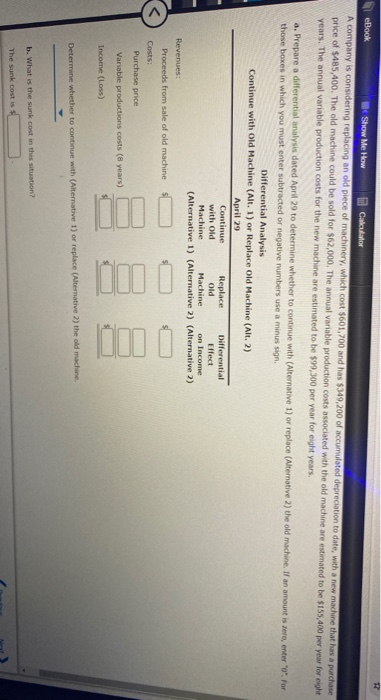
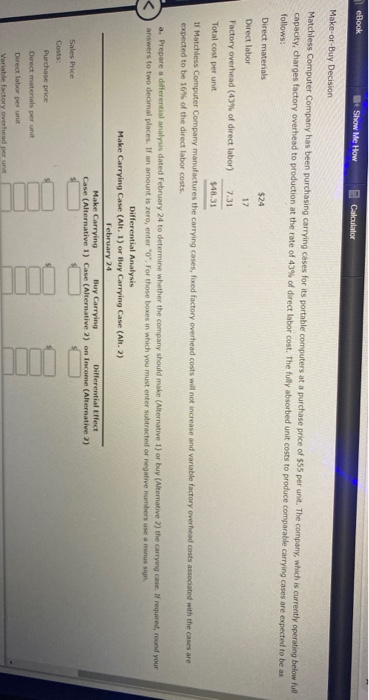
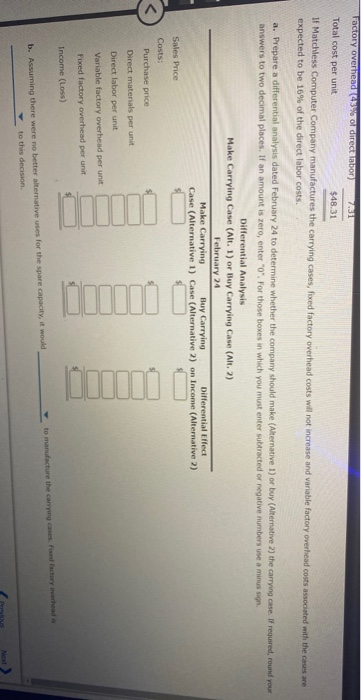
Decision on Accepting Additional Business Country Jeans Co. has an annual plant capacity of 63,000 units, and current production is 44,800 units. Monthly fixed costs are $40,000, and variable costs are $25 per unit. The present selling price is $34 per unit. On November 12 of the current year, the company received an offer from Miller Company for 15,600 units of the product at $29 each. Miller Company will market the units in a foreign country under its own brand name. The additional business is not expected to affect the domestic selling price or quantity of sales of Country Jeans Co. a. Prepare a differential analysis dated November 12 on whether to reject (Alternative 1) or accept (Alternative 2) the Miller order. If an amount is zero, enter zero "o". For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign Differential Analysis Reject Order (Alt. 1) or Accept Order (Alt. 2) November 12 Differential Reject Accept Order Effect Order on Income (Alternative 1) (Alternative 2) (Alternative 2) Revenues Costs: Variable manufacturing costs Income (Loss) to this decision. The differential revenue is than the differential cost. Thus, accepting this additional b. Having unused capacity available is business will result in a net c. What is the minimum price per unit that would produce a positive contribution margin? Round your answer to two decimal places Sell or Process Further Jackson Lumber Company incurs a cost of $388 per hundred board feet (hbo) in processing certain "rough-cut lumber, which it sells for $550 per hof. An alternative is to produce a finished cut" at a total processing cost of $522 per hof, which can be sold for $744 per bl. Prepare a differential analysis dated August 9 on whether to sell rough-cut lumber (Alternative 1) or process further into finished-cut lumber (Alternative 2). For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign Differential Analysis Sell Rough Cut (Alt. 1) or Process Further into Finished Cut (Alt. 2) August 9 Process Differential Sell Rough-Cut Further into Effect Finished Cut on Income (Alternative 1) (Alternative 2) (Alternative 2) Revenues, per 100 board it. Costs, per 100 board ft. Income (Loss), per 100 board ft. Determine whether to sell rough-cut lumber (Alternative 1) or process further into finished-cut lumber (Alternative 2) eBook Show Me How Calculator A company is considering replacing an old piece of machinery, which cost $601,700 and has $349,200 of accumulated depreciation to date, with a new machine that has a purchase price of $485,400. The old machine could be sold for $62,000. The annual variable production costs associated with the old machine are estimated to be $155,400 per year for eight years. The annual variable production costs for the new machine are estimated to be $99,300 per year for eight years. a. Prepare a differential analysis dated April 29 to determine whether to continue with (Alternative 1) or replace (Alternative 2) the old machine. If an