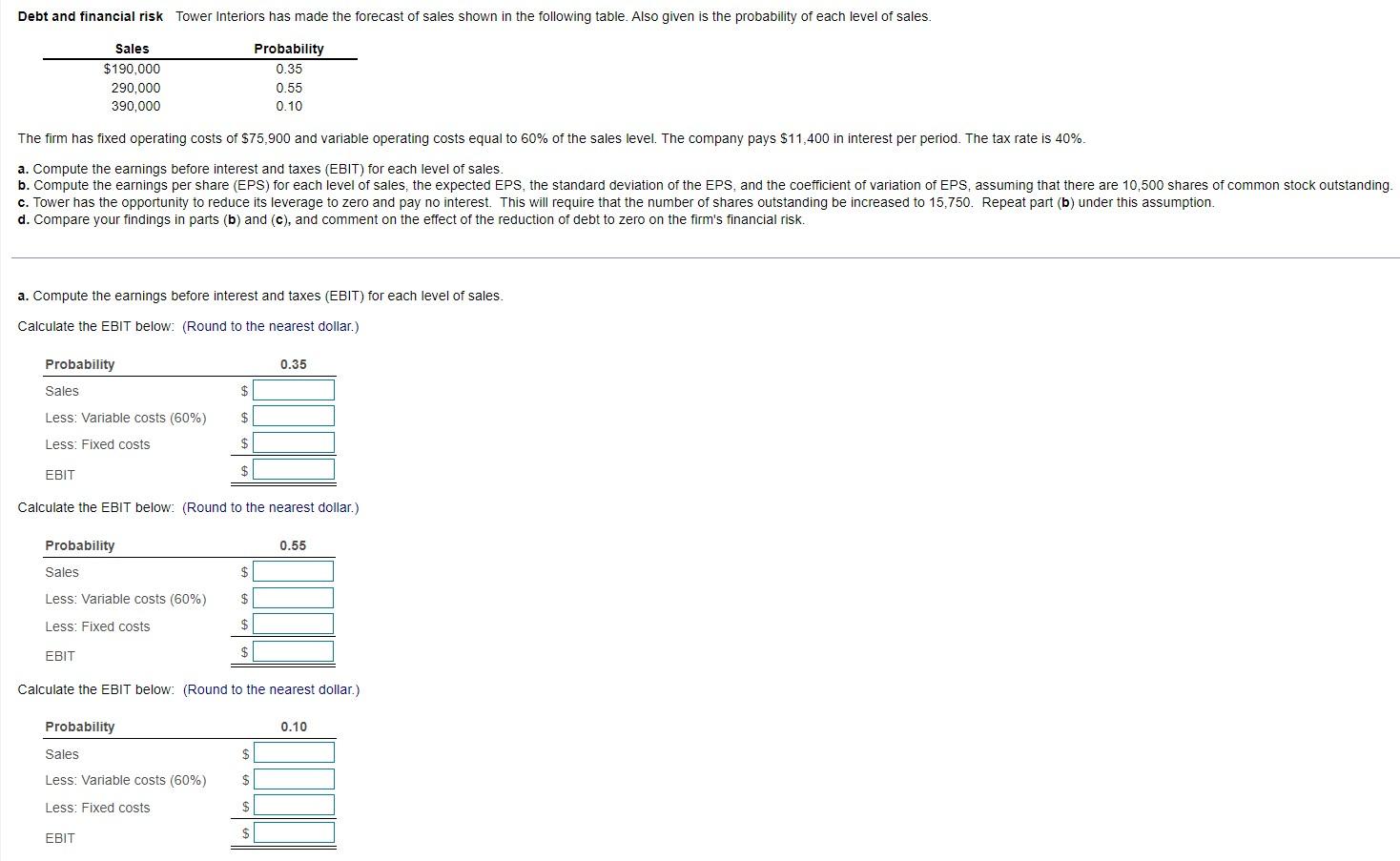
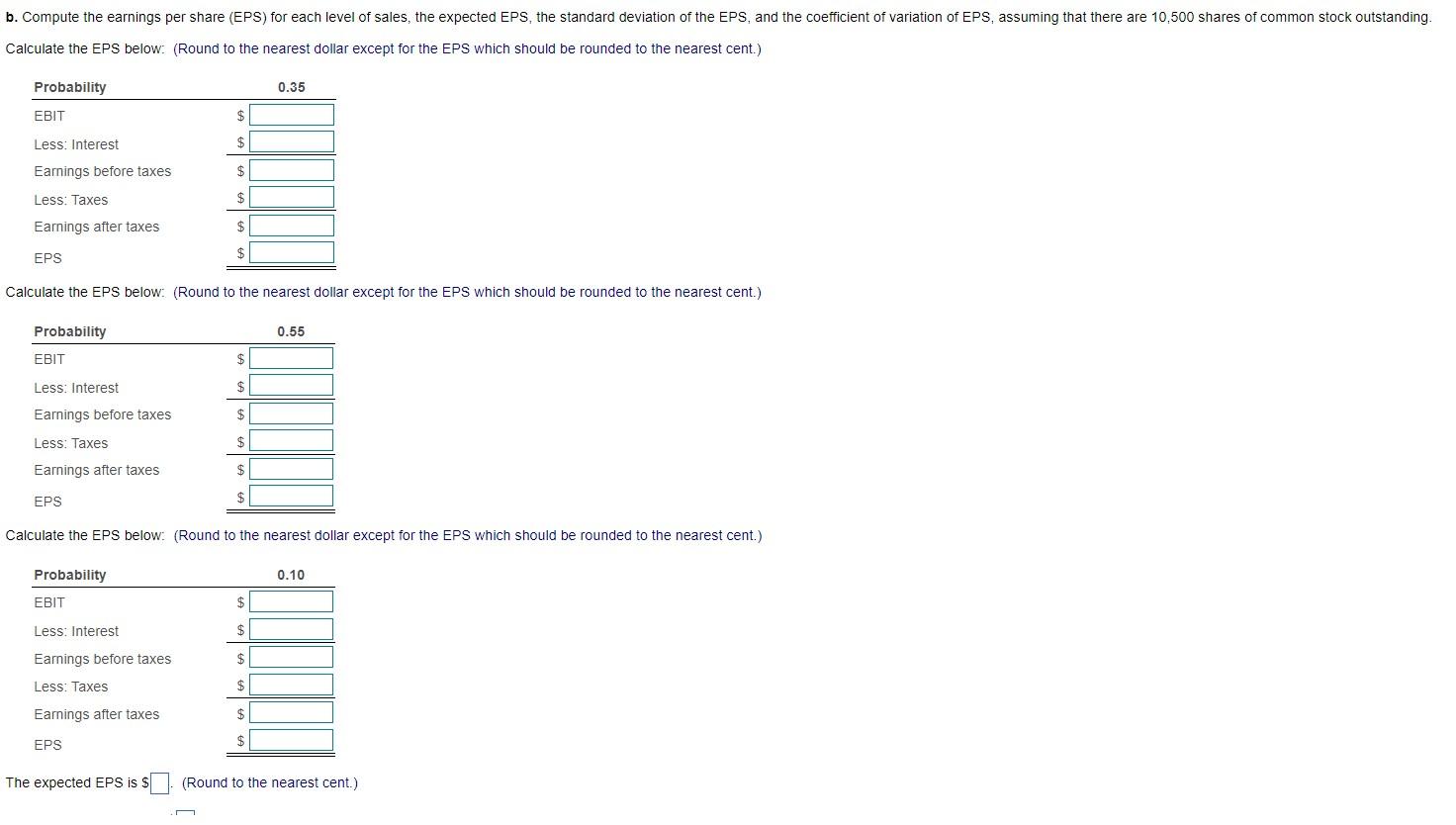
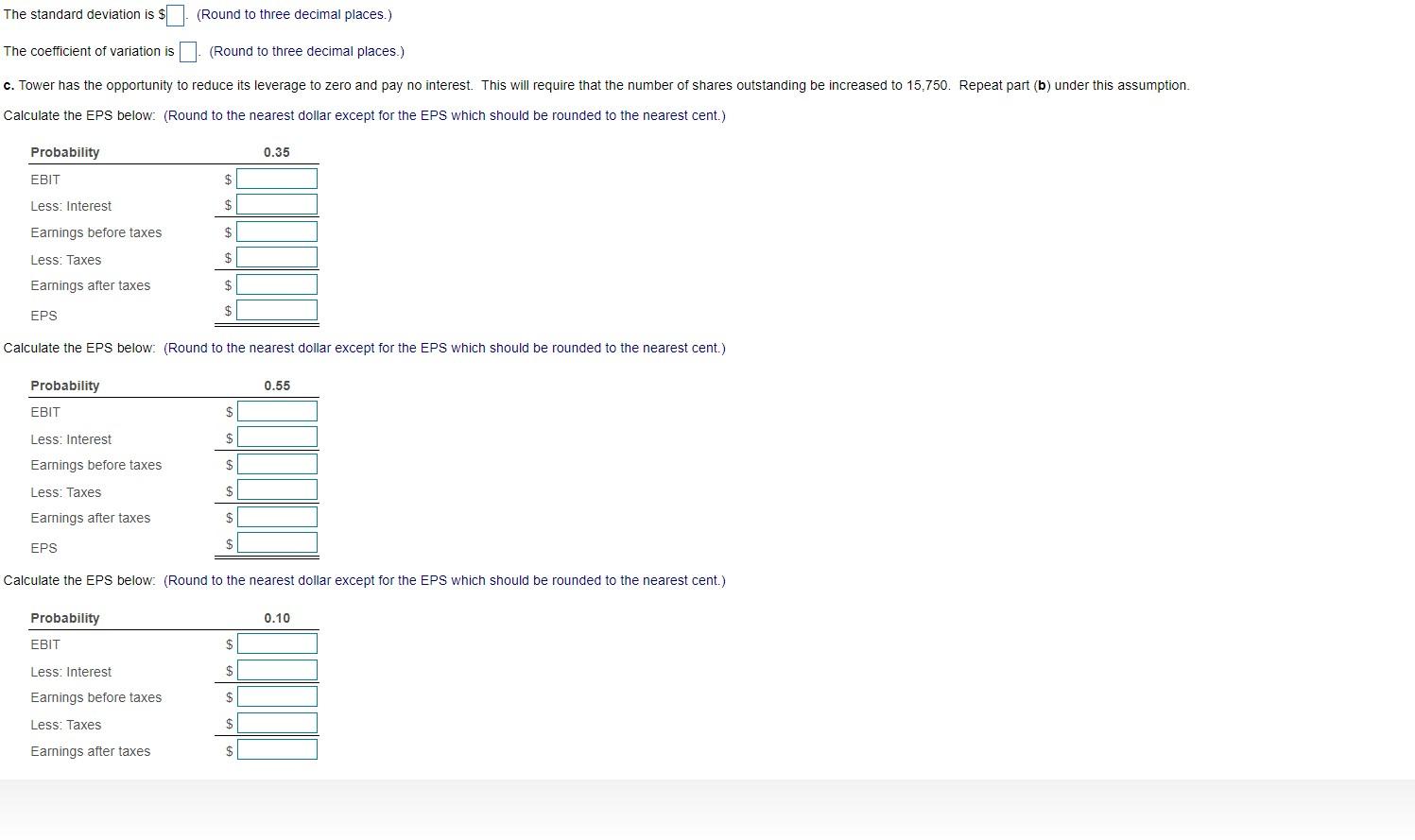

Debt and financial risk Tower Interiors has made the forecast of sales shown in the following table. Also given is the probability of each level of sales. Probability 0.35 Sales $190,000 290,000 390,000 0.55 0.10 The firm has fixed operating costs of $75,900 and variable operating costs equal to 60% of the sales level. The company pays $11,400 in interest per period. The tax rate is 40%. a. Compute the earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) for each level of sales. b. Compute the earnings per share (EPS) for each level of sales, the expected EPS, the standard deviation of the EPS, and the coefficient of variation of EPS, assuming that there are 10,500 shares of common stock outstanding. c. Tower has the opportunity to reduce its leverage to zero and pay no interest. This will require that the number of shares outstanding be increased to 15,750. Repeat part (b) under this assumption. d. Compare your findings in parts (b) and (c), and comment on the effect of the reduction of debt to zero on the firm's financial risk. a. Compute the earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) for each level of sales. Calculate the EBIT below: (Round to the nearest dollar.) Probability 0.35 Sales Less: Variable costs (60%) $ Less: Fixed costs $ EBIT Calculate the EBIT below: (Round to the nearest dollar.) Probability 0.55 Sales $ Less: Variable costs (60%) $ Less: Fixed costs $ EBIT $ Calculate the EBIT below: (Round to the nearest dollar.) Probability 0.10 Sales $ Less: Variable costs (60%) $ Less: Fixed costs $ EBIT $ b. Compute the earnings per share (EPS) for each level of sales, the expected EPS, the standard deviation of the EPS, and the coefficient of variation of EPS, assuming that there are 10,500 shares of common stock outstanding. Calculate the EPS below. (Round to the nearest dollar except for the EPS which should be rounded to the nearest cent.) Probability 0.35 EBIT $ Less: Interest $ Earnings before taxes $ Less: Taxes $ Earnings after taxes $ EPS $ Calculate the EPS below: (Round to the nearest dollar except for the EPS which should be rounded to the nearest cent.) Probability 0.55 EBIT $ Less: Interest $ Earnings before taxes $ Less: Taxes $ Earnings after taxes $ EPS $ Calculate the EPS below: (Round to the nearest dollar except for the EPS which should be rounded to the nearest cent.) Probability 0.10 EBIT $ Less: Interest $ Earnings before taxes $ Less: Taxes $ Earnings after taxes $ EPS $ The expected EPS is S (Round to the nearest cent.) The standard deviation is $ (Round to three decimal places.) The coefficient of variation is (Round to three decimal places.) c. Tower has the opportunity to reduce its leverage to zero and pay no interest. This will require that the number of shares outstanding be increased to 15,750. Repeat part (b) under this assumption. Calculate the EPS below. (Round to the nearest dollar except for the EPS which should be rounded to the nearest cent.) Probability 0.35 EBIT $ Less: Interest $ Earnings before taxes $ Less: Taxes $ Earnings after taxes $ EPS Calculate the EPS below. (Round to the nearest dollar except for the EPS which should be rounded to the nearest cent.) Probability 0.55 EBIT $ Less: Interest $ Earnings before taxes $ Less: Taxes $ Earnings after taxes $ EPS $ Calculate the EPS below. (Round to the nearest dollar except for the EPS which should be rounded to the nearest cent.) Probability 0.10 EBIT $ Less: Interest Earnings before taxes $ Less: Taxes $ Earnings after taxes $ Calculate the EPS below: (Round to the nearest dollar except for the EPS which should be rounded to the nearest cent.) Probability 0.10 EBIT $ Less: Interest Earnings before taxes $ Less: Taxes $ Earnings after taxes $ EPS $ The expected EPS is S (Round to the nearest cent.) The standard deviation is s/. (Round to three decimal places.) The coefficient of variation is (Round to three decimal places.) d. Compare your findings in parts (b) and (c), and comment on the effect of the reduction of debt to zero on the firm's financial risk. (Select the best answer below.) O A. Eliminating debt from the firm's capital structure reduces financial risk, which is measured by the coefficient of variation. O B. Eliminating debt from the firm's capital structure does not change financial risk, which is measured by the coefficient of variation. O C. Eliminating debt from the firm's capital structure increases financial risk, which is measured by the coefficient of variation. OD. Eliminating debt from the firm's capital structure sometimes increases and sometimes reduces financial risk, which is measured by the coefficient of variation










