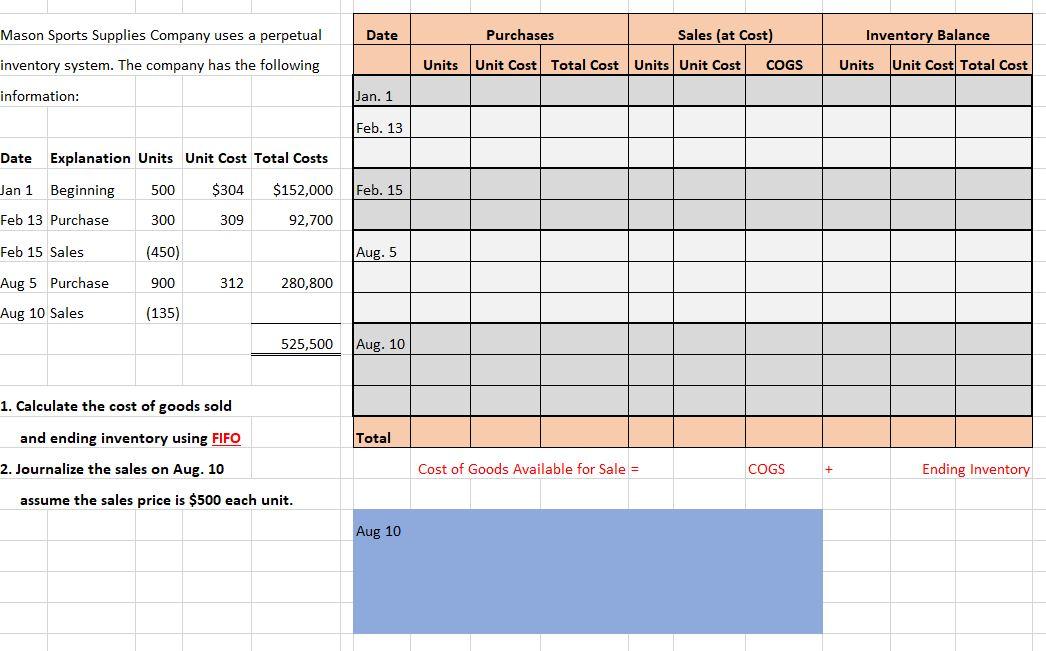
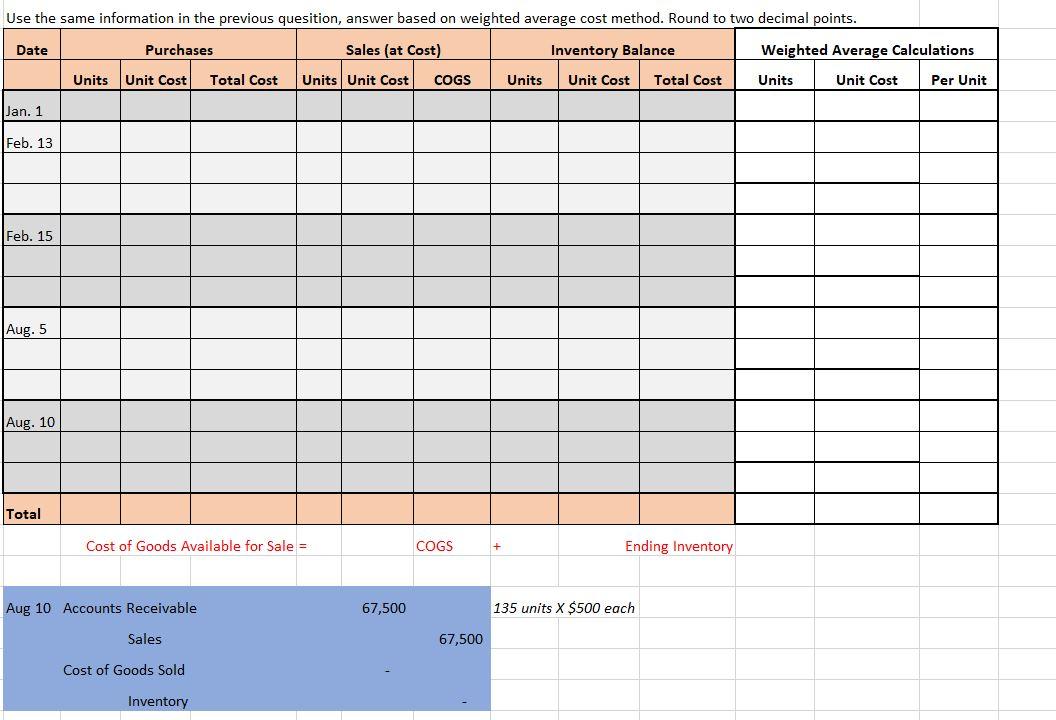
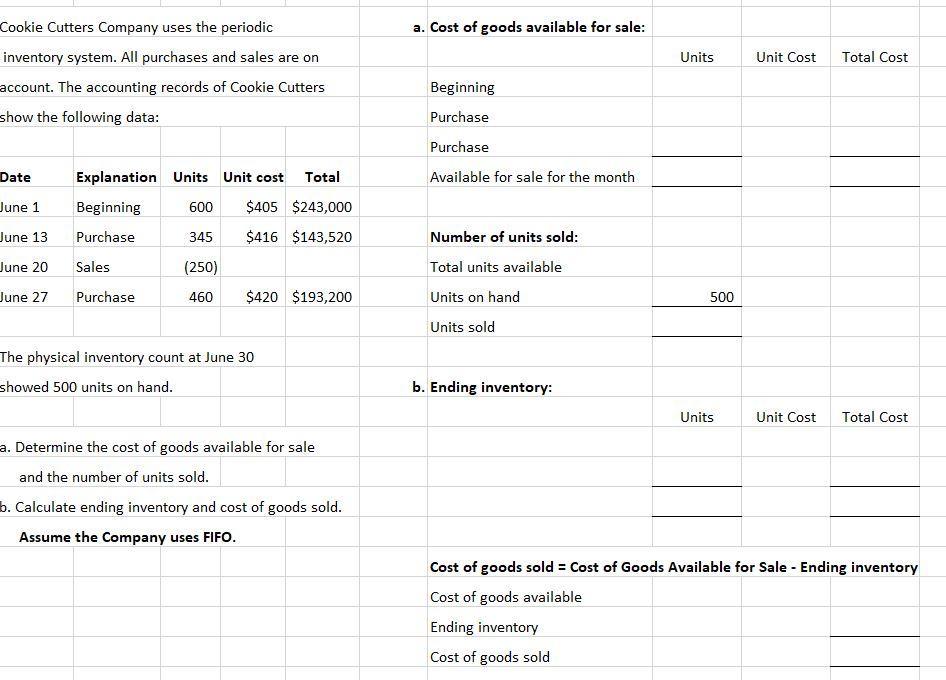
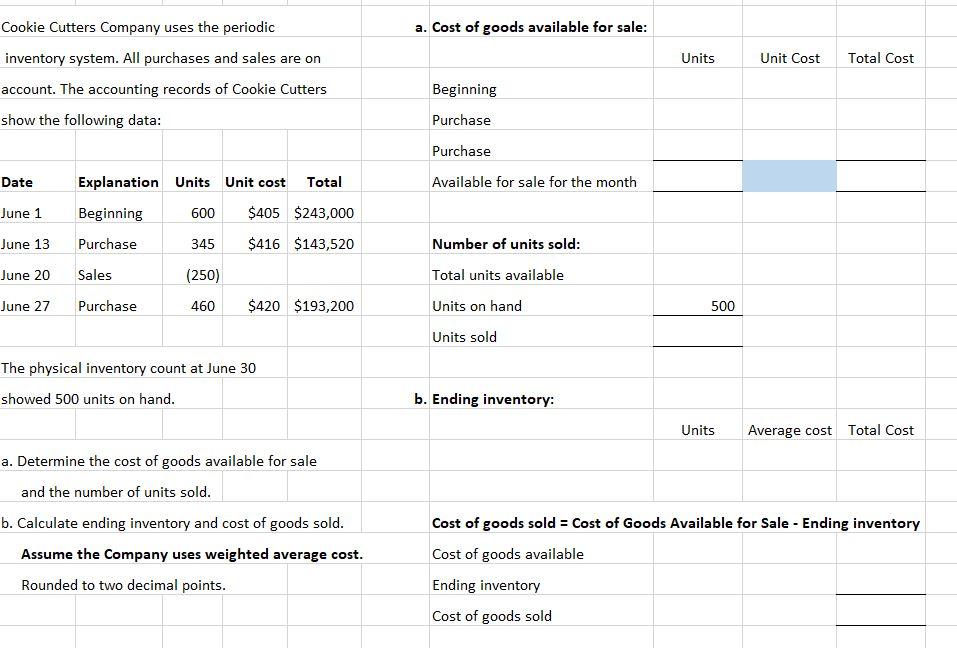
Date Purchases Sales (at Cost) Inventory Balance Mason Sports Supplies Company uses a perpetual inventory system. The company has the following information: Units Unit Cost Total Cost Units Unit Cost COGS Units Unit Cost Total Cost Jan. 1 Feb. 13 Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Costs Jan 1 Beginning 500 $304 $152,000 Feb. 15 Feb 13 Purchase 300 309 92,700 Feb 15 Sales (450) Aug. 5 Aug 5 Purchase 900 312 280,800 Aug 10 Sales (135) 525,500 Aug. 10 1. Calculate the cost of goods sold Total and ending inventory using FIFO 2. Journalize the sales on Aug. 10 Cost of Goods Available for Sale = COGS Ending Inventory assume the sales price is $500 each unit. Aug 10 Use the same information in the previous quesition, answer based on weighted average cost method. Round to two decimal points. Date Purchases Sales (at Cost) Inventory Balance Weighted Average Calculations Units Unit Cost Total Cost Units Unit Cost COGS