Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
do it like project report approx 2000 words Standard Varance Analysis 2. Rate Camutations for POH 110.000 Set 20 S per Machine Hour ours 30
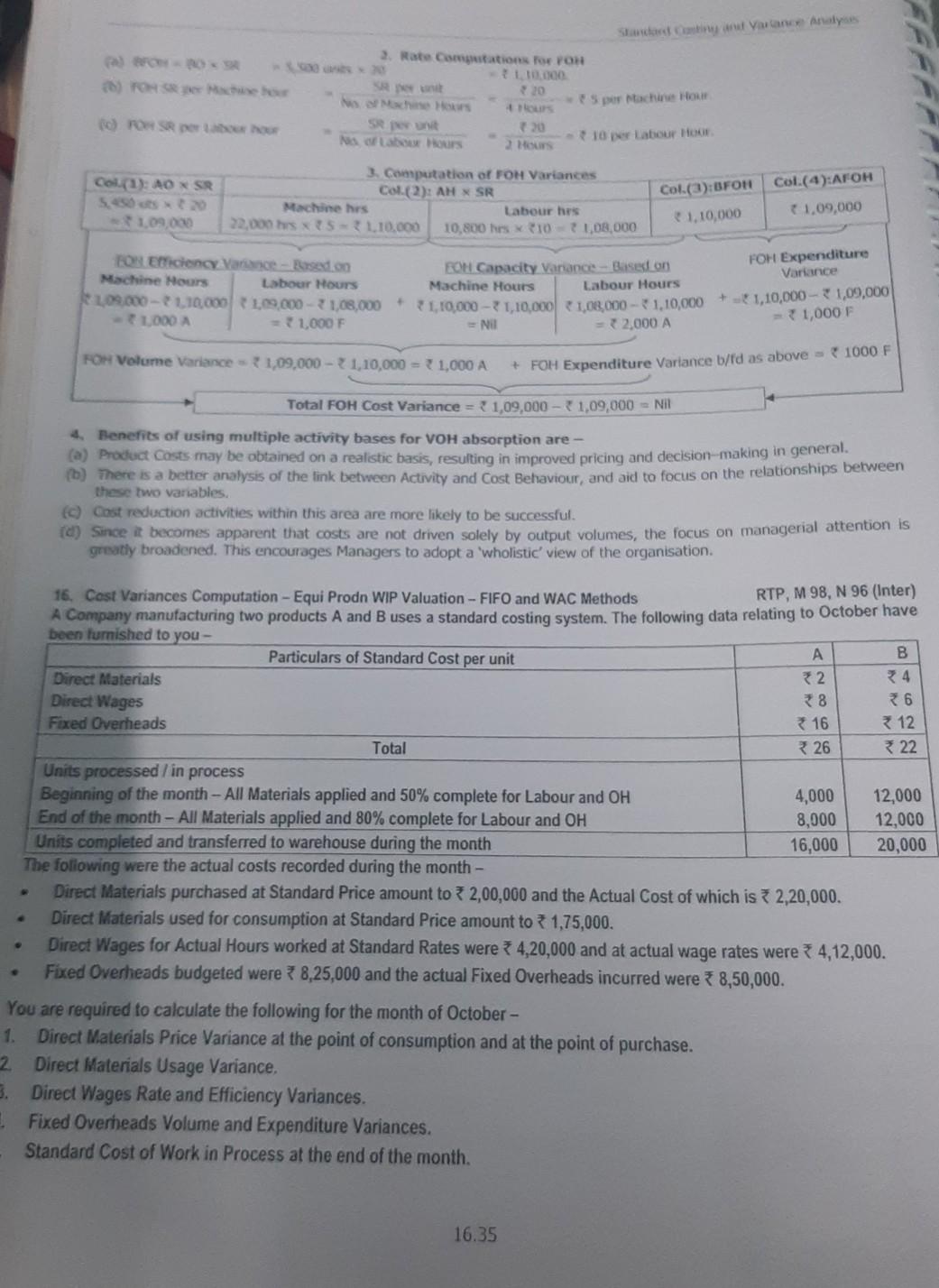

do it like project report approx 2000 words
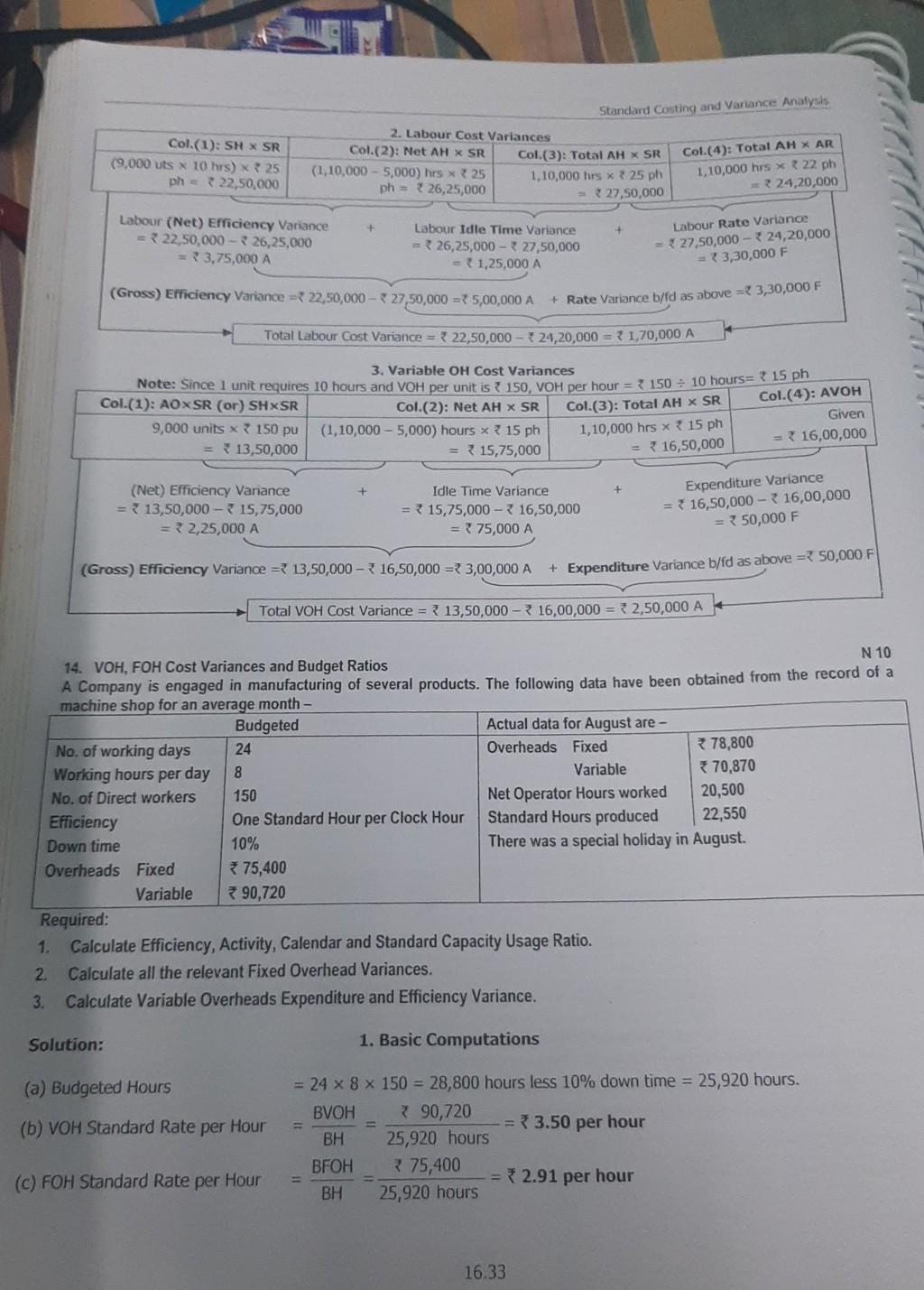
Standard Varance Analysis 2. Rate Camutations for POH 110.000 Set 20 S per Machine Hour ours 30 NS de Hours 10 per Labour HOOR 2 Hours POH SR Cl(a): AO SR Col.(4):AFOH 3. Computation of FOH Variances Col.(2): AM SR Machine hrs Labour hes 22.000 hess-110.000 10,800 hex 101,08,000 Col.(a):BFON 1,10,000 + 1.09,000 109,000 FOR Eficiency Yare - Based on Machine Hours Labour Hours 109.000-110.000 1.19.000 - 1,08,000 1000 A 1,000 F EOH Capacity Varance - Bases on FOH Expenditure Machine Hours Labour Hours Variance 1,10,000 - 1,10,000 1,03,000 -1,10,000+ - 1,10,000 - 2 1,09,000 - Nil 2.000 A 31,000 F + FOH Volume Variance - 1,09,000 - 1,10,000 = 1,000 A + FOH Expenditure Variance b/fd as above = 1000 F Total FOH Cost Variance = { 1,09,000 - 1,09,000 = Nil 4. Benefits of using multiple activity bases for VOH absorption are - (a) Product Costs may be obtained on a realistic basis, resulting in improved pricing and decision-making in general. (b) There is a better analysis of the link between Activity and Cost Behaviour, and aid to focus on the relationships between these two variables. Cost reduction activities within this area are more likely to be successful. (0) Since it becomes apparent that costs are not driven solely by output volumes, the focus on managerial attention is greatly broadened. This encourages Managers to adopt a 'wholistic view of the organisation. INN 16. Cast Variances Computation - Equi Prodn WIP Valuation - FIFO and WAC Methods RTP, M 98, N 96 (Inter) A Company manufacturing two products A and B uses a standard costing system. The following data relating to October have been furnished to you - Particulars of Standard Cost per unit A B Direct Materials 32 24 Direct Wages 78 6 Fixed Overheads 316 312 Total 26 22 Units processed in process Beginning of the month - All Materials applied and 50% complete for Labour and OH 4,000 12,000 End of the month - All Materials applied and 80% complete for Labour and OH 8,000 12,000 Units completed and transferred to warehouse during the month 16,000 20,000 The following were the actual costs recorded during the month - Direct Materials purchased at Standard Price amount to R2,00,000 and the Actual Cost of which is 2,20,000. Direct Materials used for consumption at Standard Price amount to 1,75,000 Direct Wages for Actual Hours worked at Standard Rates were 4,20,000 and at actual wage rates were 4,12,000. Fixed Overheads budgeted were ? 8,25,000 and the actual Fixed Overheads incurred were 38,50,000. You are required to calculate the following for the month of October - Direct Materials Price Variance at the point of consumption and at the point of purchase. 2 Direct Materials Usage Variance, 3. Direct Wages Rate and Efficiency Variances. Fixed Overheads Volume and Expenditure Variances. Standard Cost of Work in Process at the end of the month. . 16.35 Standard Costing and Variance Analysis Col.(1): SH X SR (9,000 uts x 10 hrs) x 25 ph222,50,000 2. Labour Cost Variances Col.(2): Net AH X SR Col.(3): Total AH X SR (1,10.000 - 5,000) hrs x 25 1,10,000 hrs x 25 ph ph = 26,25,000 = 27,50,000 Col.(4): Total AH X AR 1,10,000 hrs x 22 ph 24,20,000 + Labour (Net) Efficiency Variance = 22,50,000 -26,25,000 = 3,75,000 A Labour Idle Time Variance = 26,25,000 -27,50,000 1,25,000 A Labour Rate Variance = 27,50,000 - 24,20,000 = 73,30,000 F (Gross) Efficiency Variance = 22,50,000 -27,50,000 = 5,00,000 A + Rate Variance b/ld as above = 3,30,000 F Total Labour Cost Variance = * 22,50,000 - 24,20,000 = 7 1,70,000 A 3. Variable OH Cost Variances Note: Since 1 unit requires 10 hours and VOH per unit is 150, VOH per hour = 150 10 hours= * 15 ph Col.(1): AOXSR (or) SHX SR Col.(2): Net AH X SR Col.(3): Total AH X SR Col.(4): AVOH 9,000 units x 150 pu Given (1,10,000 - 5,000) hours x 15 ph 1,10,000 hrs x 15 ph 13,50,000 = 16,00,000 = { 15,75,000 = * 16,50,000 + (Net) Efficiency Variance => 13,50,000 -15,75,000 = 2,25,000 A Idle Time Variance = 15,75,000 - 2 16,50,000 = 75,000 A Expenditure Variance = 16,50,000 -16,00,000 = 50,000 F (Gross) Efficiency Variance = 13,50,000 - 16,50,000 = 3,00,000 A + Expenditure Variance b/fd as above = 50,000 F Total VOH Cost