amount is zero, enter "o". For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign. Differential Analysis Continue with Old Machine (Alt. 1) or Replace Old Machine (Alt. 2) April 29 Continue Replace Differential with Old Old Effect Machine Machine on Income (Alternative 1) (Alternative 2) (Alternative 2) Revenues: Proceeds from sale of old machine Costs: Purchase price Variable productions costs (8 years) in 0 Income (Loss) Determine whether to continue with (Alternative 1) or replace (Alternative 2) the old machine b. What is the sunk cost in this situation? The sunk cost is Rock Show Me How Calculator Make-or-Buy Decision Matchless Computer Company has been purchasing carrying cases for its portable computers at a purchase price of $55 per unit. The company, which is currently operating below full capacity, charges factory overhead to production at the rate of 43% of direct labor cost. The fully absorbed unit costs to produce comparable carrying cases are expected to be as follows: Direct materials $24 Direct labor 17 Factory overhead (43% of direct labor) 7.31 Total cost per unit $48.31 11 Matchless Computer Company manufactures the carrying cases, foxed factory overhead costs will not increase and variable factory overhead costs associated with the cases are expected to be 16% of the direct labor costs. a. Prepare a differential analysis dated February 24 to determine whether the company should make (Alternative 1) or buy (Alternative 2) the carrying case. If required, round your answers to two decimal places. If an amount is zero, enter "o". For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign Differential Analysis Make Carrying Case (Alt. 1) or Buy Carrying Case (Alt. 2) February 24 Make Carrying Buy Carrying Differential Effect Case (Alternative I) Case (Alternative?) on Income (Alternative 2) Sales Price Costs Purchase price Direct materials per unit Direct labor per unit Variable factory overhead per unit Factory overhead 45% of direct labor Total cost per unit $48.31 If Matchless Computer Company manufactures the carrying cases, fixed factory overhead costs will not increase and variable factory overhead costs associated with the cases are expected to be 16% of the direct labor costs. a. Prepare a differential analysis dated February 24 to determine whether the company should make (Alternative 1) or buy (Alternative 2) the carrying case. If required, round your answers to two decimal places. If an amount is zero, enter "O". For those boxes in which you must enter subtracted or negative numbers use a minus sign. Differential Analysis Make Carrying Case (Alt. 1) or Buy Carrying Case (Alt. 2) February 24 Make Carrying Buy Carrying Differential Effect Case (Alternative 1) Case (Alternative 2) on Income (Alternative ?) Sales Price Costs: Purchase price Direct materials per unit Direct labor per unit Variable factory overhead per unit Fixed factory overhead per unit Income (Loss) to manufacture the carrying cases, fed factory overheads b. Assuming there were no better alternative uses for the spare capacity, it would to this decision