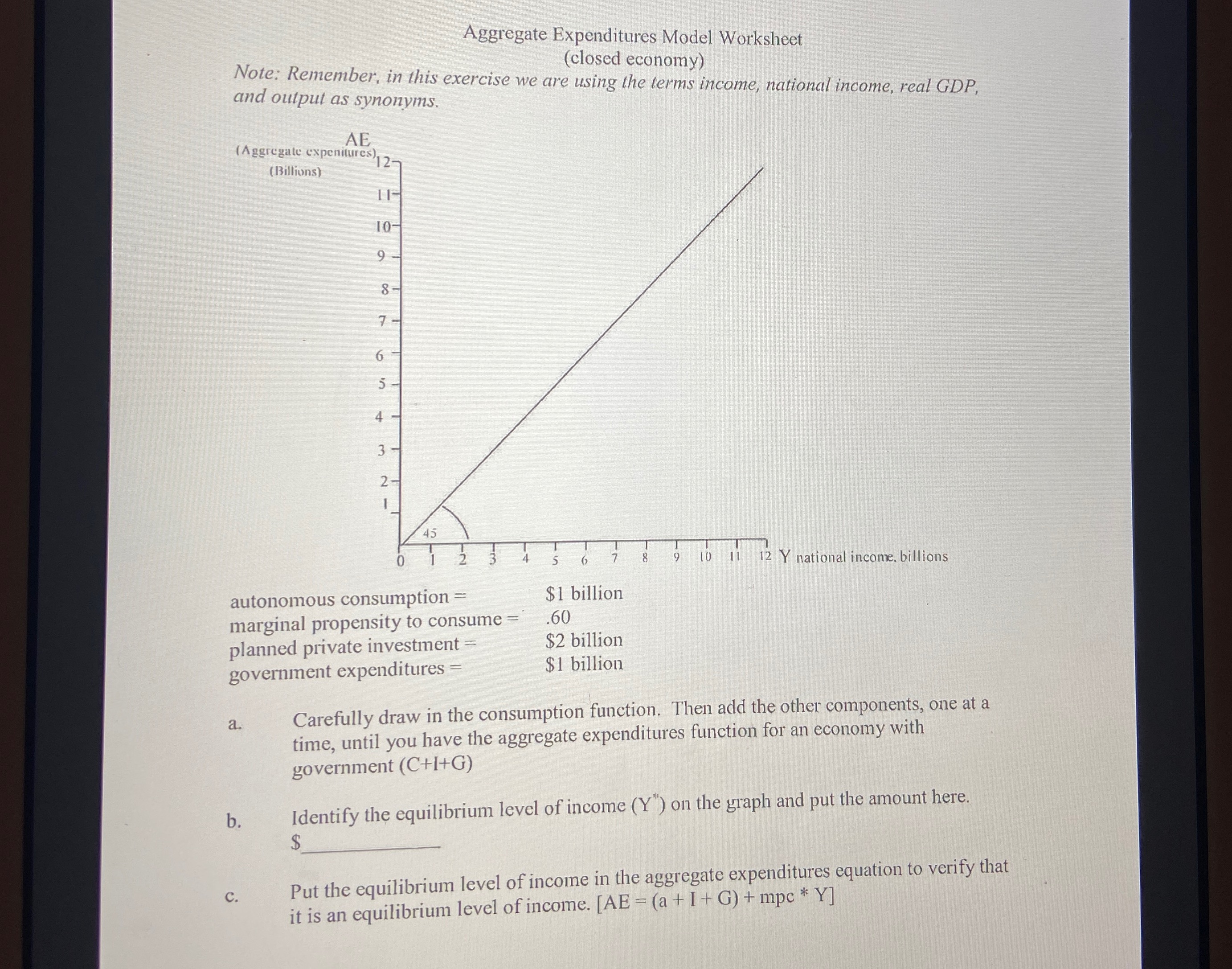
Question
D. - What is the value of aggregated expenditures when the actual income is $1 billion greater than the equilibrium level of income? - At
D. - What is the value of aggregated expenditures when the actual income is $1 billion greater than the equilibrium level of income? - At this level of income, which is greater, income or expenditures? - What does this mean in regards to planned private investments and inventories? - How would producers respond to the change in planned private investment? - what will eventually happen to the actual level of income when it is above the equilibrium level? E. - what is the value of aggregate expenditures when the actual income is $1 billion less than the equilibrium level of income?- At this level of income, which is greater, income or expenditures? - What does this mean in regards to planned private investments and inventories? - How would producers respond to the change in planned private investment? - How would producers respond to the change in planned private investment? F. Suppose that planned private investment decreased from $2 billion to $1 billion, what would the new equilibrium level of income be? G. - Given the answer to question F. what is the value of the spending multiplier (using the method multiplier = change in real GDP/initial change in spending)? - is this the same answer you would get if you calculated the multiplier as 1/mps?H.- suppose that the equilibrium level of income is below the full employment level of income. How could the government use its fiscal policy (spending only) to increase employment? - how would this type of fiscal policy affect the graph? I. - suppose that the equilibrium level of income is above the full employment level of income. How could the government use its fiscal policy (spending only) to decrease employment? - how would this type of fiscal policy affect the graph? J. Explain briefly how the government could use its fiscal policy (taxes only) to influence the level of income/output K. In this worksheet we have ignored the international sector (imports and exports). If the international sector were to be added, would the equilibrium level of income increase, decrease, or stay the same?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


