Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Develop a constant-pressure-reactor model using the same chemistry and thermodynamics as in Example 6.1. Using an initial volume of 0.008 m 3 , P =
Develop a constant-pressure-reactor model using the same chemistry and thermodynamics as in Example 6.1. Using an initial volume of 0.008 m3, P = 1 atm and To= 1000 K, (a) find the combustion durations such that the reaction is 99 percent complete. Use ? = 1 and assume the reactor is adiabatic.
b) Study the effect of variation in?P?[0.2 ? 10 atm]?and?T0?[700???1400 K] on combustion durations. Use ? = 1 and assume the reactor is adiabatic.
Assumptions in example 6.1 are as follow:
- One-step global kinetics using the rate parameters for ethane C2H6?(Table 5.1)
- Fuel, air, and products all have equal molecular weights: MWF= MWOx= MWP= 29
- The specific heats of the fuel, air and products are constants and equal:
- cp,F= cp,Ox= cp,Pr= 1200 J/kgK
- The enthalpy of formation of the air and products are zero, and that of the fuel is
- 4*107j/kg
- The stoichiometric air-fuel ratio is 16.0 and restrict combustion to stoichiometric or lean conditions.excel must be formatted as following
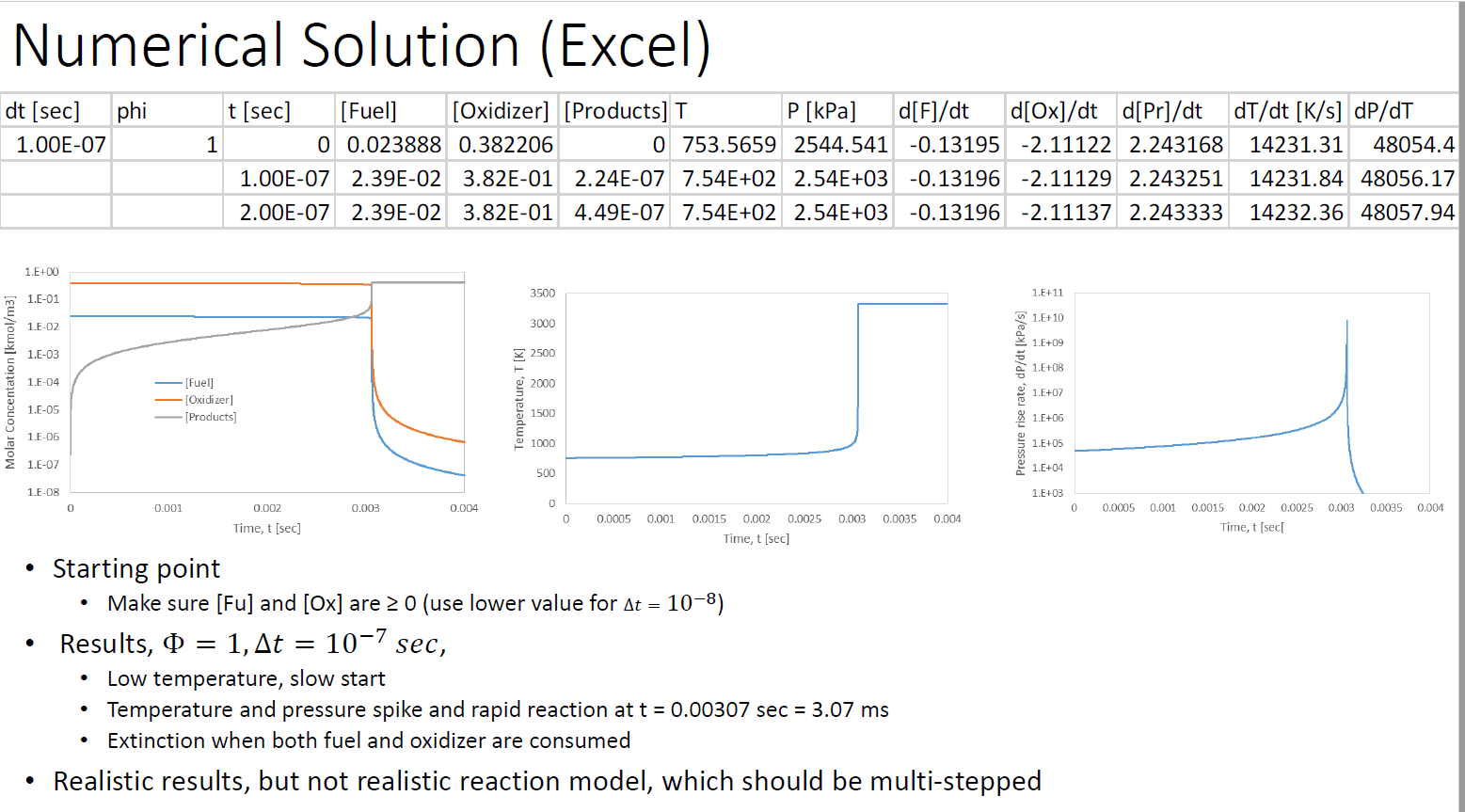
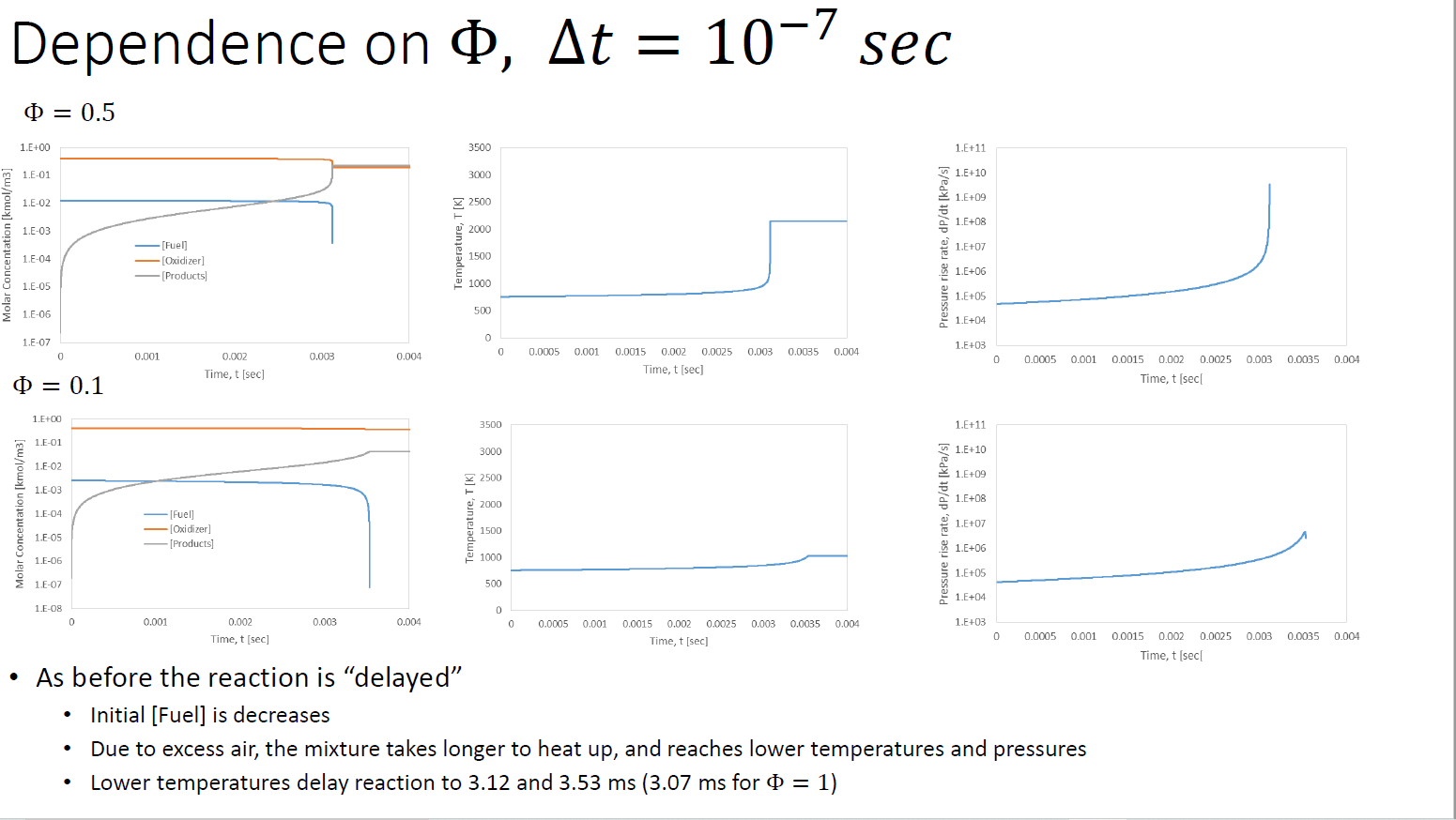
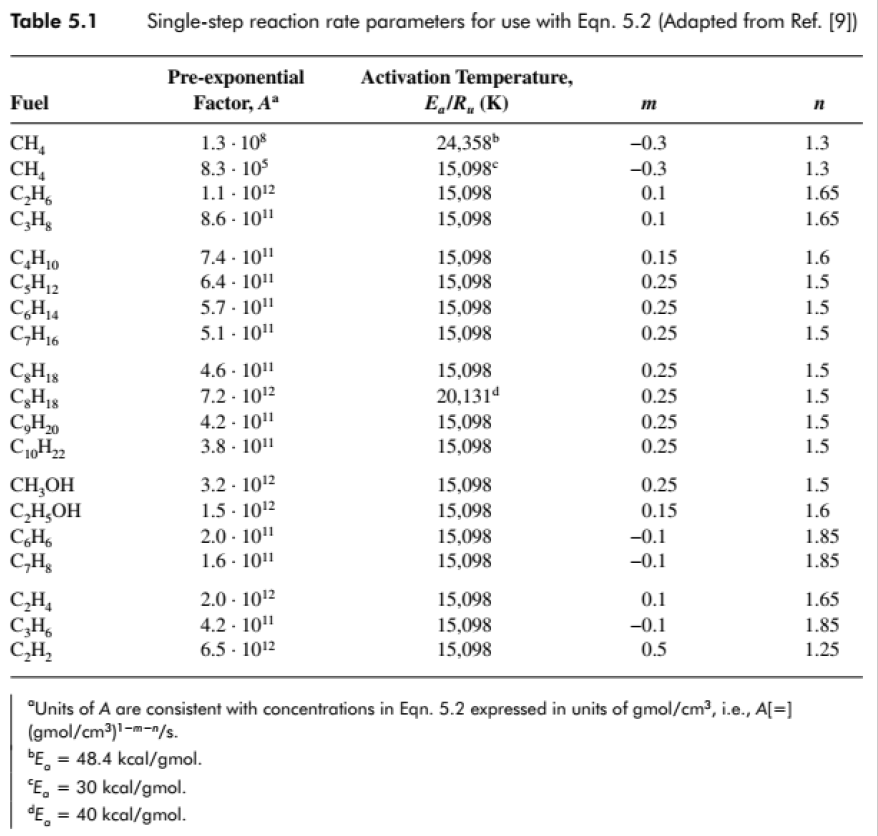
Table 5.1 Fuel CH CHA CH C3H8 CH0 CH12 CH4 CH16 C8H18 C8H18 CH0 C10H2 CHOH CHOH C6H6 CH8 CH C3H6 CH Single-step reaction rate parameters for use with Eqn. 5.2 (Adapted from Ref. [9]) Pre-exponential Factor, A 1.3.108 8.3 105 1.1 - 102 8.6-101 7.4-10 6.4. 101 5.7.10 5.1 10 4.6-1011 7.2.102 4.2.10 3.8 101 3.2 102 1.5-102 2.0-10 1.6-101 2.0-102 4.2.101 6.5 - 102 Activation Temperature, E/R (K) bE = 48.4 kcal/gmol. E = 30 kcal/gmol. E = 40 kcal/gmol. 24,358b 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 20,1314 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 15,098 m -0.3 -0.3 0.1 0.1 0.15 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.15 -0.1 -0.1 0.1 -0.1 0.5 "Units of A are consistent with concentrations in Eqn. 5.2 expressed in units of gmol/cm, i.e., A[=] (gmol/cm)1-m-n/s. n 1.3 1.3 1.65 1.65 1.6 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.6 1.85 1.85 1.65 1.85 1.25 Numerical Solution (Excel) phi P [kPa] d[F]/dt d[Ox]/dt d[Pr]/dt dT/dt [K/s] dp/dT [Fuel] [Oxidizer] [Products] T 0 0.023888 0.382206 0 753.5659 2544.541 -0.13195 -2.11122 2.243168 14231.31 48054.4 1.00E-07 2.39E-02 3.82E-01 2.24E-07 7.54E+02 2.54E+03 -0.13196 -2.11129 2.243251 14231.84 48056.17 2.00E-07 2.39E-02 3.82E-01 4.49E-07 7.54E+02 2.54E+03 -0.13196 -2.11137 2.243333 14232.36 48057.94 dt [sec] 1.00E-07 Molar Concentation [kmol/m3] 1.E+00 1.E-01 1.E-02 1.E-03 1.E-04 1.E-05 1.E-06 1.E-07 1.E-08 0 1 0.001 t [sec] [Fuel] - [Oxidizer] [Products] 0.002 Time, t [sec] Results, = 1, At 0.003 = 0.004 Temperature, T [K] 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 0.0005 0.001 Starting point Make sure [Fu] and [Ox] are 0 (use lower value for At = 10-8) 10-7 sec, 0.0015 0.002 0.0025 0.003 0.0035 0.004 Time, t [sec] Pressure rise rate, dp/dt [kPa/s] 1.E+11 1.E+10 1.E+09 1.E+08 1.E+07 1.E+06 1.E+05 1.E+04 1.E+03 Low temperature, slow start Temperature and pressure spike and rapid reaction at t = 0.00307 sec = 3.07 ms Extinction when both fuel and oxidizer are consumed Realistic results, but not realistic reaction model, which should be multi-stepped 0 0.0005 0.001 0.0015 0.002 0.0025 0.003 0.0035 0.004 Time, t [sec[ Dependence on , = 0.5 1.E+00 1.E-01 Molar Concentation [kmol/m3] 1.E-02 1.E-03 1.F-04 1.E-05 1.E-06 1.E-07 0 = 