Describe the product/service that is being offered by Tesla using concepts from Block 4, Reading 31, and information from the case study.
?Use concepts from Reading 31, particularly Sections 1, 2 and 3
?Start by stating what you think the product is, in terms of an environmentallysustainable car producer Tesla is offering a product/good-electric car)-as a concept of a product/service in marketing terms
?Provide a brief introduction to the module concepts you will use and why
?Analyse the nature (tangible or intangible) and benefits of the product service 'offering' offered in the case study, using the module concepts summarised above
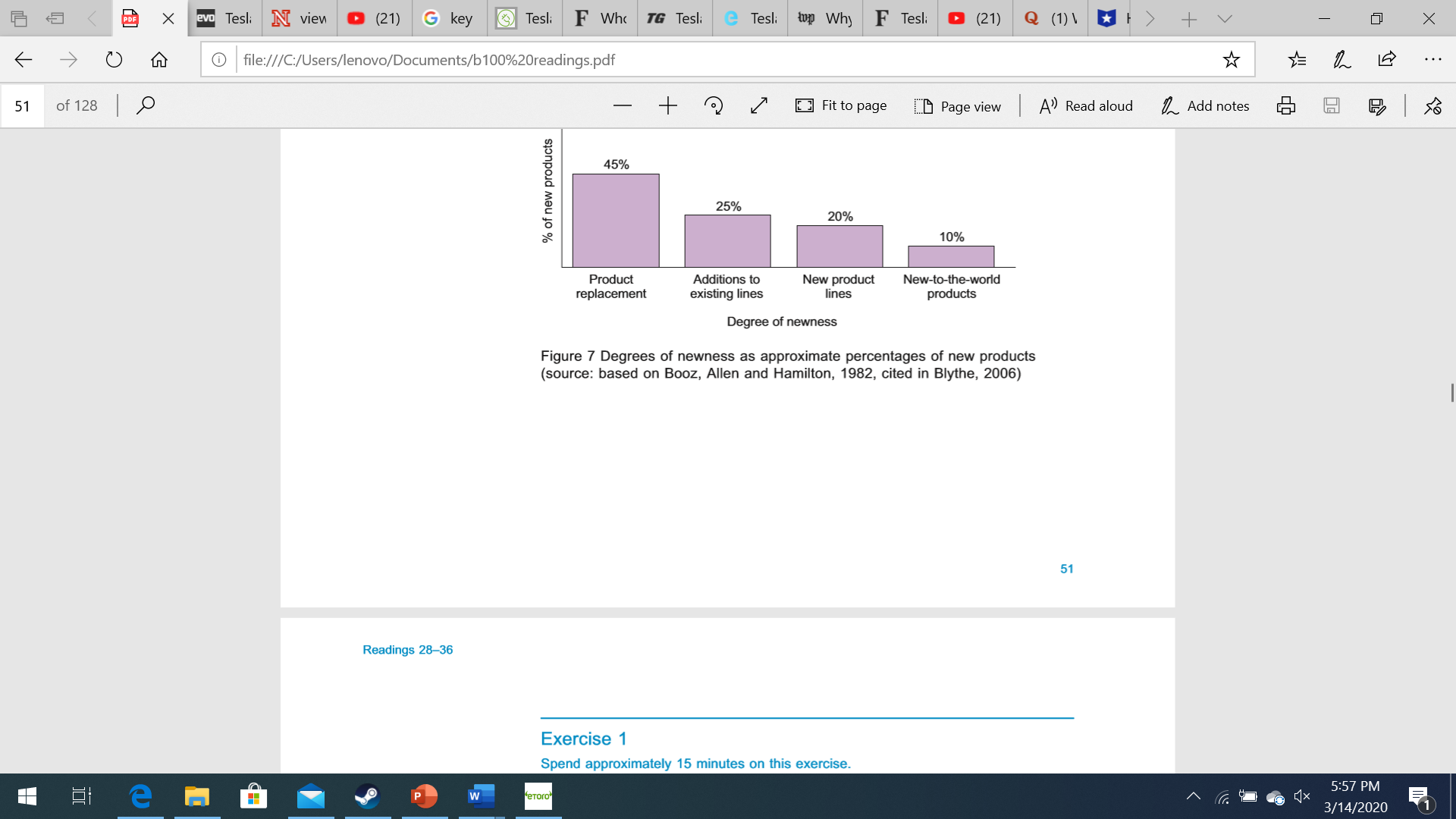
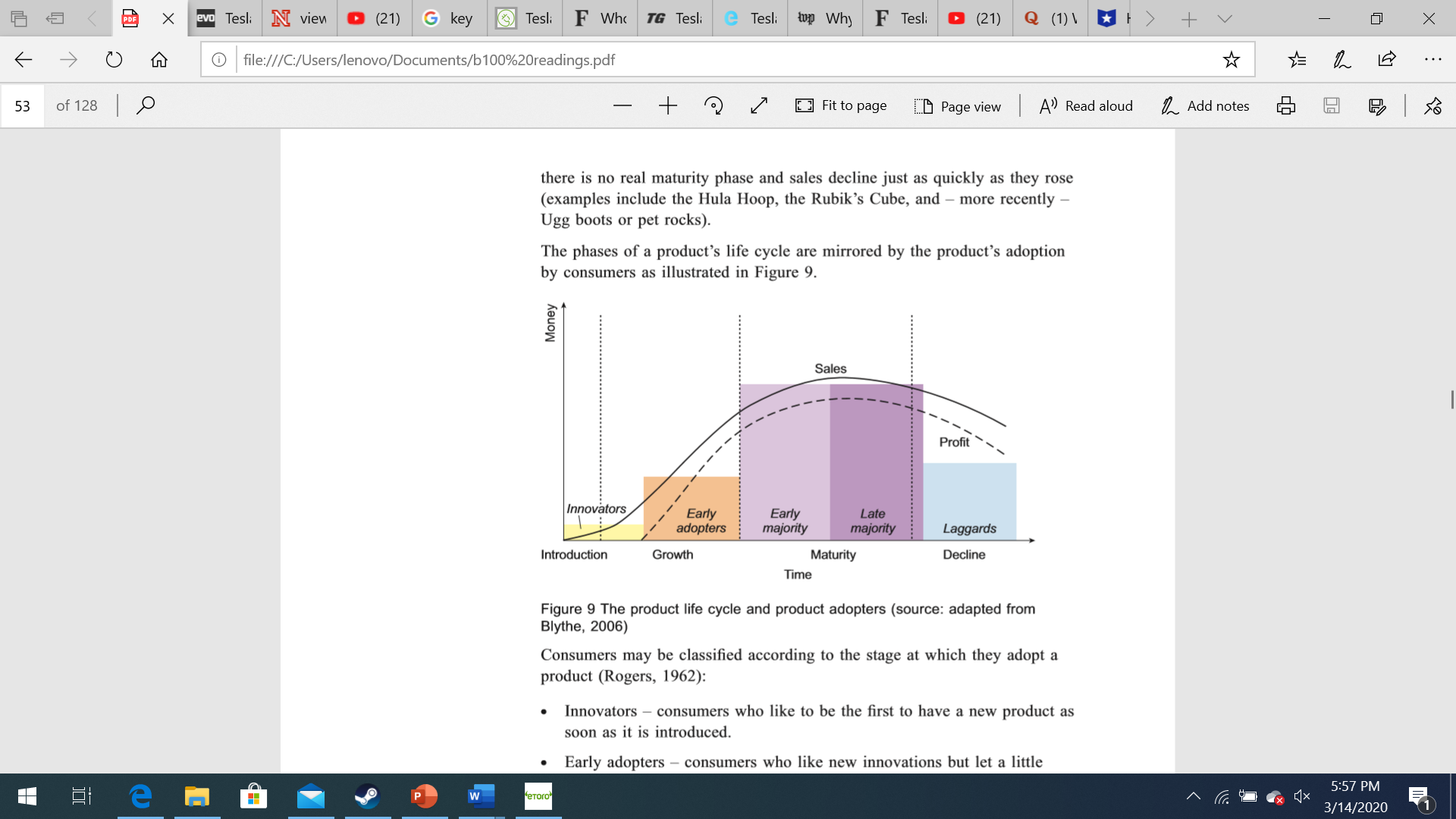
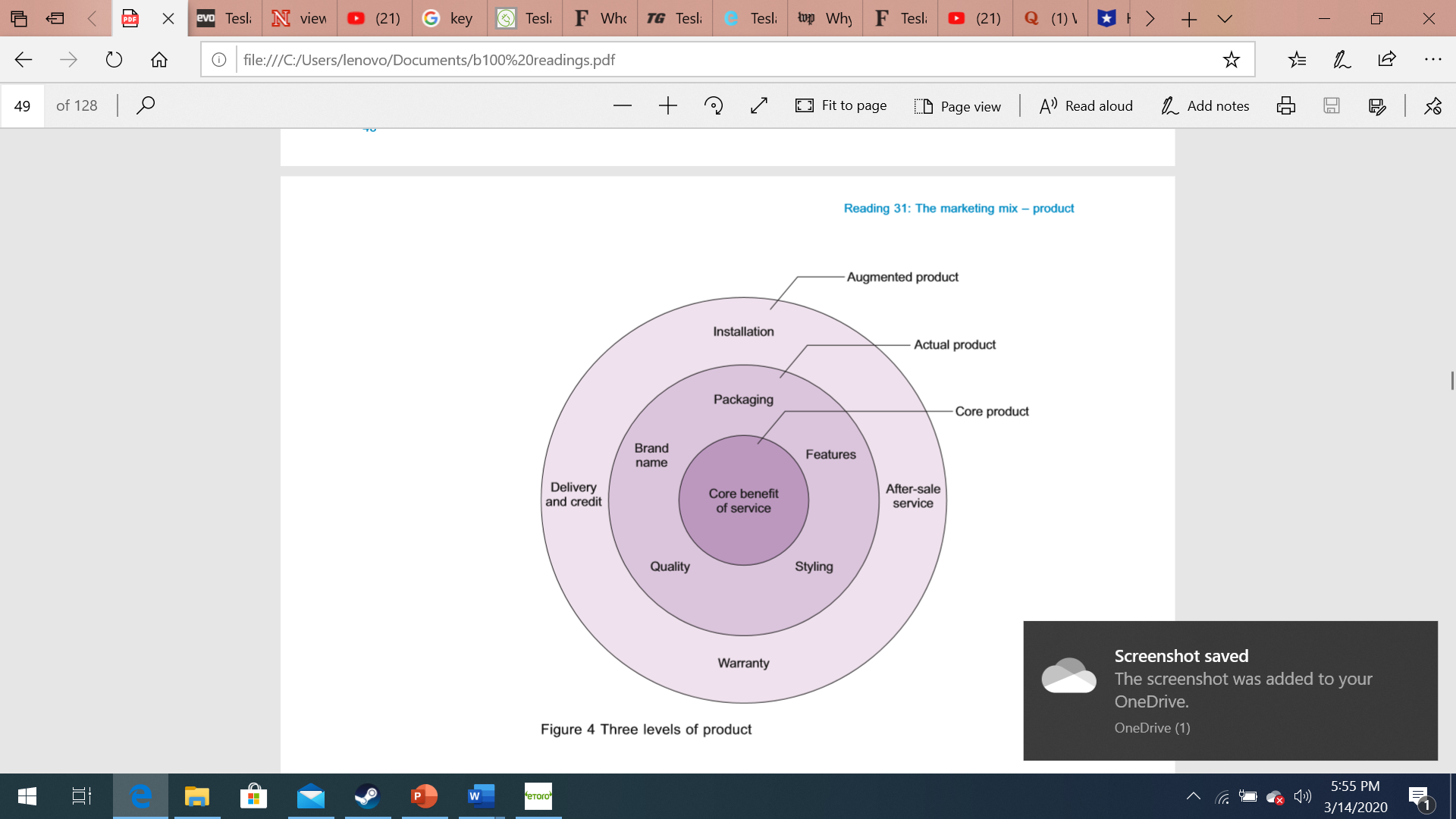
a e 9 O u G le:///C:/Users/lenovo/Documents/b100%20readingspdf * {5 L IE 450i123|,0 _+q|/I Figure 1 Mobile phones Fit to page E:D Page view I A\" Read aloud L Add notes .43: B I {5.3 Of course, not all products are aimed at consumers. Industrial products may he bought by other businesses, perhaps as 'materials or parts' for incorporating into the business buyer's offerings or as 'capital items' for use in the business buyer's production or operations (for example. premises or equipment) or as \"supplies and services' that are used in operations or maintenance (for example printer paper, electricity and cleaning) (Kotler and Armstrong, 2010). Furthermore, not all products are 'things'. The concept of a product can also be extended to ideas and even people. Think, for example, how common it is nowadays to refer to bands in the music industry as having I been 'manufactured'. Other examples of different forms of products include cities, events (such as festivals, The Olympic Games). movements (for example, 'slow cooking') and even languages (some of you may remember the created language Esperanto). 