Question: does these codes match to do this import java.util.Random; public class Matrix { private int[][] matrix; // A constructor that initializes a matrix with random
does these codes match to do this
import java.util.Random;
public class Matrix { private int[][] matrix;
// A constructor that initializes a matrix with random values public Matrix(int rows, int cols, int maxRand) { // Creating a new 2D array with the specified number of rows and columns int[][] mVals = new int[rows][cols]; // Creating a new Random object Random rand = new Random(); // Filling the matrix with random values for (int i = 0; i
// A constructor that initializes a matrix with a given 2D array of values public Matrix(int[][] mVals) { // Setting the matrix values using the helper method setMatrixVals(mVals); }
// A method to return a copy of the matrix values public int[][] getMatrixVals() { // Creating a new 2D array with the same dimensions as the matrix int[][] copy = new int[matrix.length][matrix[0].length]; // Copying the values from the matrix to the new array for (int i = 0; i
// A method to check if two matrices are the same size public boolean sameSize(Matrix m2) { // If the number of rows and columns are the same, the matrices are the same size return matrix.length == m2.matrix.length && matrix[0].length == m2.matrix[0].length; }
// A method to transpose the matrix public Matrix transpose() { // Creating a new 2D array with the transposed dimensions int[][] tVals = new int[matrix[0].length][matrix.length]; // Transposing the matrix values for (int i = 0; i
// A method to multiply the matrix by a scalar value public Matrix scalarMult(int scVal) { // Creating a new 2D array with the same dimensions as the matrix int[][] smVals = new int[matrix.length][matrix[0].length]; // Multiplying each value in the matrix by the scalar value for (int i = 0; i
// A method to add two matrices together public Matrix add(Matrix m2) { // Check if matrices are the same size if (!sameSize(m2)) { System.out.println("Matrix A and Matrix B are not the same size, they cannot be added"); return null; } // Initialize the sum of matrices int[][] sumVals = new int[matrix.length][matrix[0].length]; // