Question: CS270 Introduction to Computer Architecture II Homework 3 Instructions: Copy the questions into a word-processing document such as Microsoft Word. Then add your answers and
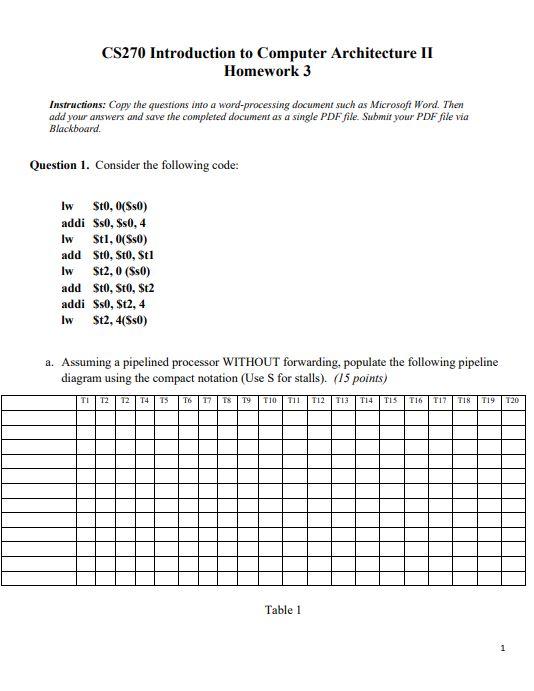
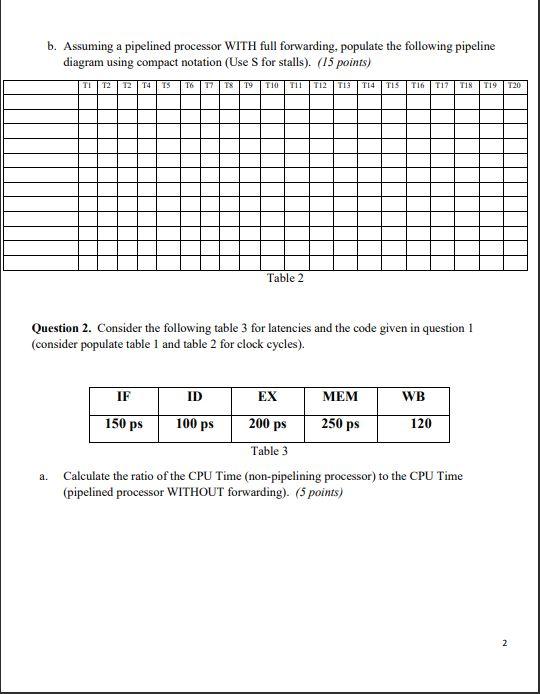

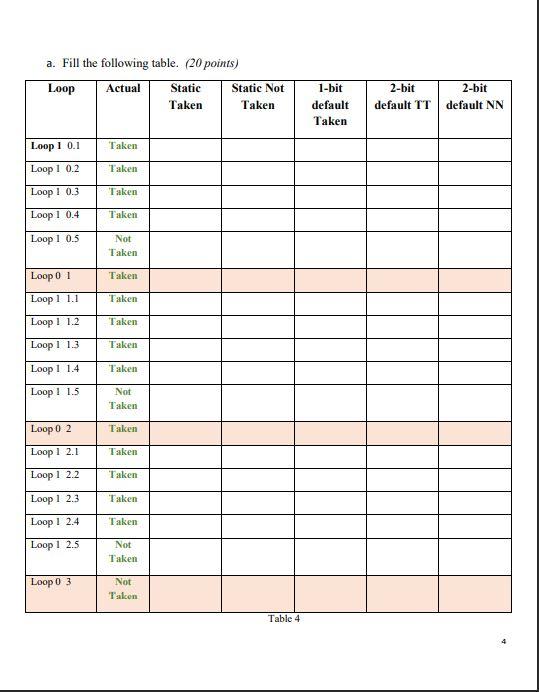

CS270 Introduction to Computer Architecture II Homework 3 Instructions: Copy the questions into a word-processing document such as Microsoft Word. Then add your answers and save the completed document as a single PDF file. Submit your PDF file via Blackboard Question 1. Consider the following code: Iw $t0,($s0) addi $s0, $50,4 Iw st1, 0($s0) add $t0,$t0,$t1 Iw $t2, 0 (550) add $t0,$t0,$t2 addi $so, $t2, 4 lw St2, 4(50) a. Assuming a pipelined processor WITHOUT forwarding, populate the following pipeline diagram using the compact notation (Use S for stalls). (15 points) TI T2 T2 T4 TS T6 17 18 19 T10 T11 T12T13 T14 TISTIG TI? T18 T19 120 Table 1 1 b. Assuming a pipelined processor WITH full forwarding, populate the following pipeline diagram using compact notation (Use S for stalls). (15 points) TI 12 12 T4 TS T6 77 18 19 T10 TI1 T12 T13 T14 TIS T16 T17 TIR T19 T20 Table 2 Question 2. Consider the following table 3 for latencies and the code given in question 1 (consider populate table 1 and table 2 for clock cycles). 100 ps 200 ps 250 ps IF ID EX MEM WB 150 ps 120 Table 3 a. Calculate the ratio of the CPU Time (non-pipelining processor) to the CPU Time (pipelined processor WITHOUT forwarding). (5 points) 2 b. Calculate the ratio of the CPU Time (non-pipelining processor) to the CPU Time (pipelined processor WITH forwarding). (10 points) c. Calculate the ratio of the CPU Time (pipelined processor WITHOUT forwarding) to the CPU Time (pipelined processor WITH forwarding). (10 points) Question 3 Use the following loop to answer the questions below on Branch Prediction. Assume Loop runs 3 times, and Loopl runs 5 times for each iteration of Loopo. Loopo: Loopl: BEQ rs, rt, Loopl BEQ rs, rt, Loop a. Fill the following table. (20 points) Loop Actual Static Static Not Taken Taken 1-bit default Taken 2-bit default TT 2-bit default NN Loop 1 0.1 Taken Loop 1 0.2 Taken Loop 1 0.3 Taken Loop 1 0.4 Taken Loop 1 0.5 Not Taken Loop 01 Taken Loop 1 1.1 Taken Loop 1 1.2 Taken Loop 1 1.3 Taken Loop 1 1.4 Taken Loop ! 1.5 Not Taken Loop 02 Taken Loop 1 2.1 Taken Loop 1 2.2 Taken Loop 1 2.3 Taken Loop ! 2.4 Taken Loop 1 2.5 Not Taken Loop 0 3 Not Talcon Table 4 b. What is the percentage of correct predictions if Branch Taken is assumed, i.e. Static Taken in the Table 4? (5 points) c. What is the percentage of correct predictions if Branch Not Taken is assumed, i.e. Static Not Taken in the Table 4? (5 points) d. What is the percentage of correct predictions if 1-bit prediction is assumed? Predictions are defaulted to Branch Taken. (5 points) e. What is the percentage of correct predictions if 2-bit prediction is assumed? Predictions are defaulted to Predict Taken (TT: Taken, Taken). (5 points) f. What is the percentage of correct