Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
CS161 Introduction to Computer Science II Implementation Requirements The following class relationship diagram shows the required classes and how they interact. BlackjackTableGUI Extends Application
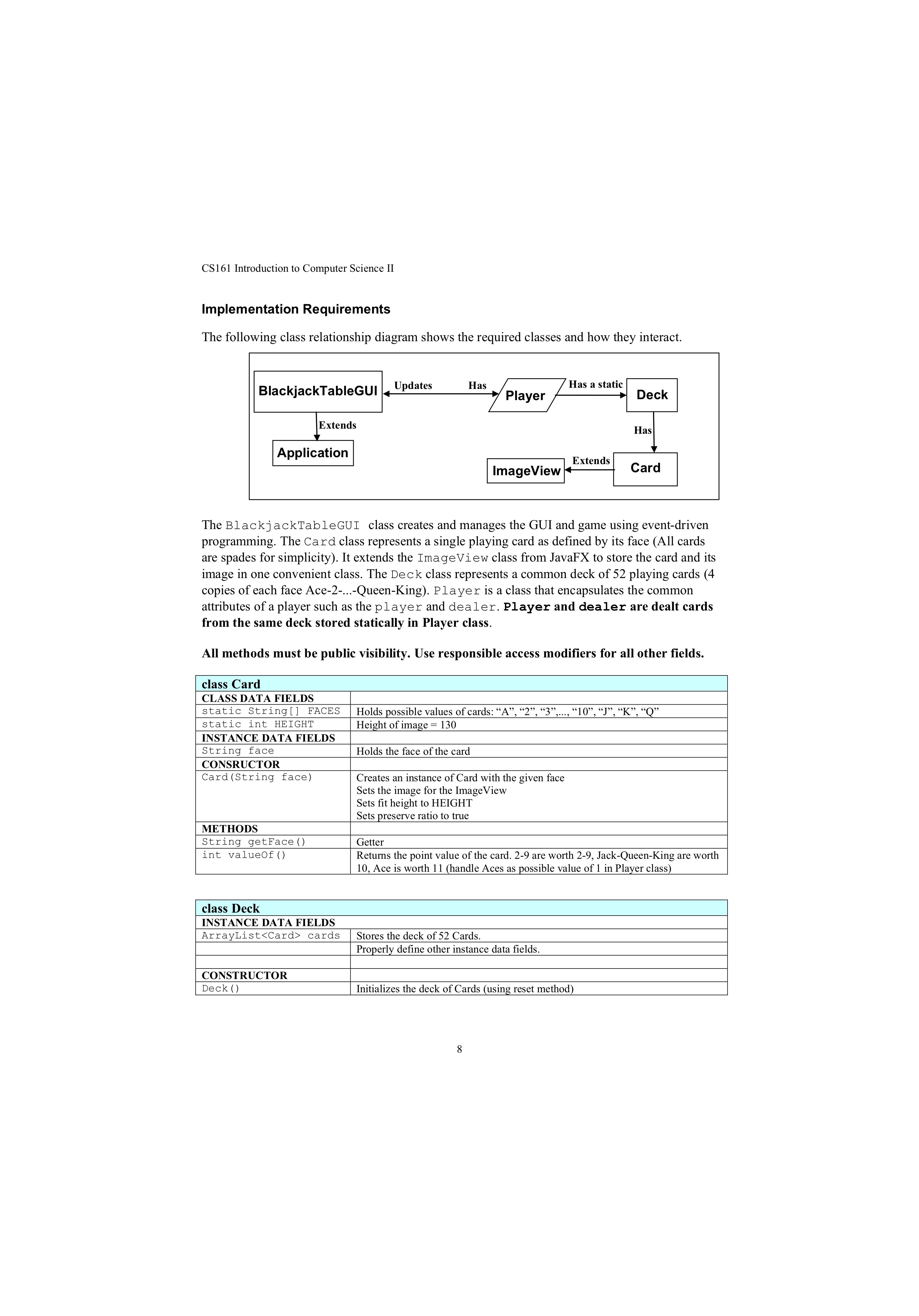
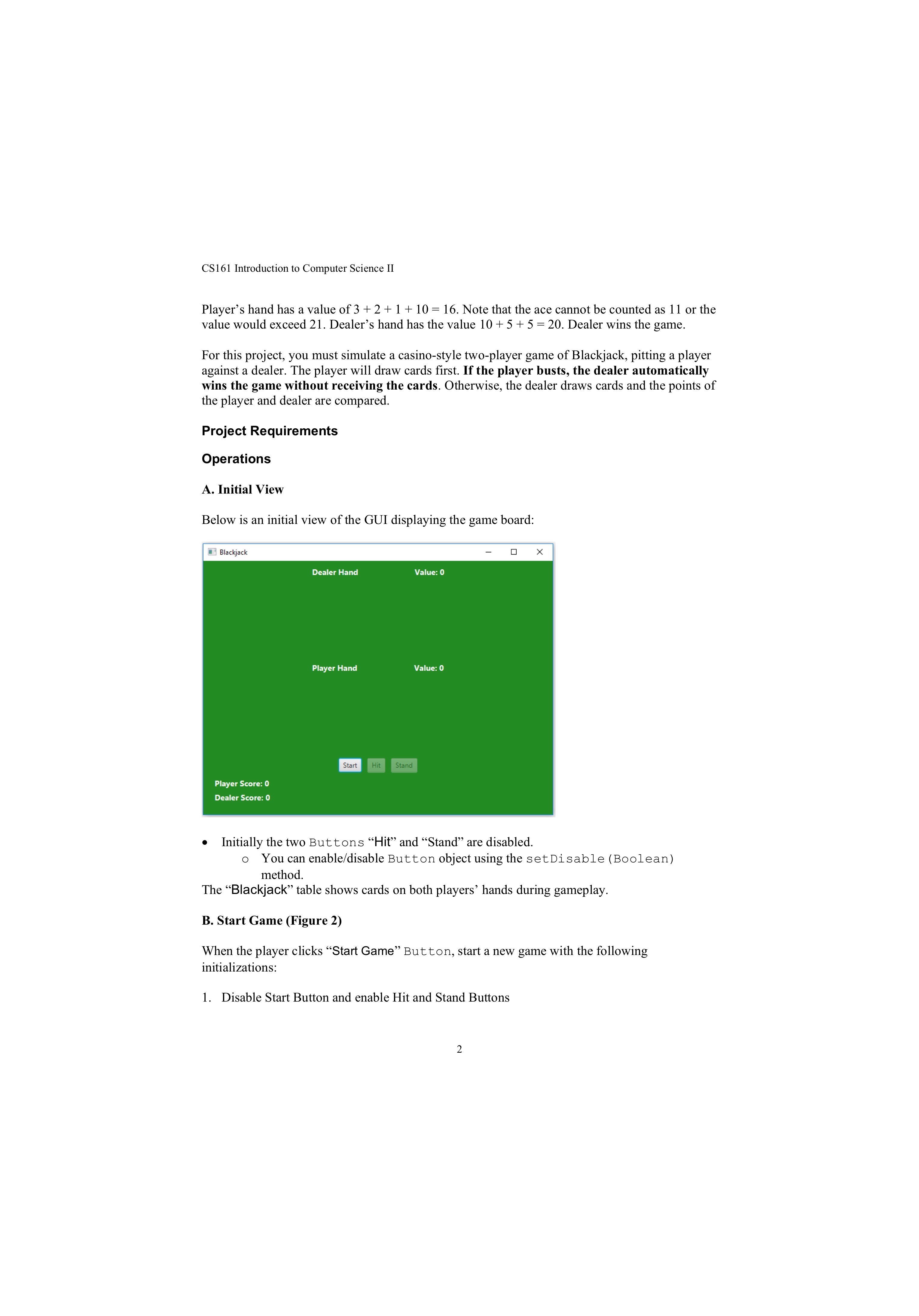
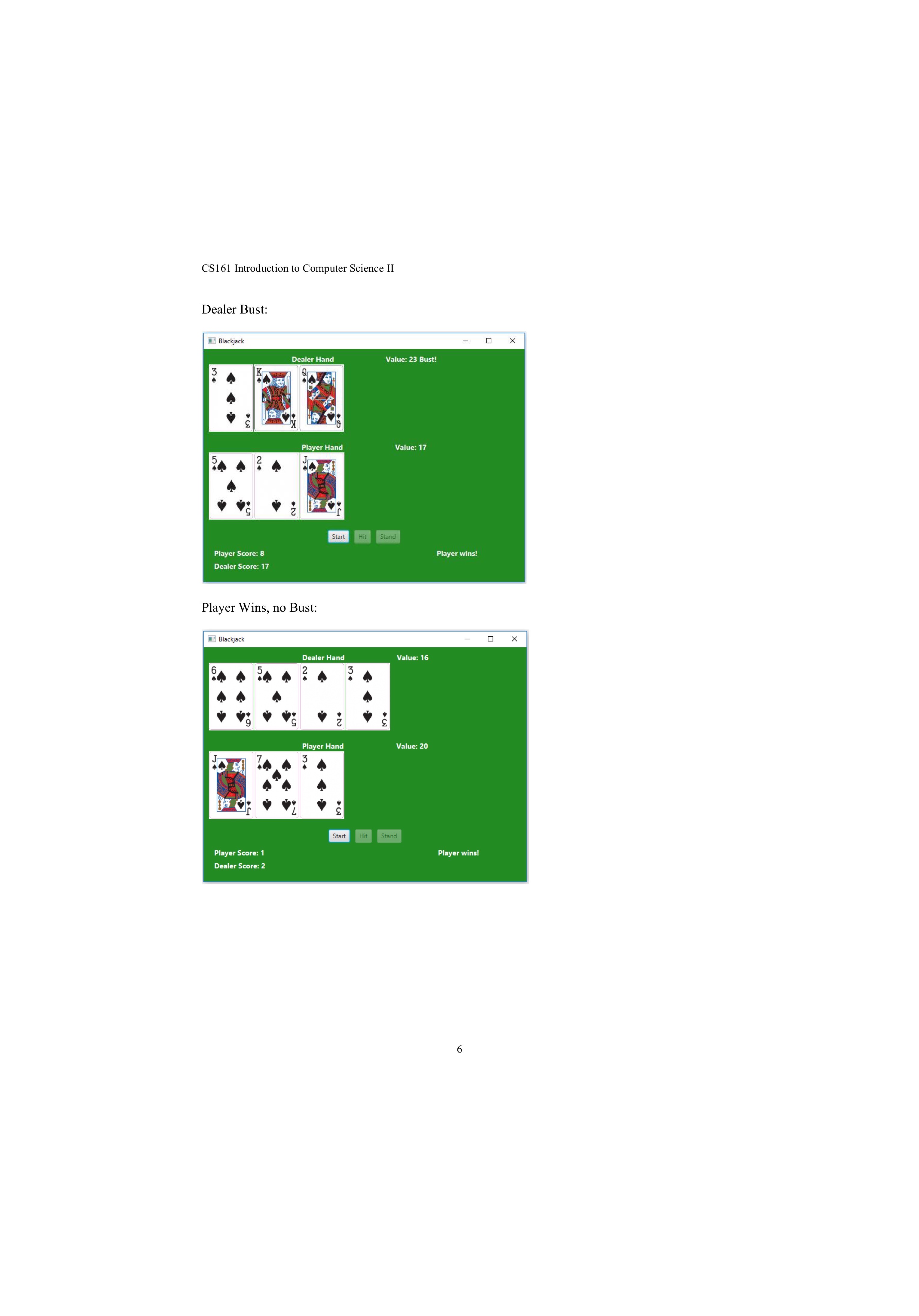




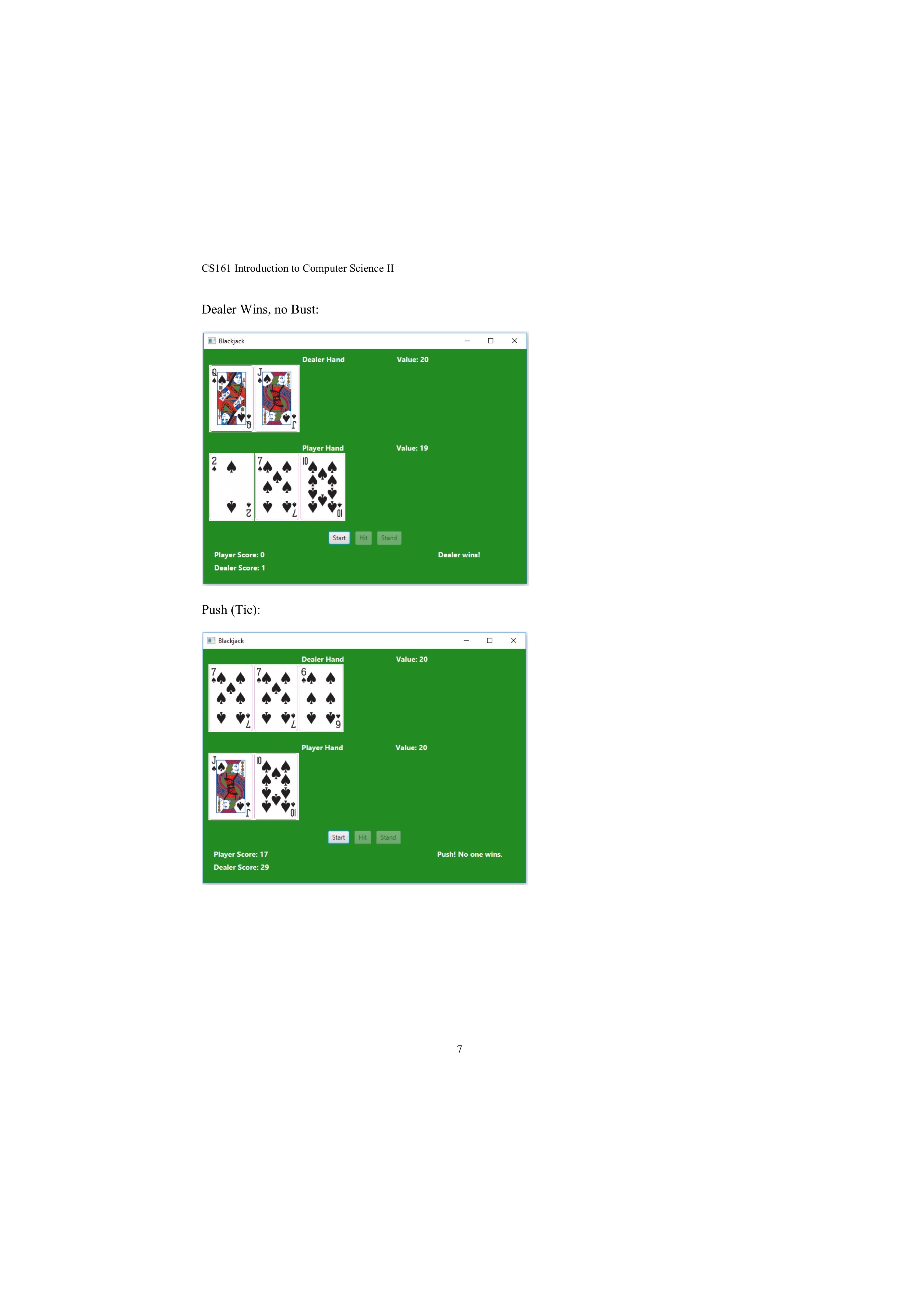
CS161 Introduction to Computer Science II Implementation Requirements The following class relationship diagram shows the required classes and how they interact. BlackjackTableGUI Extends Application Updates Has Has a static Player Deck Has Extends ImageView Card The BlackjackTableGUI class creates and manages the GUI and game using event-driven programming. The Card class represents a single playing card as defined by its face (All cards are spades for simplicity). It extends the ImageView class from JavaFX to store the card and its image in one convenient class. The Deck class represents a common deck of 52 playing cards (4 copies of each face Ace-2-...-Queen-King). Player is a class that encapsulates the common attributes of a player such as the player and dealer. Player and dealer are dealt cards from the same deck stored statically in Player class. All methods must be public visibility. Use responsible access modifiers for all other fields. class Card CLASS DATA FIELDS static String[] FACES static int HEIGHT INSTANCE DATA FIELDS String face CONSRUCTOR Card (String face) METHODS String getFace() int valueOf() Holds possible values of cards: A, 2, 3,..., 10, J, K, Q Height of image = 130 Holds the face of the card Creates an instance