Variance = { 13,50,000 - 3 16,00,000 = 32,50,000 A N 10 14. VOH, FOH Cost Variances and Budget Ratios A Company is engaged in manufacturing of several products. The following data have been obtained from the record of a machine shop for an average month Budgeted Actual data for August are- No. of working days 24 Overheads Fixed 78,800 Working hours per day 8 Variable *70,870 No. of Direct workers 150 Net Operator Hours worked 20,500 Efficiency One Standard Hour per Clock Hour Standard Hours produced 22,550 Down time 10% There was a special holiday in August. Overheads Fixed 75,400 Variable 390,720 Required: 1. Calculate Efficiency, Activity, Calendar and Standard Capacity Usage Ratio. 2. Calculate all the relevant Fixed Overhead Variances. 3. Calculate Variable Overheads Expenditure and Efficiency Variance. Solution: 1. Basic Computations (a) Budgeted Hours (b) VOH Standard Rate per Hour = 24 x 8 x 150 = 28,800 hours less 10% down time = 25,920 hours. BVOH 790,720 = 3.50 per hour BH 25,920 hours BFOH 375,400 2.91 per hour BH 25,920 hours (C) FOH Standard Rate per Hour 16.33 a) sono Hoe lacesso Con System? Explos Standard Core ABC System Do you see? M NA M02 Horst of resources presented in Variance Reports under Standard Costing M02 3. Bethe meme concerning centros et operations that a murustacturing Company can be expected to experience in smo Standard Casing during periods of nation 38 Outline en between Standard Costing and Budgetary Control 3 short notes on the Behavioural Aspects of Standard Costing RIP N 97 Case Study 1: Reasons for Variation Mart Om Ladies Manufacturing Company specializing in a single product. It has installed a Standard Costing System, and recognises that Variance Analysis is one of the methods of effective Performance Evaluation The Company's Standard Costs comprise Direct Materials, Direct Labour, Variable Production OH and Fixed Production OH. All SOH and AOH are considered as Period Costs and not included for Inventory Valuation The Company has trained all its Employees and has created adequate awareness of the importance of adherence to Standards, and has a Rewards Scheme for its Employees for achieving Saving in Standard Costs. From the above, answer the following questions, each being independent of the others - 1. What are the possible reasons for differences between Budgeted & Actual Performance / Profits? 