Question
Defense Electronics This is a comprehensive project evaluation problem bringing together much of what you have learned in this and previous chapters. Suppose you have
 Defense Electronics
Defense Electronics
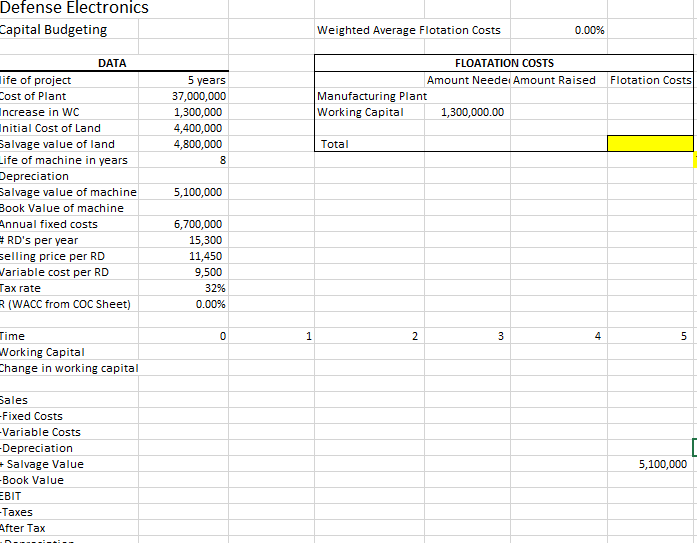
This is a comprehensive project evaluation problem bringing together much of what you have learned in this and previous chapters. Suppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Inc. (DEI), a large publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas to produce a new line of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. In order to facilitate this project, DEI purchased some land where they will build their new manufacturing plant, which cost $4.4 million on an after-tax basis. In five years, the after-tax value of the land will be $4.8 million. The plant and equipment will cost $37 million to build.
DEIs tax rate is 32 percent. The project requires $1,300,000 in initial net working capital investment to get operational. The manufacturing plant has an eight-year tax life, and DEI uses straight-line depreciation. At the end of the project (that is, the end of Year 5), the plant and equipment can be scrapped for $5.1 million.
The company will incur $6,700,000 in annual fixed costs. The plan is to manufacture 15,300 RDSs per year and sell them at $11,450 per machine; the variable production costs are $9,500 per RDS.
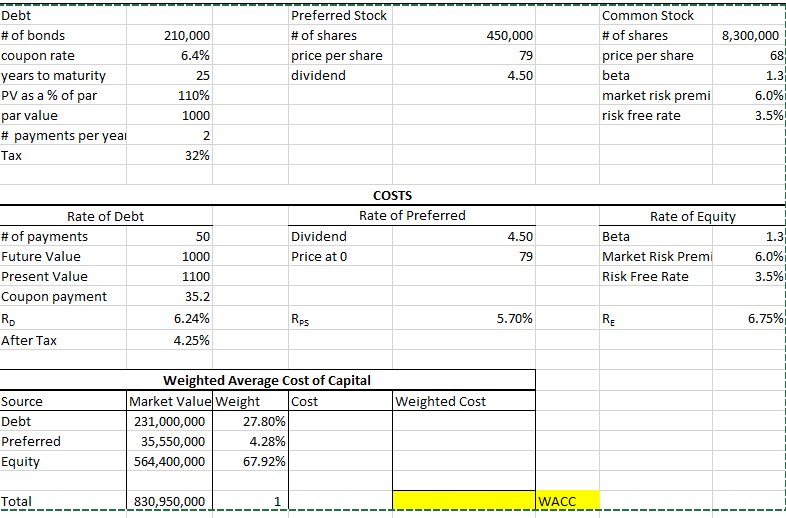
The following market data on DEIs securities are current:
Debt: 210,000 6.4% coupon bonds outstanding, 25 years to maturity, selling for 110 percent of par; the bonds have a $1,000 par value each and make semiannual payments.
Common stock: 8,300,000 shares outstanding, selling for $68 per share; the beta is 1.3.
Preferred stock: 450,000 shares of preferred stock outstanding, selling for $79 per share with a dividend of $4.50.
Market: 6 percent expected market risk premium; 3.5 percent risk-free rate.
DEI uses HSOB as its lead underwriter. HSOB charges DEI 10% flotation costs on new common stock issues, 6% on new preferred stock issues, and 4% on new debt issues. Assume DEI raises all equity for new projects externally.
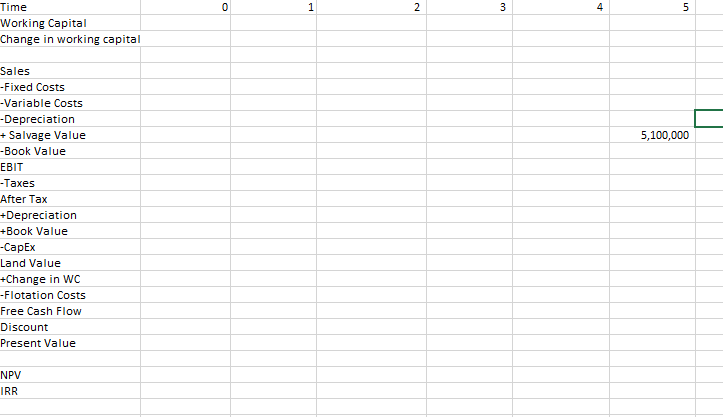
Calculate the NPV and the IRR of the proposed project.