Units Unit Cost Total Cost Units Unit Cost Per Unit Jan. 1 Feb. 13 Feb. 15 Aug. 5 Aug. 10 Total Cost of Goods Available for Sale = COGS + Ending Inventory Aug 10 Accounts Receivable 67,500 135 units X $500 each Sales 67,500 Cost of Goods Sold Inventory a. Cost of goods available for sale: Units Unit Cost Total Cost Cookie Cutters Company uses the periodic inventory system. All purchases and sales are on account. The accounting records of Cookie Cutters show the following data: Beginning Purchase Purchase Date Available for sale for the month June 1 June 13 June 20 Explanation Units Unit cost Total Beginning 600 $405 $243,000 Purchase 345 $416 $143,520 Sales (250) Number of units sold: Total units available Units on hand Units sold June 27 Purchase 460 $420 $193,200 500 The physical inventory count at June 30 showed 500 units on hand. b. Ending inventory: Units Unit Cost Total Cost a. Determine the cost of goods available for sale and the number of units sold. b. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold. Assume the Company uses FIFO. Cost of goods sold = Cost of Goods Available for Sale - Ending inventory Cost of goods available Ending inventory Cost of goods sold a. Cost of goods available for sale: Units Unit Cost Total Cost Cookie Cutters Company uses the periodic inventory system. All purchases and sales are on account. The accounting records of Cookie Cutters show the following data: Beginning Purchase Purchase Date Explanation Units Unit cost Total Available for sale for the month June 1 600 $405 $243,000 Beginning Purchase June 13 345 $416 $143,520 Number of units sold: June 20 Sales (250) Total units available Units on hand June 27 Purchase 460 $420 $193,200 500 Units sold The physical inventory count at June 30 showed 500 units on hand. b. Ending inventory: Units Average cost Total Cost a. Determine the cost of goods available for sale and the number of units sold. b. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold. Assume the Company uses weighted average cost. Rounded to two decimal points. Cost of goods sold = Cost of Goods Available for Sale - Ending inventory Cost of goods available Ending inventory Cost of goods sold










