Question
Describe PDAs for the following languages: (a) {w {a,b} | num(aaa,w) = num(bb,w)} Note: Be careful in your counting: bbbb contains the substring bbb two
Describe PDAs for the following languages:
(a) {w {a,b} | num(aaa,w) = num(bb,w)}
Note: Be careful in your counting: bbbb contains the substring bbb two times.
(b) {w {a,b} | 2 #a(w) > 3 #b(w)}, where #a(w) denotes the number of as in w
Suggestion: Use the PDAs stack to represent an integer counter, as follows:
Conceptually think of your PDA as an NFA with a counter. Keep track of 2 #a(w) 3 #b(w). Carefully consider how to update the value in the counter (especially taking into account all cases of positive, zero, negative for the starting value of the counter, and the possibility of the counters value changing signs).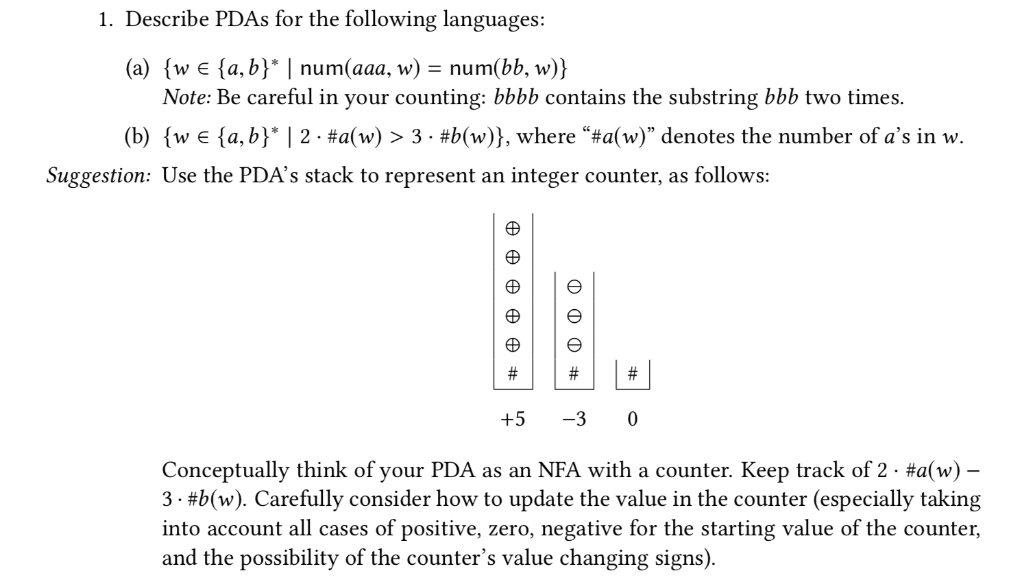
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


