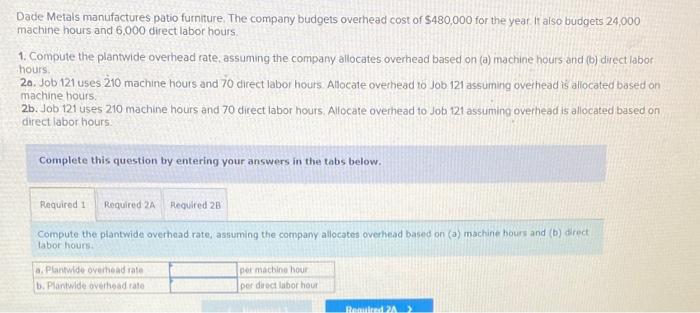
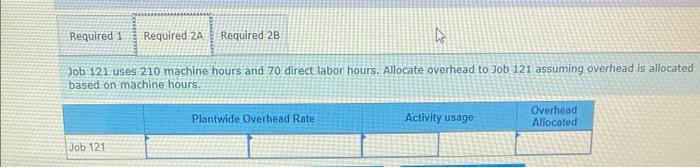
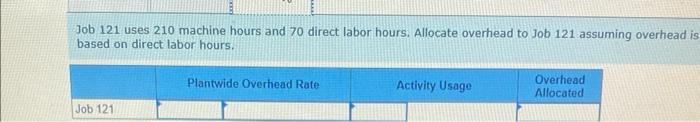
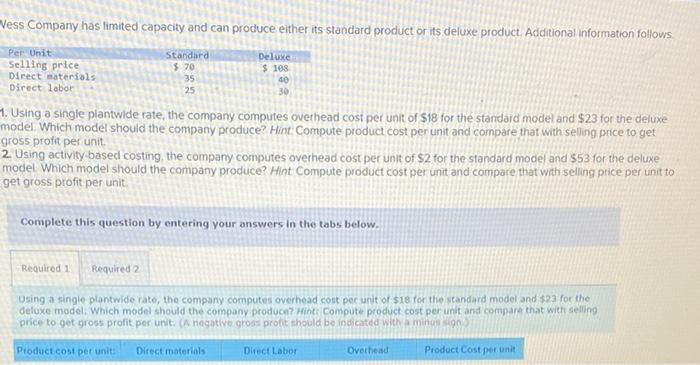
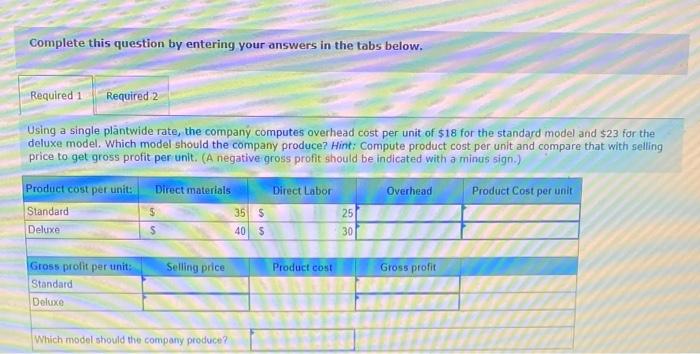
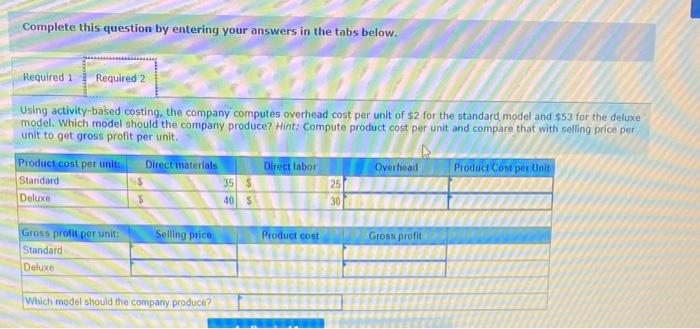
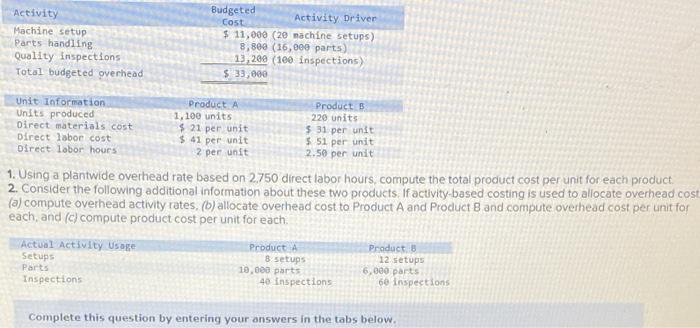
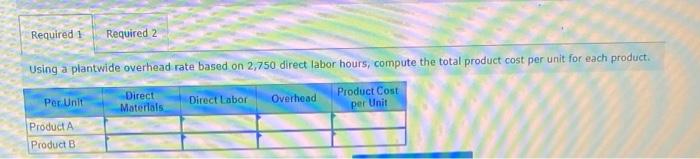
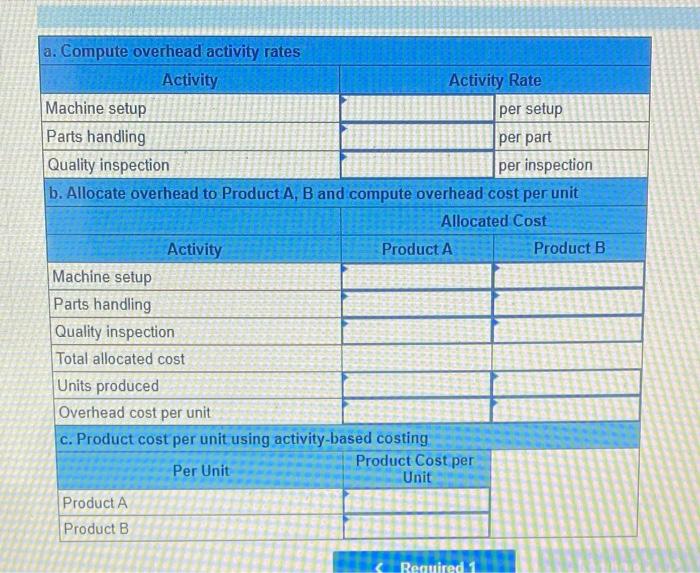
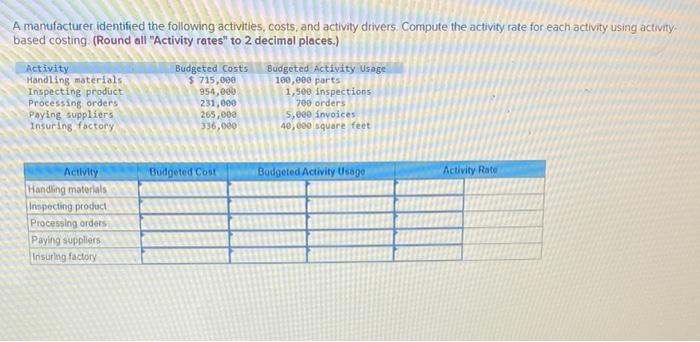
Dade Metals manufactures patio furniture. The company budgets overhead cost of $480,000 for the year. It also budgets 24,000 machine hours and 6.000 direct labor hours. 1. Compute the plantwide overhead rate, assuming the company allocates overhead based on (a) machine hours and (b) direct labor hours. 2a. Job 121 uses 210 machine hours and 70 direct labor hours. Allocate ovethead to Job 121 assuming overhead is allocated based on machine hours: 2b. Job 121 uses 210 machine hours and 70 direct labor hours. Allocate overhead to Job 121 assuming overhead is allocated based on direst labor hours. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute the plantwide overhead rate, assuming the company allocates ovemead based on (a) machine hours and (b) direct tabor hours. Job:121 uses 210 machine hours and 70 direct labor hours. Allocate overhead to Job 121 assuming overhead is atlocated based on machine hours. Job 121 uses 210 machine hours and 70 direct labor hours. Allocate overhead to Job 121 assuming overhead is based on direct labor hours. Using a single plantwide rate, the company computes overhead cost per unit of $18 for the standard model and $23 for the deluxe nodel. Which model shouid the company produce? Hint: Compute product cost per unit and compare that with selling price to get ross profit per unit. 2. Using activity based costing, the company computes overhead cost per unit of $2 for the standard model and $53 for the deluxe nodel Which model should the company produce? Hint Compute product cost per unit and compare that with selling price per unit to get gross profit per unit Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. using a single plantwide rate, the company computes overhead cost pec unit of s18 for the seandard model and $23 for the deluxe model, Which model should the company produce? Hint: Compute product cost per unit and compare that with selling price to get gross profit per unit: (A negative gross profit thould be indicated witha minke sign) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Using a single plntwide rate, the company computes overhead cost per unit of $18 for the standard model and $23 for the deluxe model. Which model should the company produce? Hint: Compute product cost per unit and compare that with selling price to get gross profit per unit. (A negative gross profit should be indicated with a minus sign.