Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Derive Equation (2.18) G'(x) = G(x) G'(0). to the value Fx = G(x) Fo by k-periodic compounding over x interest periods at interest rate
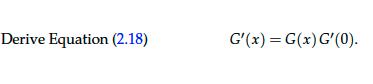

Derive Equation (2.18) G'(x) = G(x) G'(0). to the value Fx = G(x) Fo by k-periodic compounding over x interest periods at interest rate r if the growth function G(x) satisfies the following properties: G(x+y)=G(x)G(y) for all real numbers x > 0 and y 0, G(0) = 1, G(1)= (1+2), G(x) >1 for all real numbers x > 0. (2.17) The top equation in (2.17) generalizes (2.16) to a nonintegral number of pe- riods. The same intuition carries over from the integral case: compounding a principal Fo over x + y interest periods to the value The Time Value of Money Fx+y = G(x + y)Fo is identical to compounding Fo for y interest periods to the value Fy = G(y)Fo and then compounding Fy over the remaining x interest periods to the value G(x)Fy. The equation G(0) = 1 in (2.17) states that no growth occurs when there is no interest period, while G(1) = (1+) means that the growth over one interest period is given by simple interest (as we have done all along). Finally, we require the condition G(x) > 1 for all x > 0 because we assume that compound interest growth increases the principal over a nonzero interest period, even if it is fractional. Let us now solve for the growth function satisfying (2.17). For mathemati- cal modeling reasons, we shall assume that G(x) is differentiable. Applying a trick similar to the one used in deriving an exponential function, we first con- sider the derivative of the growth function at x. Using the limit definition of a derivative, we find (Exercise 2.30) G'(x)=G(x) G'(0). (2.18) Dividing by G(x), which is allowed since G(x) > 0 for all x 0, and recalling that G'(x)/G(x) is the derivative of InG(x), we obtain -=G'(0), or, equivalently, dIn G(x) dx dln G(x) = G' (0) dx. Integrating the equation from 0 to x yields:
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.52 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Lets go through the steps to derive the growth function Gx satisfying equation 217 in mor...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