Some notes that will help you with this case:
- When calculating the free cash flow for time 0, remember to include flotation costs as described above. The total cost will be the cost of the land, the cost of the building, the cost of the increase in working capital, and the flotation costs. Even though we already own the land and it might appear to be a sunk cost, remember that if we werent building the plant on the land we could use it for something else, meaning that there is an opportunity cost associated with it. Because of this, the cost of the land should be included. Be sure to put this cost under the tax line as we are dealing with after tax values.
The cost of the building and working capital will require new financing and therefore financing costs. Thus the building and working capital must be adjusted for the flotation costs as discussed in section 14-7 of the 11th edition and 14-6 of the 10th edition of the text. It is not necessary to adjust the land costs since we already own the land.
- The appropriate amount to depreciate is just the cost of the building (37,000,000). Financing costs and the cost of the land should not be included.
- In year 5, remember to include the salvage value of the land. Because the value that you are given is an after tax amount, be sure to put it under the tax line. Also remember that although the working capital will be recovered at the end of the project, the financing costs from working capital will not.
Defense Electronics apital Budgeting Weighted Average Flotation Costs 0.00% DATA FLOATATION COSTS life of project Cost of Plant Increase in W Initial Cost of Land alvage value of land ife of machine in years Depreciation alvage value of machine Book Value of machine Annual fixed costs RD's per year elling price per RD ariable cost per RD ax rate R (WACC from COC Sheet) 5 years 37,000,000 1,300,000 4,400,000 4,800,000 Amount Neede Amount Raised Flotation Costs Manufacturing Plant Working Capital 1,300,000.00 Total 5,100,000 6,700,000 15,300 11,450 9,500 32% 0.00% ime Working Capital hange in working capital ales Fixed Costs Variable Costs Depreciation Salvage Value Book Value BIT Taxes After Tax 5,100,000 ime Working Capital Change in working capital Sales Fixed Costs Variable Costs Depreciation + Salvage Value Book Value EBIT 5,100,000 Taxes After Tax +Depreciation +Book Value CapEx Land Value +Change in WC Flotation Costs Free Cash Flow Discount Present Value NPV IRR Debt # of bonds coupon rate years to maturity 210,000 6.4% 25 11096 1000 Preferred Stock # of shares rice per share dividend Common Stock # of shares rice per share beta market risk premi risk free rate 450,000 79 4.50 8,300,000 68 as a % of par par value # payments per yea! Tax 6.0% 3.5% 32% COSTS Rate of Debt Rate of Preferred Rate of Equit # of payments Future Value Present Value Coupon payment RD After Tax Dividend Beta Market Risk Premi Risk Free Rate 50 1000 1100 35.2 6.24% 4.25% 4.50 Price at 0 79 6.0% 3.5% Rps 5.70% RE 6T% Weighted Average Cost of Capital Market ValueWeight Weighted Cost Source Debt Preferred Equity Cost 27.80% 4.28% 67.92% 231,000,000 35,550,000 564,400,000 830,950,000 WACC---- Defense Electronics apital Budgeting Weighted Average Flotation Costs 0.00% DATA FLOATATION COSTS life of project Cost of Plant Increase in W Initial Cost of Land alvage value of land ife of machine in years Depreciation alvage value of machine Book Value of machine Annual fixed costs RD's per year elling price per RD ariable cost per RD ax rate R (WACC from COC Sheet) 5 years 37,000,000 1,300,000 4,400,000 4,800,000 Amount Neede Amount Raised Flotation Costs Manufacturing Plant Working Capital 1,300,000.00 Total 5,100,000 6,700,000 15,300 11,450 9,500 32% 0.00% ime Working Capital hange in working capital ales Fixed Costs Variable Costs Depreciation Salvage Value Book Value BIT Taxes After Tax 5,100,000 ime Working Capital Change in working capital Sales Fixed Costs Variable Costs Depreciation + Salvage Value Book Value EBIT 5,100,000 Taxes After Tax +Depreciation +Book Value CapEx Land Value +Change in WC Flotation Costs Free Cash Flow Discount Present Value NPV IRR Debt # of bonds coupon rate years to maturity 210,000 6.4% 25 11096 1000 Preferred Stock # of shares rice per share dividend Common Stock # of shares rice per share beta market risk premi risk free rate 450,000 79 4.50 8,300,000 68 as a % of par par value # payments per yea! Tax 6.0% 3.5% 32% COSTS Rate of Debt Rate of Preferred Rate of Equit # of payments Future Value Present Value Coupon payment RD After Tax Dividend Beta Market Risk Premi Risk Free Rate 50 1000 1100 35.2 6.24% 4.25% 4.50 Price at 0 79 6.0% 3.5% Rps 5.70% RE 6T% Weighted Average Cost of Capital Market ValueWeight Weighted Cost Source Debt Preferred Equity Cost 27.80% 4.28% 67.92% 231,000,000 35,550,000 564,400,000 830,950,000 WACC
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


