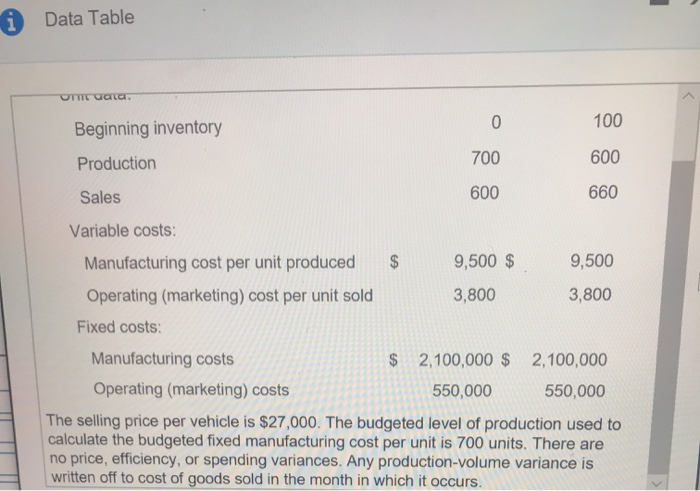
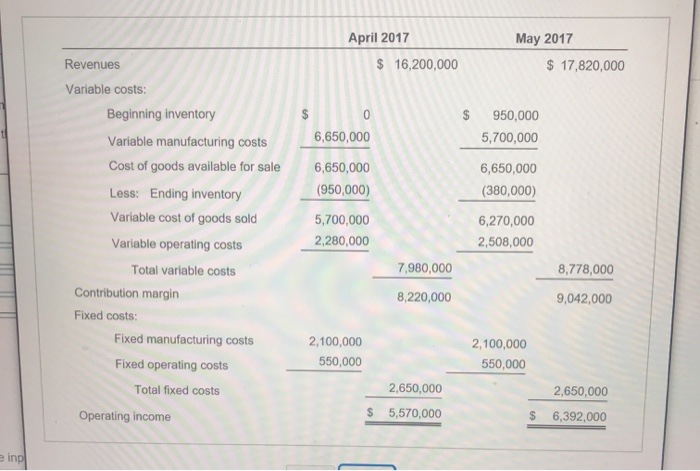
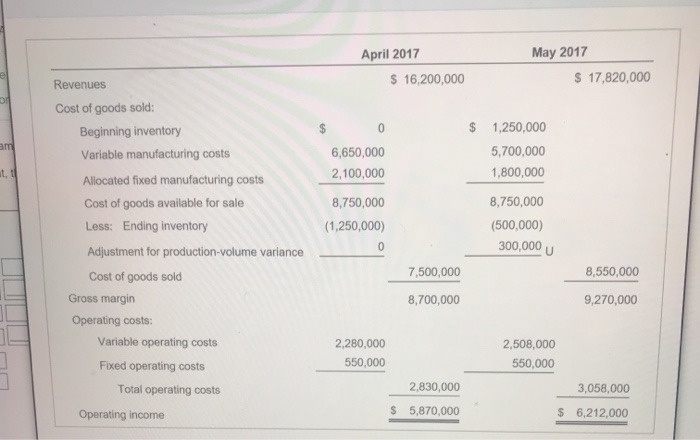
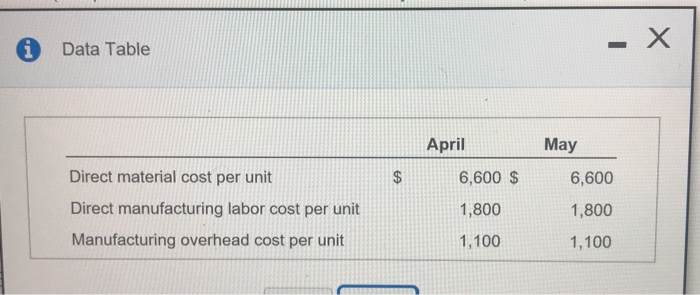
Data Table telr - OT aata 100 0 Beginning inventory 600 700 Production 660 600 Sales Variable costs: 9,500 $ 9,500 Manufacturing cost per unit produced 3,800 3,800 Operating (marketing) cost per unit sold Fixed costs: $2,100,000 $ 2,100,000 Manufacturing costs Operating (marketing) costs 550,000 550,000 The selling price per vehicle is $27,000. The budgeted level of production used to calculate the budgeted fixed manufacturing cost per unit is 700 units. There are no price, efficiency, or spending variances. Any production-volume variance is written off to cost of goods sold in the month in which it occurs. April 2017 May 2017 $16,200,000 Revenues $17,820,000 Variable costs: Beginning inventory 0 950,000 6,650,000 5,700,000 Variable manufacturing costs Cost of goods available for sale 6,650,000 6,650,000 (950,000) (380,000) Less: Ending inventory Variable cost of goods sold 5,700,000 6,270,000 2,280,000 2,508,000 Variable operating costs 7,980,000 8,778,000 Total variable costs Contribution margin 8,220,000 9,042,000 Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing costs 2,100,000 2,100,000 550,000 550,000 Fixed operating costs 2,650,000 Total fixed costs 2,650,000 $ 5,570,000 $ 6,392,000 Operating income e inp May 2017 April 2017 $ 16,200,000 $17,820,000 Revenues Cost of goods sold: $ 1,250,000 Beginning inventory am 5,700,000 6,650,000 Variable manufacturing costs 1,800,000 t, t 2,100,000 Allocated fixed manufacturing costs 8,750,000 8,750,000 Cost of goods available for sale (500,000) Less: Ending inventory (1,250,000) 300,000 0 Adjustment for production-volume variance 7,500,000 8,550,000 Cost of goods sold Gross margin 8,700,000 9,270,000 Operating costs: Variable operating costs 2,280,000 2,508,000 550,000 550,000 Fixed operating costs 2,830,000 3,058,000 Total operating costs $ 5,870,000 $ 6,212,000 Operating income X i Data Table May April Direct material cost per unit $ 6,600 $ 6,600 Direct manufacturing labor cost per unit 1,800 1,800 Manufacturing overhead cost per unit 1,100 1,100 - X i Requirements 1. Prepare income statements for Champion Motors in April and May 2017 under throughput costing. 2. Contrast the results in requirement 1 with the absorption and variable costing income statements presented. 3. Give one motivation for Champion Motors to adopt throughput costing