2 Explain whether a Production Manager should be accountable for Direct Labour and Direct Materials Cost Variances. 3 State the possible impact on Variances in each of the following independent situations - a) More units were produced than was budgeted. Careless handling of Materials by Production Personnel. (c) Purchase of inferior quality Raw Materials d) New Competition entered the market. le) New Suppliers were used. i New Production Staff were recruited. (9) Market Shares has fallen from 20% to 18% HPHU Issue 1: Differences between Budgeted & Actual Profits: The variables that cause actual performance of differ from budgeted performance are- 1 Direct substitution of products. 3. Actual total quantity different from budgeted total quantity. 2 Actual quantity of the constituents of sales 4. Difference between actual and budgeted unit cost. being different from budgeted quantity. 5. Difference between actual and budgeted unit sale price. Issue 2: Responsibility of Production Manager: 1. Performance should be measured against the element of Direct Cost which the Manager can control. 2 In Materials, the Price factor is the responsibility of the Purchase Manager (not the Production Manager). However, Material Usage Variance (Yield and Mix components) is the responsibility of Production Manager. 3. In Labour, the Rate factor may not be fully within the influence of the Production Manager. However, Efficiency Variance attributed to supervision, etc. is the responsibility of Production Manager. If the Production Manager has no influence over the prices of material, the quality of the material, the cost of labour and the quality of labour, he/she cannot be held responsible for the same. Issue 3: Impact on Variances: Situation Impact on Variances - More units were produced than was budgeted. Favourable Fixed Overhead Volume Variance - Careless handling of materials by Production Personnel Adverse Material Usage Variance Purchase of inferior quality material Adverse Material Usage &Favourable Material Price Variance 16.19Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


