Question
Dash Company adopted a standard costing system several years ago. The standard costs for the prime costs (i.e., direct materials and direct labor) of its
Dash Company adopted a standard costing system several years ago. The standard costs for the prime costs (i.e., direct materials and direct labor) of its single product are:
| Material | (5 kilograms $5.00 per kilogram) | $ 25.00 |
|---|---|---|
| Labor | (6 hours $19.50 per hour) | 117.00 |
All materials are added at the beginning of processing. The following data were taken from the companys records for November:
| In-process beginning inventory | None | |
|---|---|---|
| In-process ending inventory | 800 | units, 70% complete as to direct labor |
| Units completed | 6,400 | units |
| Budgeted output | 6,800 | units |
| Purchases of materials | 58,000 | kilograms |
| Total actual direct labor costs | $ 750,000 | |
| Actual direct labor hours | 41,000 | hours |
| Materials usage variance | $ 2,300 | Unfavorable |
| Total materials variance | $ 850 | Unfavorable |
Required:
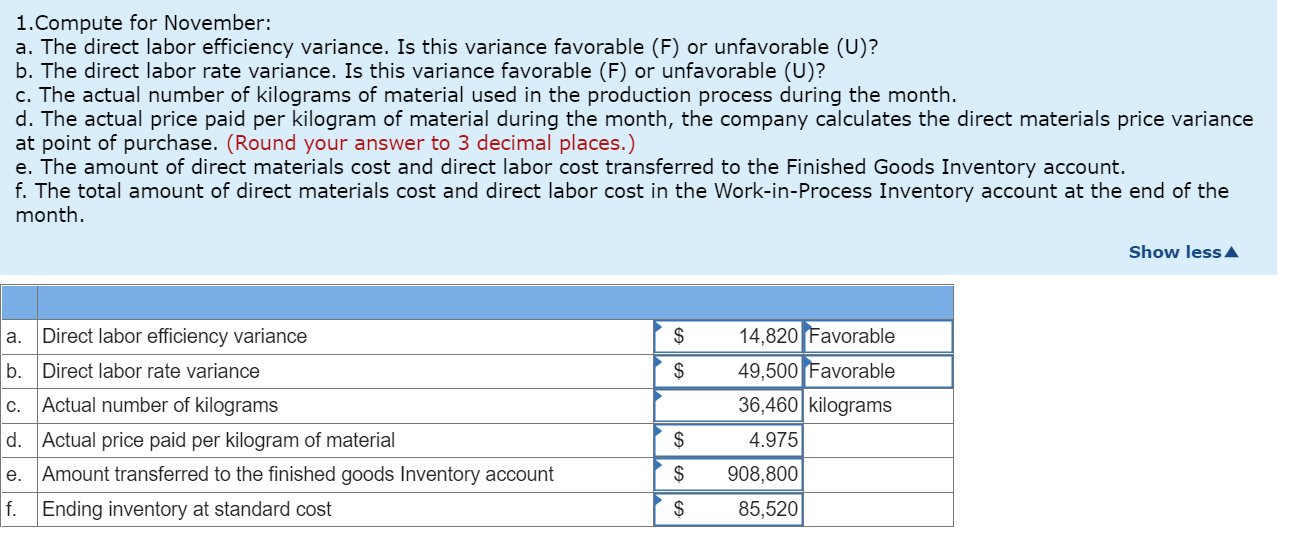
1. Compute for November:
a. The direct labor efficiency variance. Is this variance favorable (F) or unfavorable (U)?
b. The direct labor rate variance. Is this variance favorable (F) or unfavorable (U)?
c. The actual number of kilograms of material used in the production process during the month.
d. The actual price paid per kilogram of material during the month, the company calculates the direct materials price variance at point of purchase.
e. The amount of direct materials cost and direct labor cost transferred to the Finished Goods Inventory account.
f. The total amount of direct materials cost and direct labor cost in the Work-in-Process Inventory account at the end of the month.
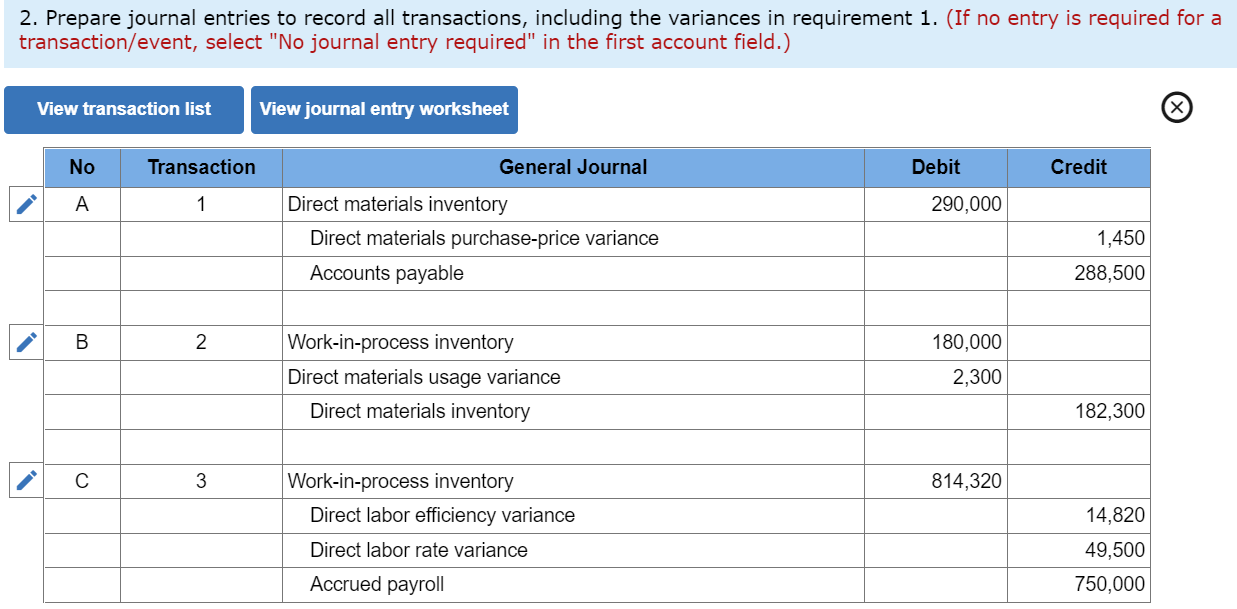
2. Prepare journal entries to record all transactions, including the variances in requirement 1.
No journal entry required, accounts payable, accounts receivable,accrued payroll,cost of goods sold, depreciation, direct labor efficiency variance, direct labor rate variance, direct materials inventory, direct materials purchase price variance,direct materials usage variance,finished goods inventory, fixed costs, fixed overhead, insurance, manufacturing, rent, salaries, sales commissions, sales revenue, selling and administrative, variable costs, variable overhead, work-in-process inventory
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