0.1 1.E+00 1.E-01 1.E-02 1.E-03 1.E-04 1.E-05 1.E-06 1.E-07 1.E-08 0 [Fuel] -[Oxidizer] [Products] 0.001 0.001 0.002 Time, t [sec] [Fuel] [Oxidizer] [Products] 0.002 Time, t [sec] 0.003 0.003 0.004 0.004 Temperature, T [K] 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Temperature, T [K] 0 0 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 At = 10-7 sec 0.0005 0.001 0.0015 0.002 0.0025 Time, t [sec] 0.0005 0.001 0.003 0.0035 0.004 0.0015 0.002 0.0025 0.003 0.0035 0.004 Time, t [sec] Pressure rise rate, dp/dt [kPa/s] Pressure rise rate, dp/dt [kPa/s] 1.E+11 1.E+10 1.E+09 1.E+08 1.E+07 1.E+06 1.E+05 1.E+04 1.E+03 1.E+11 1.E+10 . 1.E+09 1.E+08 1.E+07 1.E+06 1.E+05 1.E+04 1.E+03 0 0.0005 0.001 0.0015 0.002 0 0.0005 0.001 As before the reaction is "delayed" Initial [Fuel] is decreases Due to excess air, the mixture takes longer to heat up, and reaches lower temperatures and pressures Lower temperatures delay reaction to 3.12 and 3.53 ms (3.07 ms for $ = 1) 0.0025 0.003 0.0035 0.004 Time, t [sec[ 0.0015 0.002 0.0025 0.003 0.0035 0.004 Time, t [sec[
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.64 Rating (177 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


