Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Curve 5 in Figure 3 corresponds to the design condition in which the flow is expanded isentropically in the nozzle to the back pressure.
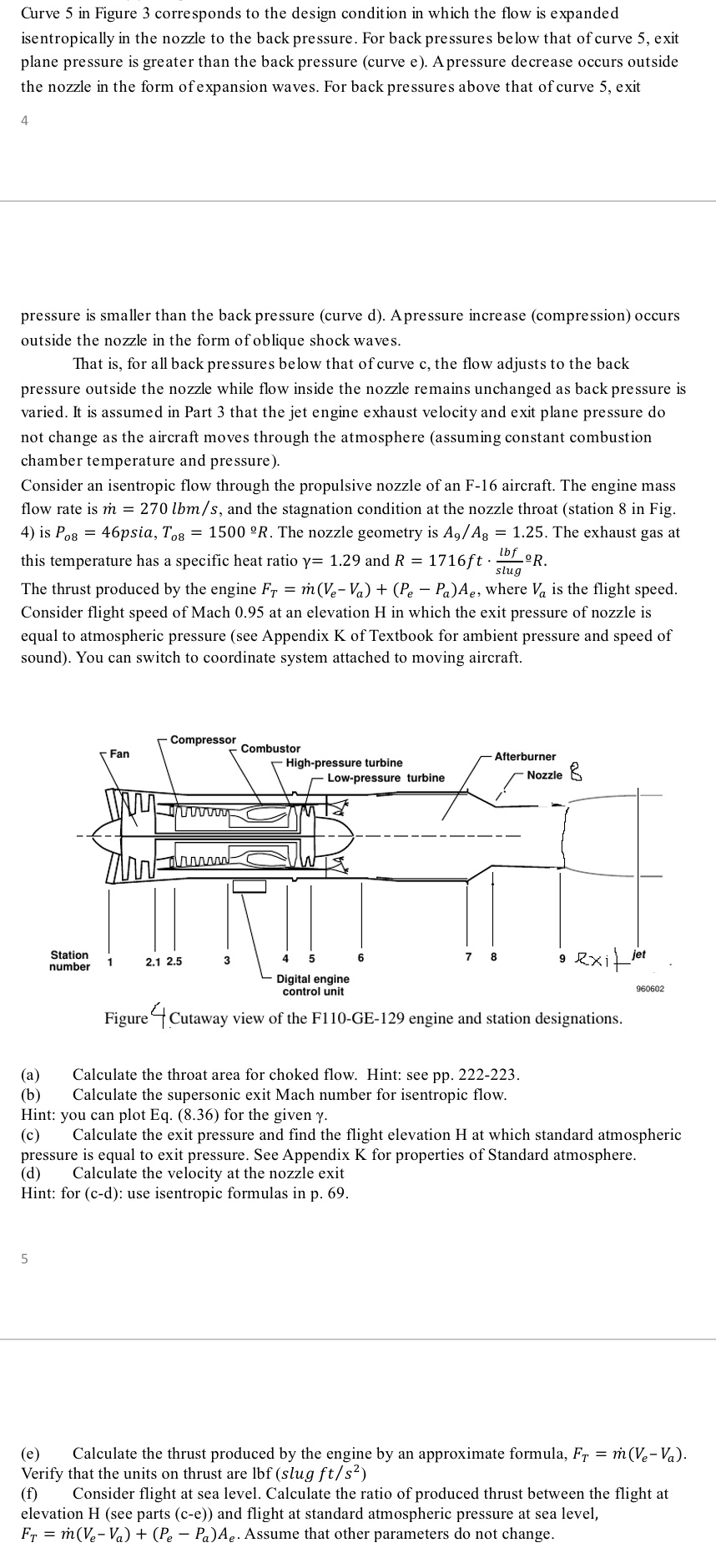
Curve 5 in Figure 3 corresponds to the design condition in which the flow is expanded isentropically in the nozzle to the back pressure. For back pressures below that of curve 5, exit plane pressure is greater than the back pressure (curve e). A pressure decrease occurs outside the nozzle in the form of expansion waves. For back pressures above that of curve 5, exit 4 pressure is smaller than the back pressure (curve d). Apressure increase (compression) occurs outside the nozzle in the form of oblique shock waves. That is, for all back pressures below that of curve c, the flow adjusts to the back pressure outside the nozzle while flow inside the nozzle remains unchanged as back pressure is varied. It is assumed in Part 3 that the jet engine exhaust velocity and exit plane pressure do not change as the aircraft moves through the atmosphere (assuming constant combustion chamber temperature and pressure). Consider an isentropic flow through the propulsive nozzle of an F-16 aircraft. The engine mass flow rate is m = 270 lbm/s, and the stagnation condition at the nozzle throat (station 8 in Fig. 4) is Po8 = 46psia, To8 = 1500 R. The nozzle geometry is Ag/Ag = 1.25. The exhaust gas at lbf this temperature has a specific heat ratio y= 1.29 and R = 1716ft. R. slug The thrust produced by the engine Fr = m(Ve-Va) + (Pe - Pa)Ae, where Va is the flight speed. Consider flight speed of Mach 0.95 at an elevation H in which the exit pressure of nozzle is equal to atmospheric pressure (see Appendix K of Textbook for ambient pressure and speed of sound). You can switch to coordinate system attached to moving aircraft. (a) (b) Station number 5 Fan 1 Compressor www 2.1 2.5 3 Combustor High-pressure turbine Low-pressure turbine 6 7 Afterburner Nozzle 8 it jet Calculate the throat area for choked flow. Hint: see pp. 222-223. Calculate the supersonic exit Mach number for isentropic flow. 9 exi Digital engine control unit Figure4Cutaway view of the F110-GE-129 engine and station designations. 960602 Hint: you can plot Eq. (8.36) for the given y. (c) Calculate the exit pressure and find the flight elevation H at which standard atmospheric pressure is equal to exit pressure. See Appendix K for properties of Standard atmosphere. (d) Calculate the velocity at the nozzle exit Hint: for (c-d): use isentropic formulas in p. 69. (e) Calculate the thrust produced by the engine by an approximate formula, FT = m(Ve-Va). Verify that the units on thrust are lbf (slug ft/s) Consider flight at sea level. Calculate the ratio of produced thrust between the flight at elevation H (see parts (c-e)) and flight at standard atmospheric pressure at sea level, FT = m(Ve-Va) + (Pe - Pa)Ae. Assume that other parameters do not change.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