5155 PM 111442020 51 PDF X evo Tesli N view D (21) Gkey Tesl: F Who TG Tesli C Tesli top Why F Tesli (21) Q ( 1 ) 1 * 1 > + V X O file:///C:/Users/lenovo/Documents/b100%20readings.pdf * . . . 50 of 128 - + 2 Fit to page Page view A' Read aloud _ Add notes So in 200o and its futuristic new look at that time bore little discernible resemblance to the preceding model. STA MD06 RKX Figure 5 Honda Civic 2006 50 Reading 31: The marketing mix - product P w "eToro" 5:56 PM 3/14/2020EvieuEDQnEeryE-TesltEthtElITesltE3TesleEWWlnEFTeslt|(21)EQ(t)\\E-E) +v 7 X E 4-5 + V X O file:///C:/Users/lenovo/Documents/b100%20readings.pdf * . . . 51 of 128 - +2 Fit to page Page view A' Read aloud Add notes So % of new products 45% 25% 20% 10% Product Additions to New product New-to-the-world replacement existing lines lines products Degree of newness Figure 7 Degrees of newness as approximate percentages of new products (source: based on Booz, Allen and Hamilton, 1982, cited in Blythe, 2006) 51 Readings 28-36 Exercise 1 Spend approximately 15 minutes on this exercise. P w "eToro" x 5:57 PM 3/14/2020E 4-5 + V X file:///C:/Users/lenovo/Documents/b 100%20readings.pdf * . . . 53 of 128 + 2 Fit to page CD Page view A' Read aloud Add notes So there is no real maturity phase and sales decline just as quickly as they rose (examples include the Hula Hoop, the Rubik's Cube, and - more recently - Ugg boots or pet rocks). The phases of a product's life cycle are mirrored by the