of Card with the given face Sets the image for the ImageView Sets fit height to HEIGHT Sets preserve ratio to true Getter Returns the point value of the card. 2-9 are worth 2-9, Jack-Queen-King are worth 10, Ace is worth 11 (handle Aces as possible value of 1 in Player class) class Deck INSTANCE DATA FIELDS ArrayList cards Stores the deck of 52 Cards. Properly define other instance data fields. CONSTRUCTOR Deck () Initializes the deck of Cards (using reset method) 8 CS161 Introduction to Computer Science II Player's hand has a value of 3 + 2 + 1 + 10 = 16. Note that the ace cannot be counted as 11 or the value would exceed 21. Dealer's hand has the value 10+5 +5 = 20. Dealer wins the game. For this project, you must simulate a casino-style two-player game of Blackjack, pitting a player against a dealer. The player will draw cards first. If the player busts, the dealer automatically wins the game without receiving the cards. Otherwise, the dealer draws cards and the points of the player and dealer are compared. Project Requirements Operations A. Initial View Below is an initial view of the GUI displaying the game board: Blackjack Player Score: 0 Dealer Score: 0 Dealer Hand Value: 0 Player Hand Value: 0 Start Hit Stand Initially the two Buttons "Hit and Stand are disabled. You can enable/disable Button object using the set Disable (Boolean) method. The Blackjack table shows cards on both players' hands during gameplay. B. Start Game (Figure 2) When the player clicks Start Game Button, start a new game with the following initializations: 1. Disable Start Button and enable Hit and Stand Buttons 2 CS161 Introduction to Computer Science II Dealer Bust: Blackjack Dealer Hand Value: 23 Bust! Player Hand Value: 17 3 M+ 31 24 24 Player Score: 8 Dealer Score: 17 Start Player Wins, no Bust: Hit HH Stand Player wins! Dealer Hand Value: 16 6 5 2+ 2 Me 3 Blackjack A Player Hand Value: 20 M+ 3 Start Hit Stand Player Score: 1 Player wins! Dealer Score: 2 6 CS161 Introduction to Computer Science II METHODS void reset () Card dealCard () Clears all existing cards from the deck and remakes the deck with 52 Cards (4 of each face) Removes and returns a random Card from the deck. class Player INSTANCE DATA FIELDS ArrayList hand Static Deck CONSTRUCTOR Holds a maximum of 12 cards. Holds and deals Cards for all Players. Player () METHODS Instantiate the player's hand Properly defines constructors, accessor/modifiers, and other methods. get Hand () int value Of Hand () void clearHand () boolean stand (int otherPlayerValue) void hit () boolean bust ( ) Getter Returns the point value of the hand. If the value exceeds 21 and there is one or more Aces in the hand, use them to achieve the best hand value without exceeding 21. Remove all Cards from the hand Determine whether to stand (for non-user players). Always stand when the hand value is higher than the other player. If not, then when the hand value is 16 or higher, stand 50% of the time. When the hand value is 19 or higher, always stand. Otherwise do not stand. Add a Card to the hand from the Deck If the hand value is greater than 21, it is a bust class BlackjackTableGUI You must implement the Blackjack GUI using your own interpretation of the screenshots provided. Make your GUI look as similar as possible. Below are several styling numbers that I used to organize the