Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Determine the volumetric flow rate, velocity and Reynolds number for the generations of pulmonary system in the table below. Consider the volumetric flow rate
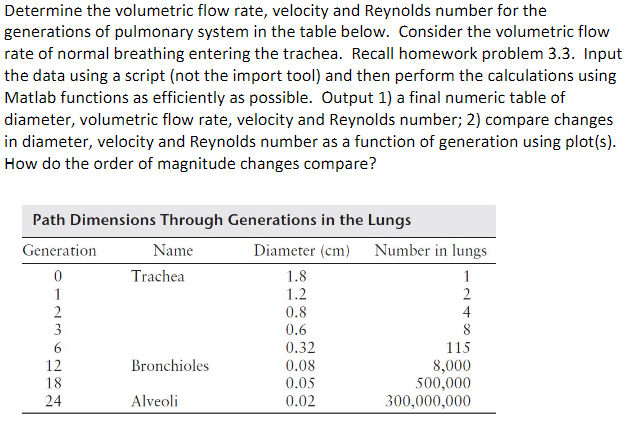
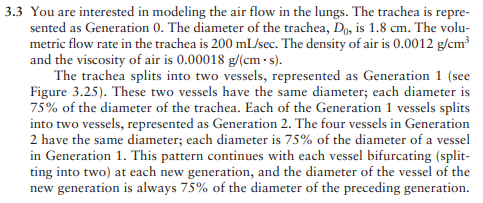
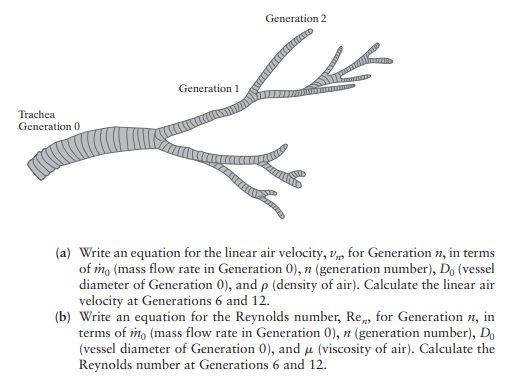
Determine the volumetric flow rate, velocity and Reynolds number for the generations of pulmonary system in the table below. Consider the volumetric flow rate of normal breathing entering the trachea. Recall homework problem 3.3. Input the data using a script (not the import tool) and then perform the calculations using Matlab functions as efficiently as possible. Output 1) a final numeric table of diameter, volumetric flow rate, velocity and Reynolds number; 2) compare changes in diameter, velocity and Reynolds number as a function of generation using plot(s). How do the order of magnitude changes compare? Path Dimensions Through Generations in the Lungs Diameter (cm) Number in lungs Generation 0 Name Trachea 1.8 1 1 1.2 2 2 0.8 4 3 0.6 8 24 6282 0.32 115 12 Bronchioles 0.08 8,000 18 0.05 500,000 Alveoli 0.02 300,000,000 3.3 You are interested in modeling the air flow in the lungs. The trachea is repre- sented as Generation 0. The diameter of the trachea, Do, is 1.8 cm. The volu- metric flow rate in the trachea is 200 mL/sec. The density of air is 0.0012 g/cm and the viscosity of air is 0.00018 g/(cms). The trachea splits into two vessels, represented as Generation 1 (see Figure 3.25). These two vessels have the same diameter; each diameter is 75% of the diameter of the trachea. Each of the Generation 1 vessels splits into two vessels, represented as Generation 2. The four vessels in Generation 2 have the same diameter; each diameter is 75% of the diameter of a vessel in Generation 1. This pattern continues with each vessel bifurcating (split- ting into two) at each new generation, and the diameter of the vessel of the new generation is always 75% of the diameter of the preceding generation. Trachea Generation 0 Generation 1 Generation 2 (a) Write an equation for the linear air velocity, v,, for Generation 1, in terms of mo (mass flow rate in Generation 0), n (generation number), Do (vessel diameter of Generation 0), and p (density of air). Calculate the linear air velocity at Generations 6 and 12. (b) Write an equation for the Reynolds number, Re,, for Generation n, in terms of mo (mass flow rate in Generation 0), n (generation number), Do (vessel diameter of Generation 0), and (viscosity of air). Calculate the Reynolds number at Generations 6 and 12.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