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Using activity-based costing, the company computes overhead cost per unit of $2 for the standard model and $53 for the deluxe model. Which model should the company produce? Hint: Compute product cost per unit and compare that with selling price per unit to get gross profit per unit. 1. Using a plantwide overhead rate based on 2.750 direct labor hours, compute the total product cost per unit for each product. 2. Consider the following additional information about these two products. If activity-based costing is used to allocate overhead cos: (a) compute overhead activity rates, (b) allocate overhead cost to Product A and Product B and compute overhead cost per unit for each, and (c) compute product cost per unit for each. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Using a plantwide overhead rate based on 2,750 direct labor hours, compute the total product cost per unit for each product. a. Compute overhead activity rates \begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|} \hline \multicolumn{1}{|c|}{ Activity } & \multicolumn{2}{c|}{ Activity Rate } \\ \hline Machine setup & & per setup \\ \hline Parts handling & & per part \\ \hline Quality inspection & & per inspection \\ \hline \end{tabular} b. Allocate overhead to Product A, B and compute overhead cost per unit Allocated Cost \begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|} \hline \multicolumn{1}{|c|}{ Activity } & Product A & Product B \\ \hline Machine setup & & \\ \hline Parts handling & & \\ \hline Quality inspection & & \\ \hline Total allocated cost & & \\ \hline Units produced & & \\ \hline Overhead cost per unit & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} c. Product cost per unit using activity-based costing \begin{tabular}{|l|c|} \hline Per Unit & Product Cost per \\ \hline Product A & \\ \hline Product B & \\ \hline \end{tabular} A manufacturer identified the following activities, costs, and activity drivers. Compute the activity rate for each activity using activitybased costing. (Round all "Activity rates" to 2 decimal places.)