UI: Space between the Player/Dealer title and Hand Value Labels: 100 Preferred size of the Player/Dealer Card area: 600 width, 150 height Preferred width of the Player/Dealer Score Label: 150 Space between the Player/Dealer Score and the game result: 280 Space between the Buttons: 10 Space between each section (Player display, Dealer display, Buttons, Game Stats): 10 Background color: forestgreen Label text style: 14 font size, white color, bold The following methods are also required (in addition to the standard GUI and event handling methods): void startGame() Reset the game Deck Clear the player and dealer hands and hand values Give the dealer one Card Disable Start button, enable Hit and Stand Buttons Clear previous game result void updateHand(Player p, HBox box, Label handValue) void endGame() For a given Player, add the Card to the Player's hand display Update the hand value Label. Determine the winner of the game, if there is one. Display the game result and update player or dealer score appropriately. Enable the Start Button and disable the Hit and Stand Buttons 9 Problem Statement Game Rules Blackjack is a popular card game that is simple to play. The object of the game is to beat the dealer in one of the following ways: Get 21 points on the player's first two cards (called a "blackjack" or "natural") without a dealer blackjack; Reach a final score higher than the dealer without exceeding 21 Let the dealer draw additional cards until their hand exceeds 21 ("busted"). The player and the dealer receive two cards at the start and one at a time afterwards. The player decides whether to receive another card based on the value of his hand. Each face