Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
*** DESIGN OF PRE STRESSED CONCRETE PROBLEM *** BELOW IS TABLE 2.13 . A simply supported precast pre-tensioned normal weight concrete beam with symmetrical I
*** DESIGN OF PRE STRESSED CONCRETE PROBLEM ***
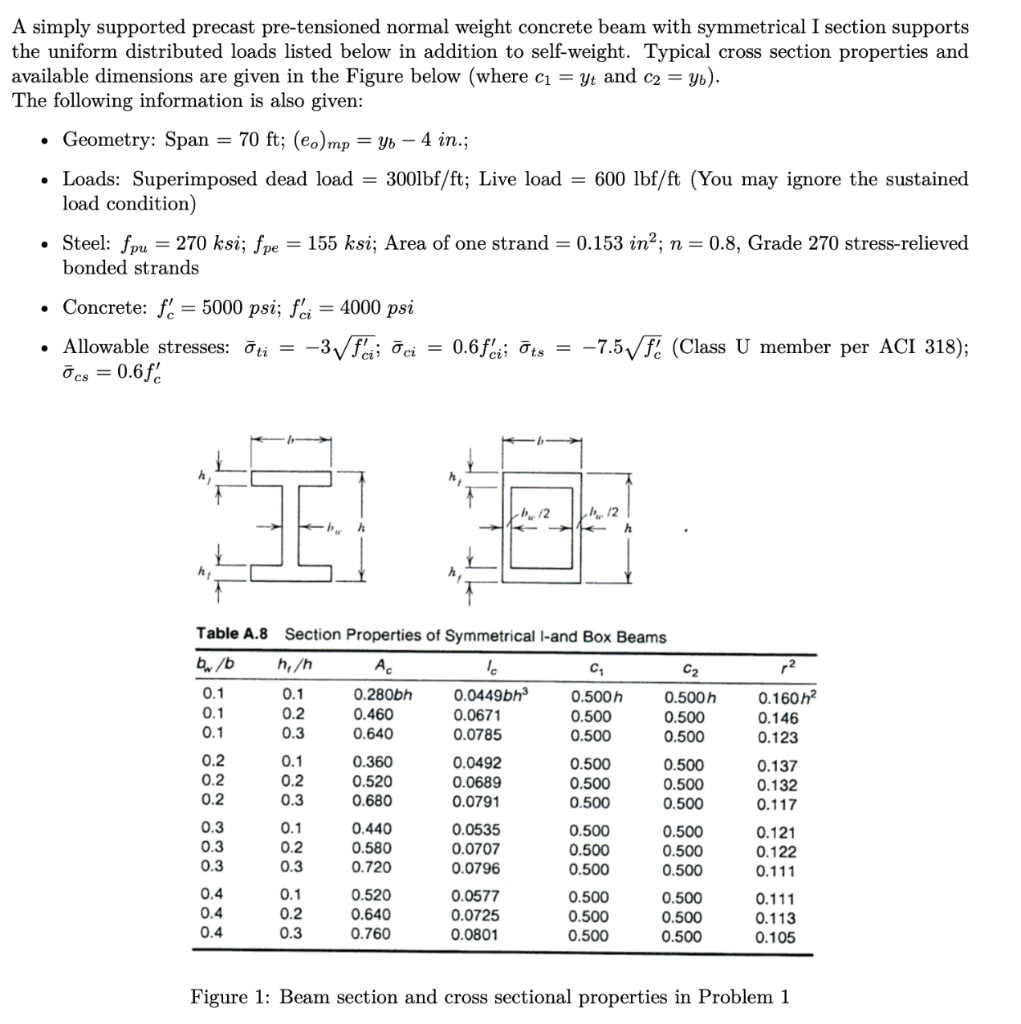


BELOW IS TABLE 2.13
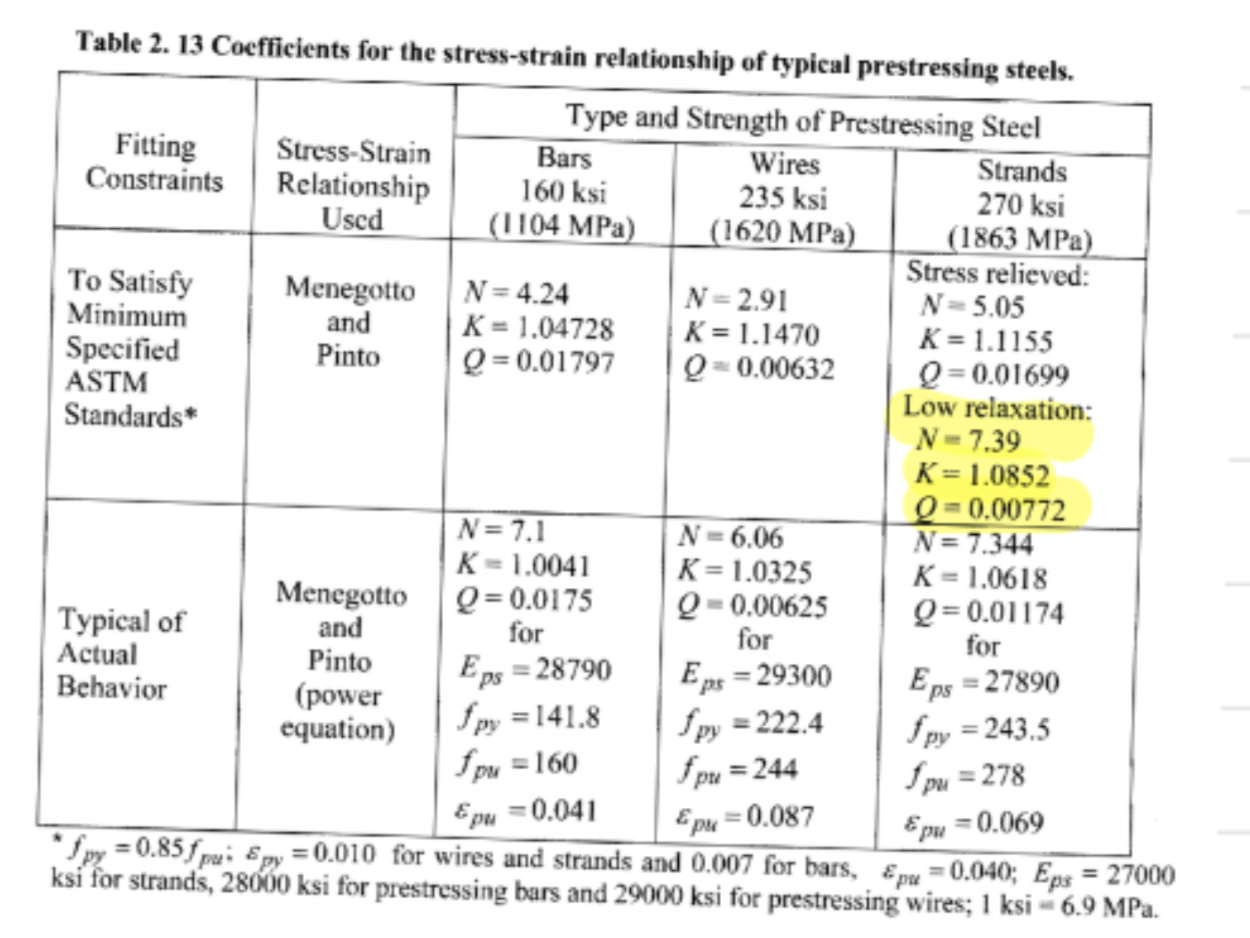
. A simply supported precast pre-tensioned normal weight concrete beam with symmetrical I section supports the uniform distributed loads listed below in addition to self-weight. Typical cross section properties and available dimensions are given in the Figure below (where c = yt and c2 = y). The following information is also given: Geometry: Span = 70 ft; (eo) mp = yo 4 in.; Loads: Superimposed dead load = 300lbf/ft; Live load = 600 lbf/ft (You may ignore the sustained load condition) Steel: fpu = 270 ksi; fpe = 155 ksi; Area of one strand = 0.153 in?; n=0.8, Grade 270 stress-relieved bonded strands Concrete: fo = 5000 psi; fi = 4000 psi Allowable stresses: ti = -3fci; ci 0.6fci; ts = -7.57 f. (Class U member per ACI 318); cs = 0.6$. 12 L1, 12 r2 0.160 m2 0.146 0.123 Table A.8 Section Properties of Symmetrical l-and Box Beams bb hn . lo C C2 0.1 0.1 0.280bh 0.0449bh3 0.500 h 0.500 h 0.1 0.2 0.460 0.0671 0.500 0.500 0.1 0.3 0.640 0.0785 0.500 0.500 0.2 0.1 0.360 0.0492 0.500 0.500 0.2 0.2 0.520 0.0689 0.500 0.500 0.2 0.3 0.680 0.0791 0.500 0.500 0.3 0.1 0.440 0.0535 0.500 0.500 0.3 0.2 0.580 0.0707 0.500 0.500 0.3 0.3 0.720 0.0796 0.500 0.500 0.4 0.1 0.520 0.0577 0.500 0.500 0.4 0.2 0.640 0.0725 0.500 0.500 0.4 0.3 0.760 0.0801 0.500 0.500 0.137 0.132 0.117 . 