Question: Design and Verification of 4-bit Adder - Subtractor - Multiplier : Binary Multiplier A combinational multiplier is a good example of how simple logic functions

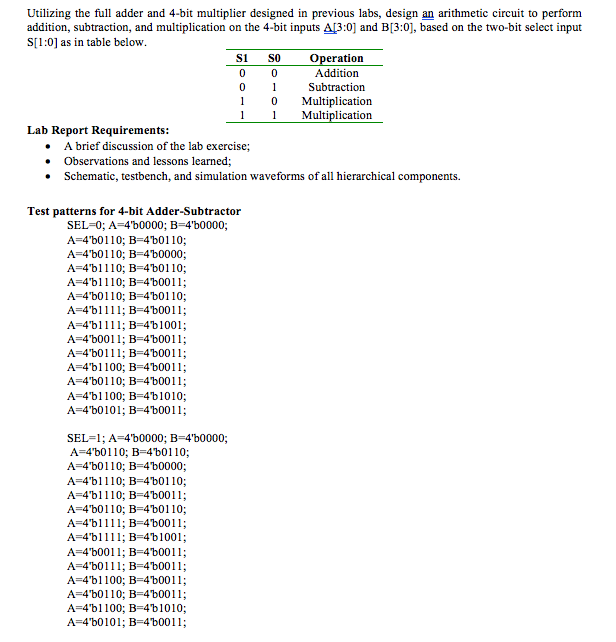

Design and Verification of 4-bit Adder - Subtractor - Multiplier : Binary Multiplier A combinational multiplier is a good example of how simple logic functions can be combined to construct a much more complex function. In particular, it is possible to construct a 4-bit combinational multiplier from an array of AND gates, half-adders, and full-adders, taking what you have designed recently and extending it to a more complex circuit. In the course of multiplying two binary numbers, each bit in the multiplier is multiplied with the multiplicand. Each of the four products is aligned (shifted left) accordingly to the position of the bit in the multiplier that is being multiplied with the multiplicand. The four resulting products are added to form the final product. For an n-bit multiplier and multiplicand, the result is 2n bits wide. The result of our desired 4-bit multiplication is thus 8-bit result A faster way to implement multiplication is to resort to an approach similar to manually computing a multiplication. All the partial products are generated at the same time and organized in an array. A multi operand addition is applied to compute the partial product. The approach is illustrated in figure below. This set of operations can be mapped directly into hardware. The resulting structure is called an array multiplier and combines the following three functions: partial-product generation, partial-product accumulation, and final addition a3 a2 al a0 x b3 b2b bo bOa3 b0a2 b0al b0a0 b2a3 b2a2 b2al b2a0 0 0 bla3 bla2 blal bla0 0 0 0 b3a3 b3a2 b3a1 b3a0 0 Figure 1: Binary Multiplication 2: 4-bit adder-subtractor With the knowledge of the two's complement representation, subtraction can be performed using a binary adder. To compute A B, you can compute A (-B), which is the same as A + B 1 in two's complement. Thus, to perform subtraction, inverter B, and input a 1 to the carry-in of a binary adder Design a 4-bit adder-subtractor by using an array of full adders and XOR gates. A selection between addition and subtraction should be provided. Make sure to use buses as inputs. 3: Arithmetic Unit A combinational arithmetic circuit is a good example of how simple logic functions can be combined to construct a much more complex function. In particular, it is possible to construct a 4-bit combinational arithmetic circuit from an array of AND OR gates, full-adders, and multiplexers. Design and Verification of 4-bit Adder - Subtractor - Multiplier : Binary Multiplier A combinational multiplier is a good example of how simple logic functions can be combined to construct a much more complex function. In particular, it is possible to construct a 4-bit combinational multiplier from an array of AND gates, half-adders, and full-adders, taking what you have designed recently and extending it to a more complex circuit. In the course of multiplying two binary numbers, each bit in the multiplier is multiplied with the multiplicand. Each of the four products is aligned (shifted left) accordingly to the position of the bit in the multiplier that is being multiplied with the multiplicand. The four resulting products are added to form the final product. For an n-bit multiplier and multiplicand, the result is 2n bits wide. The result of our desired 4-bit multiplication is thus 8-bit result A faster way to implement multiplication is to resort to an approach similar to manually computing a multiplication. All the partial products are generated at the same time and organized in an array. A multi operand addition is applied to compute the partial product. The approach is illustrated in figure below. This set of operations can be mapped directly into hardware. The resulting structure is called an array multiplier and combines the following three functions: partial-product generation, partial-product accumulation, and final addition a3 a2 al a0 x b3 b2b bo bOa3 b0a2 b0al b0a0 b2a3 b2a2 b2al b2a0 0 0 bla3 bla2 blal bla0 0 0 0 b3a3 b3a2 b3a1 b3a0 0 Figure 1: Binary Multiplication 2: 4-bit adder-subtractor With the knowledge of the two's complement representation, subtraction can be performed using a binary adder. To compute A B, you can compute A (-B), which is the same as A + B 1 in two's complement. Thus, to perform subtraction, inverter B, and input a 1 to the carry-in of a binary adder Design a 4-bit adder-subtractor by using an array of full adders and XOR gates. A selection between addition and subtraction should be provided. Make sure to use buses as inputs. 3: Arithmetic Unit A combinational arithmetic circuit is a good example of how simple logic functions can be combined to construct a much more complex function. In particular, it is possible to construct a 4-bit combinational arithmetic circuit from an array of AND OR gates, full-adders, and multiplexers
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