card has a value of 10, an ace may be counted as 1 or 11, and the other cards have values equal to their number. The player or dealer whose hand is closest to 21 wins the game. If a player goes over 21, he/she automatically loses (called a "bust"). If the player chooses to "stand", the player is finished playing and waits for the dealer to play until standing or busting. If the player and dealer have equal points, then the game is called a "push", and no one wins. For example, consider the following hands: Player 1 Dealer CS161 Introduction to Computer Science II E. Ending the Game To end the game, the victor or a tie must be decided. The game result can be determined based on the following: If the player busted during their, the dealer automatically wins (the dealer does not even play in this scenario) o Display "Bust!" by the player's hand value If the dealer busted, the player automatically wins (implies the player did not bust) Display "Bust!" by the dealer's hand value If neither player nor dealer busted, compare the value of each hand The one with a higher hand value wins In case of a tie, it is called a "push" and no one wins After determining the winner, display the result and update the player or dealer score accordingly. Return the game buttons to their initial state Here are screenshots of each end game result: Player Bust: Blackjack Dealer Hand Value: 8 8 A 00 I Player Hand Value: 27 Bust! M+ 3 10 Player Score: 0 Dealer Score: 2 C Start Hit Stand 9 Dealer wins! 15 CS161 Introduction to Computer Science II 2. Reset the Deck 3. Clear any existing game information such as hand values 4. Put one card into the Dealer's hand 5. Update the Label