0.121 0.122 0.111 0.111 0.113 0.105 Figure 1: Beam section and cross sectional properties in Problem 1 (a) Select the cross sectional dimensions that lead to the least weight beam which satisfies the allowable stresses listed above. (20 points) (b) Use the inequalities to sketch the feasibility domain and determine the corresponding values of Fpi and e, at midspan. (20 points) (c) Select the number and size of strands required. (5 points) (d) Use the strain-compatibility method to determine the nominal moment capacity of the beam at mid- span. Please, use the stress-strain relationship based on the Menegotto and Pinto model shown in Table 2.13 in your textbook. (15 points) (e) Determine the value of the strength reduction factor for flexure per ACI 318. (10 points) Table 2. 13 Coefficients for the stress-strain relationship of typical prestressing steels. Type and Strength of Prestressing Steel Fitting Stress-Strain Bars Wires Strands Constraints Relationship 160 ksi 235 ksi 270 ksi Used (1104 MPa) (1620 MPa) (1863 MPa) To Satisfy Stress relieved: Menegotto N = 4.24 N = 2.91 N=5.05 Minimum and K = 1.04728 K = 1.1470 K = 1.1155 Specified Pinto Q=0.01797 Q=0.00632 ASTM Q=0.01699 Low relaxation: Standards* N-7.39 K = 1.0852 Q=0.00772 N= 7.1 N-6.06 N = 7.344 K-1.0041 K=1.0325 K= 1.0618 Menegotto Q=0.0175 Q-0.00625 Typical of Q=0.01174 and for for Actual Pinto Behavior Eps = 28790 Eps = 29300 (power Eps = 27890 equation) Spy = 141.8 fpy = 222.4 py = 243.5 pu = 278 Epu=0.041 * Upy = 0.85fpi Epy = 0.010 for wires and strands and 0.007 for bars, pe=0.040; Eps = 27000 ksi for strands, 28000 ksi for prestressing bars and 29000 ksi for prestressing wires; 1 ksi-6.9 MPa. for fpu = 160 fp = 244 Epu=0.087 Epw = 0.069
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


