Question
Define a class named Bits that holds a single integer variable. You will use this integer simply as a container of bits. The number of
Define a class named Bits that holds a single integer variable. You will use this integer simply as a container of bits. The number of bits you can support depends on the type of integer you use. We will use an unsigned long long, which on most platforms occupies 64 bits. However, DO NOT HARD-CODE the type of integer you use throughout your code. You should be able to change only one line of code for your class to work with a different size integer (see the using statement on the second code line below). The code skeleton below gets you started, and also shows you the interface your class needs to implement.
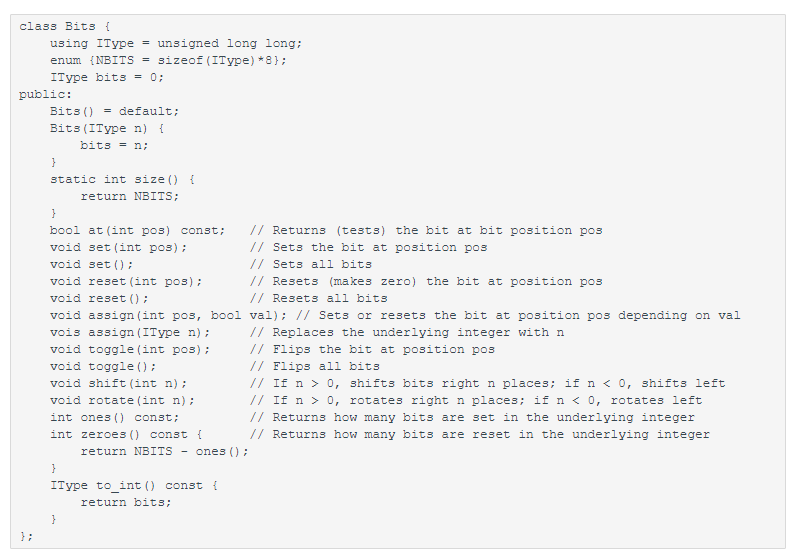
Also define the following non-member functions:
- an output stream operator (
- the equality operator ==
- the inequality operator !=
Remember that bit positions are numbered right-to-left, so bit position 0 is the low-order bit. "Rotate" means that bits that run off one end replace the vacated bits on the other.
Define all functions inline in a header file named bits.h.
rotate is the most interesting function to implement.
I suggest that you develop your code offline in the development environment of your own choice, implementing and testing one function at a time. When you are satisfied everything is working, submit your code for grading.
Something think about
What will you do if a user of your Bits class tries to use a bit position out of range of what the integer holds?
I'm not asking for you to do them all, but if you could show how to overwrite the operators and solve a few of the functions I think I'd know enough to work on the assignment.
class Bits { using IType unsigned long long; enum {NBITS = sizeof(IType) *8}; IType bits = 0; public: Bits() = default; Bits (IType n) { bits = n; } static int size() { return NBITS; } bool at (int pos const; // Returns (tests) the bit at bit sition pos void set (int pos); // Sets the bit at position pos void set(); // Sets all bits void reset(int pos); // Resets (makes zero) the bit at position pos void reset(); // Resets all bits void assign(int pos, bool val); // Sets or resets the bit at position pos depending on val vois assign (IType n) ; // Replaces the underlying integer with n void toggle(int pos); // Flips the bit at position pos void toggle(); // Flips all bits void shift (int n) ; // If n > 0, shifts bits right n places; if nStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