predictions if 2-bit prediction is assumed? Predictions are defaulted to Predict not taken (NN: Not Taken, Not Taken). (5 points) 5 CS270 Introduction to Computer Architecture II Homework 3 Instructions: Copy the questions into a word-processing document such as Microsoft Word. Then add your answers and save the completed document as a single PDF file. Submit your PDF file via Blackboard Question 1. Consider the following code: Iw $t0,($s0) addi $s0, $50,4 Iw st1, 0($s0) add $t0,$t0,$t1 Iw $t2, 0 (550) add $t0,$t0,$t2 addi $so, $t2, 4 lw St2, 4(50) a. Assuming a pipelined processor WITHOUT forwarding, populate the following pipeline diagram using the compact notation (Use S for stalls). (15 points) TI T2 T2 T4 TS T6 17 18 19 T10 T11 T12T13 T14 TISTIG TI? T18 T19 120 Table 1 1 b. Assuming a pipelined processor WITH full forwarding, populate the following pipeline diagram using compact notation (Use S for stalls). (15 points) TI 12 12 T4 TS T6 77 18 19 T10 TI1 T12 T13 T14 TIS T16 T17 TIR T19 T20 Table 2 Question 2. Consider the following table 3 for latencies and the code given in question 1 (consider populate table 1 and table 2 for clock cycles). 100 ps 200 ps 250 ps IF ID EX MEM WB 150 ps 120 Table 3 a. Calculate the ratio of the CPU Time (non-pipelining processor) to the CPU Time (pipelined processor WITHOUT forwarding). (5 points) 2 b. Calculate the ratio of the CPU Time (non-pipelining processor) to the CPU Time (pipelined processor WITH forwarding). (10 points) c. Calculate the ratio of the CPU Time (pipelined processor WITHOUT forwarding) to the CPU Time (pipelined processor WITH forwarding). (10 points) Question 3 Use the following loop to answer the questions below on Branch Prediction. Assume Loop runs 3 times, and Loopl runs 5 times for each iteration of Loopo. Loopo: Loopl: BEQ rs, rt, Loopl BEQ rs, rt, Loop a. Fill the following table. (20 points) Loop Actual Static Static Not Taken Taken 1-bit default Taken 2-bit default TT 2-bit default NN Loop 1 0.1 Taken Loop 1 0.2 Taken Loop 1 0.3 Taken Loop 1 0.4 Taken Loop 1 0.5 Not Taken Loop 01 Taken Loop 1 1.1 Taken Loop 1 1.2 Taken Loop 1 1.3 Taken Loop 1 1.4 Taken Loop ! 1.5 Not Taken Loop 02 Taken Loop 1 2.1 Taken Loop 1 2.2 Taken Loop 1 2.3 Taken Loop ! 2.4 Taken Loop 1 2.5 Not Taken Loop 0 3 Not Talcon Table 4 b. What is the percentage of correct predictions if Branch Taken is assumed, i.e. Static Taken in the Table 4? (5 points) c. What is the percentage of correct predictions if Branch Not Taken is assumed, i.e. Static Not Taken in the Table 4? (5 points) d. What is the percentage of correct predictions if 1-bit prediction is assumed? Predictions are defaulted to Branch Taken. (5 points) e. What is the percentage of correct predictions if 2-bit prediction is assumed? Predictions are defaulted to Predict Taken (TT: Taken, Taken). (5 points) f. What is the percentage of correct predictions if 2-bit prediction is assumed? Predictions are defaulted to Predict not taken (NN: Not Taken, Not Taken). (5 points) 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