value of the Dealer's hand The GUI will look like this (the first card may be different each time obviously): 3 Blackjack W Dealer Hand Value: 3 Player Hand Value: 0 Start Hit Stand Player Score: 0 Dealer Score: 0 C. Player Plays the Game When the player clicks the "Hit" button: 1. A Card is added to the player hand 2. The value of the player's hand is updated 3. If the player has busted, end the game If the hit did not bust the player, it will look something like this: 3 CS161 Introduction to Computer Science II 3 M+ Blackjack Dealer Hand Value: 3 C Player Hand Value: 7 Start Hit Stand Player Score: 0 Dealer Score: 0 Clicking Hit again: Blackjack Dealer Hand Value: 3 Player Hand Value: 12 5 Start Hit Stand Player Score: 0 Dealer Score: 0 I D. Dealer Plays the Game If the player has not busted and clicks "Stand", the dealer begins playing the game. 1. Using algorithms developed in the Player class, simulate the dealer's actions (hit or stand) 2. Update the value of the dealer's hand on each hit 3. Once the dealer has busted or decided to stand, end the game 4 CS161 Introduction to Computer Science II Dealer Wins, no Bust: Blackjack Dealer Hand Value: 20 2+ A Player Score: 0 Dealer Score: 1 Push (Tie): Blackjack Player Hand Value: 19 10 01 1 X Start Hit Stand Dealer wins! Dealer Hand Value: 20 6 Player Hand Value: 20 10 Player Score: 17 Dealer Score: 29 01 Start Hit Stand Push! No one wins. 7
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Based on the provided class relationship diagram and the description of each class we can implement the classes Card Deck Player and BlackjackTableGUI ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