product's adoption by consumers as illustrated in Figure 9. Money Sales Profit Innovators Early Early Late adopters majority majority Laggards Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Time Figure 9 The product life cycle and product adopters (source: adapted from Blythe, 2006) Consumers may be classified according to the stage at which they adopt a product (Rogers, 1962): Innovators - consumers who like to be the first to have a new product as soon as it is introduced. Early adopters - consumers who like new innovations but let a little P w *eToro" 5:57 PM 3/14/2020EviemEDQnEeryE-TesliEFMirElITeshE3Tesli'lwhyEFTeslt|(21)EQ(1)\\E-E) +v 7 X E 4-5 + V X O file:///C:/Users/lenovo/Documents/b100%20readings.pdf . . . 49 of 128 + 2 Fit to page Page view A' Read aloud Add notes So Reading 31: The marketing mix - product Augmented product Installation Actual product Packaging Core product Brand name Features Delivery and credit Core benefit After-sale of service service Quality Styling Warranty Screenshot saved The screenshot was added to your OneDrive. Figure 4 Three levels of product OneDrive (1) e P w eToro 5:55 PM 3/14/2020@ e 9 O Q G le:///C:/Users/|enovo/Documents/b100%20readings.pdt * {5 L IE 490f128|,0 +/ Fit to page E:D Page view I A') Read aloud L Add notes .43: B I {s3 4 New product development The process of creating new products is more of an art than an exact science and it is difcult to generalise about it. However, a frequently quoted model of the new product development process was proposed by Crawford (1991). Only a small number of new products are successful and the model is meant to reduce the risk of new products failing. In this model, a number of steps of new product development are shown in the following sequence: 1 New product planning A business looks at its current products, how I well they are performing, and where the marketing environment poses threats to existing products and opportunities for new products. 2 Idea generation Specic ideas for new products are generated and collected, perhaps through group discussion techniques such as brainstorming. 3 Idea screening and evaluation 7 The ideas generated in the previous step are examined for their feasibility and marketability. 4 Technical development The technical aspects of the product are investigated and a prototype is developed. 5 Market appraisal Market research is carried out to assess whether the product would be successful in the market. 6 Launch The product is produced and offered in the market. E45 +v *IX 9 9 O Q G le:///C:/Users/Ienovo/Documents/b100%20readings.pdf {Ar {5 L E 500f128|,0 +/ Although most businesses are likely to cover all these stages in some form. they may not give the same priority to each stage and may not follow a strict sequence. The businesses most successful at developing new products often any out several of these stages simultaneously, For example, during the 1980s and l990s it was thought that Japanese car makers were much better at bringing out new models quickly because they were able to shorten the new product development process by doing several steps at the same time. Some businesses are much better at developing new products than others and this may be because of their organisational culture. which values innovativeness and does not kill off new ideas too quickly. E tE