d. A method (named "set_longitude") that takes a floating point number as a parameter and sets the attribute longitude. This method must make sure the longitude is in the range [-180, 180) e. A method (named "get_longitude") that takes no parameter and gets the value of longitude. A method (named "set_geometry'') that takes a Geometry based reference as a parameter and sets the attribute geometry. g. A method (named "get_geometry") that takes no parameter and gets the value of geometry. h. A method (named "distance") that takes a position as a parameter, delegates the calculation to the Geometry class, i.e., the curry_distance() method, and finally returns the value obtained from a curry_distance() call from the this position's geometry. f. 8. The Position class (in new_position.py of Package2). It should contain the methods required to perform the necessary actions, which includes: a. An init method, which takes four arguments: latitude, latitude cardinal direction string, longitude, and longitude cardinal direction string, then initializes the attributes phi, theta, and geometry. The fatitude and longitude attributes designate latitude and longitude angle values of the position. You must determine if they are positive or negative, given the cardinal direction strings (ie., S and W relate negative latitude and longitude angles, respectively). The geometry attribute is a reference to an instance of a Geometry type or subtype object. b. A method (named "set_latitude") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter, converts it from degrees into radians and passes the result to method set_phi() to set the phi. C. A method (named "get_latitude") that takes no parameter and gets the latitude converted back from phi, from radians to degrees. CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator d. A method (named "set_longitude") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter, converts it from degrees into radians and passes the result to method set_phi() to set the theta. e. A method (named "get_longitude") that takes no parameter and gets the latitude converted back from theta, from radians to degrees. f. A method (named "set_phi") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter and sets the value phi. This method must make sure phi is set to a value between (-1/2, 1/2]. g. A method (named "get_phi") that takes no parameter and gets the value of phi. h. A method (named "set_theta") that takes a floating-point number as a parameter and sets the value of theto. This method must make sure theto is set to a value between (-11, ). i. A method (named "get_theta") that takes no parameter and gets the value of theta. j A method (named "set geometry") that takes a Geometry based reference as a parameter and sets the attribute geometry. k. A method (named "get geometry") that takes no parameter and gets the value of geometry. 1. A method (named "distance") that takes a position as a parameter and returns the value obtained from a curry_distance() call from the this position's geometry. The output and interface should be neat and well-described. See the example provided in the Testing Phase section. Flowchart You must design a flowchart that illustrates the algorithm you design to solve the problem. Implementation Phase Using the pseudocode developed, write the Python code for your assignment. This is a two-week assignment. Choose example coordinates for all three distances to computer their distances. Testing Phase . Your program should include code to validate user input and ensure that all input meets the specifications. If input is not valid, your program should keep looping to force the user to provide valid input. Each time your program loops, it should provide information to the user to indicate what is considered valid input. Build your program incrementally, carefully testing each method as you go. . Example: When testing each version of the proble your Application.py, need to comment out/change relevant import statements. For instance, in phase 1, need to import position1 from Packagel as shown below: CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator Pages festay schody tra Packagalingont position fra Potere ter ATATAN 091120_21_43 Por $ is app Lass Application abject): il ciel 1995 stem Doctor LA Santa staticnathos del assign_coordipas, unite] passat_geantrylge) prostem.situnitslant) Sticles stetice that of run_exacla: 1997 SEO i PRI kalamazoo = aration Position (42-2017, 14.407 ps2 p16111m.Positan.7436, 12, Application as a coordekatana 200 posities, ani). positios. Grant) AL - - - - - -- : Rosanotte Para Clusers 411Pycharnerajects (51120_821_L45werk.Seristalpythos, and Cr/Users/14841fycharmeraject(CS1120_21_413/main.pl Distance better position and position 2 29: 760.000257012827 Process finished with antt code Then in phase 2, need to change some things in Application.py again. This time, Package1 should be called Package2 at the import line, and need to change Geometry() constructors to SphericalGeo(): e 0511292 23 babae class doplication cajast): des Tass Peso bakau 1 staticated dessin corpos unst 960) posset.getrv(990) pos.get_gametry().set_witsluit) creley forany tech dut rur_examplo): scrario Balanszoo = position. Pasitis(12:2011. T. 85.5372 ) pos2 = position, sitian 1.7454 S 34.12.) 21 Aplicatian.sign.cordialaatto, gestion tits). position.Sorerica) fortsatian, Essign.ctord10:2 priedon Units). position, Speicale) intestatct to the line to 24", kata distantelp:2) kalamazoo.gtamtry).gat_units).get()) Action taman -Brera/E43\pycharrojects101122_521_LA! v'crists phenet:/Users/XL/Pycharmerojects/6517_21_LA2/main.cy Distance betreet position i and sositio: 2 is: 710.0987:5448707 i Process finistes hits axit sede CS 1120 (Python) - Spring 2021 LA3 OOP distance calculator Then in phase 3, need to make sure kilometer is imported and change Units() constructors to Kilometer() constructors as shown below: BI: - Brings In C51120.8.1.143 ALAY s potication cajet] cy bre staticheted Et assign.coordipos, init, gas) poet_cott(e) pes.get_goty). nits(int) des Diruttaramana static.tacd defen_example): 1881 in 2 Ralamazoo = position. Position (42.2914, 31.07.09 ps2 position. Position 1.7456 3.1.1121 ) Application saiat cseed (kutanazcu, states kiloetar:C). position Speedcat.600) Application. 219.012, kitomter Kilometer). position. Sherica 00) print "tanca bi postiosoit last.distance 2). Atanazou.get, geometry().et mits().getar) 22 C:\Users\M1847yerererujarts\C51128_521_445.Strapsyenot c-/Users/x/841/tycarrojects CS117_521_143/main.TV Distance between position and stis: 11993.822243254 Precast time nith exit tode? Additional Requirements Coding Standards You must adhere to all conventions in the CS 1120 Python coding standards (discussed in class and in the Lab). This includes the use of white spaces and indentations for readability, and the use of comments to explain the meaning of various methods and attributes. Be sure to follow the conventions also for naming classes, variables, method parameters and methods. Assignment Submission Generate a .zip file that contains all your files including: o Program Files Any input or output files a Flowchart. . Submit the .zip file to the appropriate folder on ELearningStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


