Question
Demand for hot dogs on Main Street in Small town is:Q = 100 -20P Assume that there are fixed costs of $1200 and that MC

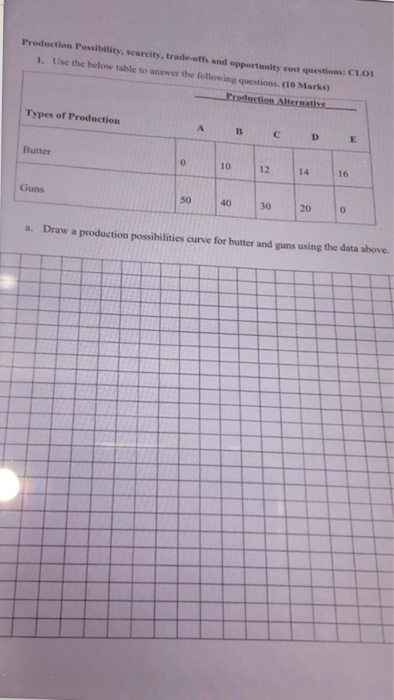
Demand for hot dogs on Main Street in Small town is:Q = 100 -20P
Assume that there are fixed costs of $1200 and that MC = $1.00. The purpose of this problem is to examine duopoly equilibria in this market (different behavioral assumptions lead to different equilibria) and to compare these equilibria to both the competitive and monopoly equilibria as well as to each other.
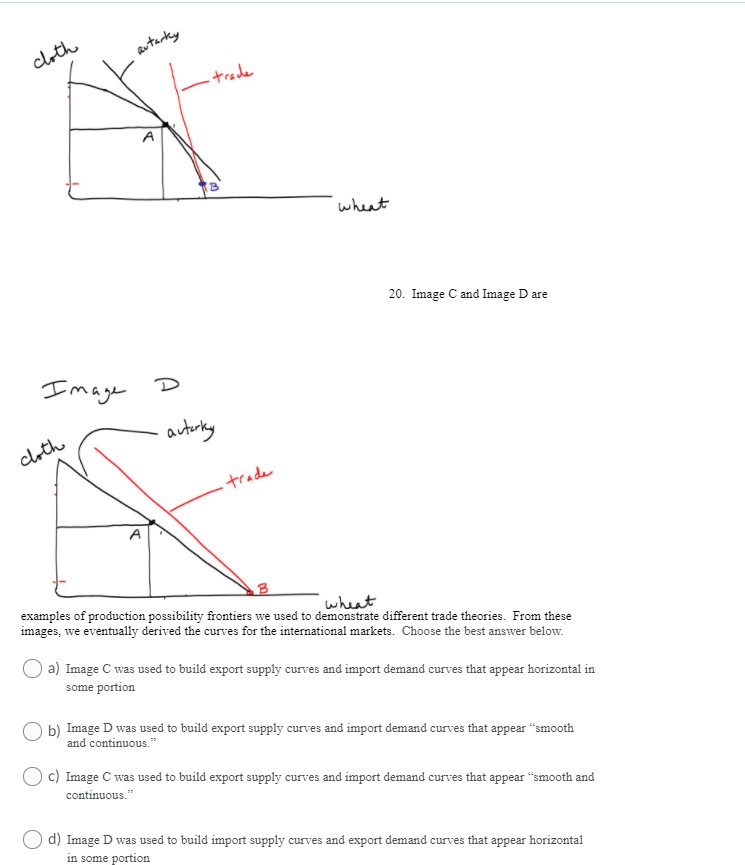
Graph the Demand and MR.
Indicate the competitive price and quantity with P* and Q*.
Indicate the monopoly price and quantity with Pm and Qm.
The town grants vending rights to Doug's Dogs and Frank's Franks, at no charge. Other vendors are excluded. Assume for now that both Doug and Frank are Cournot Duopolists---they take each other's production as fixed and adjust their own to maximize their profits. Let qD represent Doug's production and qF represent Frank's: Q = qD + qF.
Write Doug's profits as a function of qD and qF . [Hint:as a first step, invert the demand function and replace Q with qD + qF.] D = (1)
Suppose that Doug's knows qF. If he assumes that this will not change once Frank knows qD , What value of qD should Doug Choose to maximize his profits as a function of qF? This is Doug's "reaction function". Draw it one the diagram. qD = (2)
Now, find Frank's reaction function and add it to the diagram. qF = (3)
Suppose that Doug had been producing at the monopoly solution before Frank arrived on the scene. Indicate his output level on the reaction function graph. What output would Frank initially choose to sell? Frank's Output to sell = (4)
Explain why this would not be an equilibrium, and describe what would happen.
Draw the path that output would follow toward the new equilibrium on the reaction function diagram. What would equilibrium P, qD,qF and Q be? P = (6), qD = (7), qF = (8),Q= (9), Doug's profits are D = (10), Frank's profits are F = (11), Their combined profits are = (12). Plot P and Q on the graph in a and label them Pc and Qc (C for Cournot) (13)
Stackelberg Model, Leader Follower.
Explain why the behavior of both Frank and Doug in b is naive.
Assume that Frank continues to behave naively, but that Doug figures out that Frank is reacting to his decisions. Specifically, Dough Knows that Frank's choice of qF is a function of his own choice of qD, as you found in b (Frank's reaction function). Dough takes this into account by substituting Frank's reaction function into his own profit equation, to get: D = (2)
Find Doug's new profit-maximizing choice of qD. qD =(3), Frank will choose qF = (4), Total Quantity produced is q = (5), The price is P = (6), Doug's profits are D = (7), Frank's profits are F = (8), Their combined profits are = (9). Plot the new Q and P on the graph in a, labelling them PLF and QLF (LF for Leader-Follower) Also, plot the point (qD, qF) on the reaction function diagram in b and label it LF.
Leader-Leader model: aka Bertrand Model. In c it was assumed that Frank continued to be naive. Suppose instead that he figures out Doug's behavior at the same time that Doug figures out his own. That is, they both simultaneously decide to lead, mistakenly thinking the other will follow.
This choice of output level will then be qF = (1) [Hint: does his problem differ in any way from Doug's in c?] qF = (1), Total output will be Q = (2), And the price will be P = (3), Doug's profits are D = (4), Frank's profits are F = (5), Their combined profits are = (6). Plot the new Q and P on the graph in a and label them QLL and PLL. Also, plot the point (qD, qF)on the reaction function diagram in b and label it LL. Finally, what do you speculate will happen once they both realize that the other is not following? (7)

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


