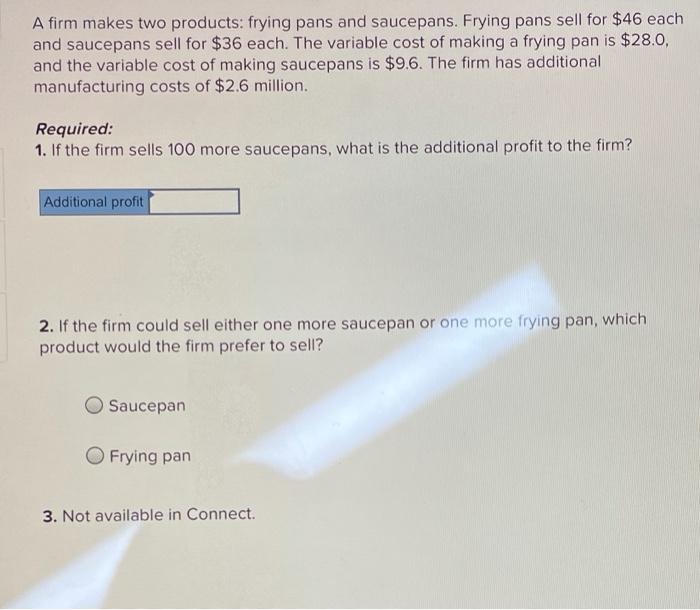
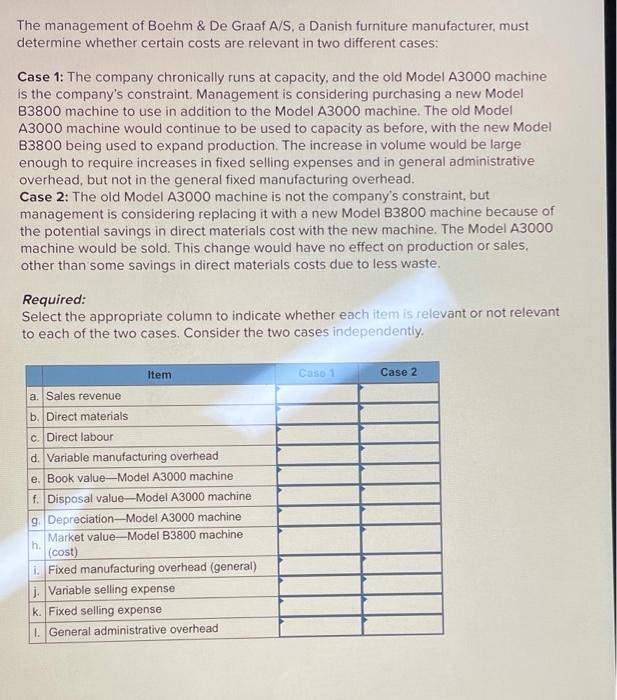
Delta Company produces a single product. The cost of producing and selling a single unit of this product at the company's normal activity level of 60,000 units per year is: Direct materials Direct labour Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative expenses Fixed selling and administrative expenses Per Unit $5.10 3.80 1.00 4.20 1.50 2.40 The normal selling price is $21 per unit. The company's capacity is 75,000 units per year. An order has been received from a mail-order house for 15.000 units at a special price of $14.00 per unit. This order would not affect regular sales Required: 1. If the order is accepted, by how much will annual profits be increased or decreased? (The order will not change the company's total fixed costs.) Annual profit would 2. Assume the company has 1,000 units of this product left over from last year that are inferior to the current model. The units must be sold through regular channels at reduced prices. What unit cost is relevant for establishing a minimum selling price for these units? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Relevant cost per unit A firm makes two products: frying pans and saucepans. Frying pans sell for $46 each and saucepans sell for $36 each. The variable cost of making a frying pan is $28.0, and the variable cost of making saucepans is $9.6. The firm has additional manufacturing costs of $2.6 million. Required: 1. If the firm sells 100 more saucepans, what is the additional profit to the firm? Additional profit 2. If the firm could sell either one more saucepan or one more frying pan, which product would the firm prefer to sell? Saucepan Frying pan 3. Not available in Connect. The management of Boehm & De Graaf A/S, a Danish furniture manufacturer, must determine whether certain costs are relevant in two different cases: Case 1: The company chronically runs at capacity, and the old Model A3000 machine is the company's constraint. Management is considering purchasing a new Model B3800 machine to use in addition to the Model A3000 machine. The old Model A3000 machine would continue to be used to capacity as before, with the new Model B3800 being used to expand production. The increase in volume would be large enough to require increases in fixed selling expenses and in general administrative overhead, but not in the general fixed manufacturing overhead. Case 2: The old Model A3000 machine is not the company's constraint, but management is considering replacing it with a new Model B3800 machine because of the potential savings in direct materials cost with the new machine. The Model A3000 machine would be sold. This change would have no effect on production or sales, other than some savings in direct materials costs due to less waste. Required: Select the appropriate column to indicate whether each item is relevant or not relevant to each of the two cases. Consider the two cases independently. Item CaSO 1 Case 2 a. Sales revenue b. Direct materials C irect labour d. Variable manufacturing overhead e. Book value-Model A3000 machine f. Disposal value-Model A3000 machine 9 Depreciation--Model A3000 machine Market value-Model B3800 machine h (cost) 1. Fixed manufacturing overhead (general) 1. Variable selling expense k. Fixed selling expense 1. General administrative overhead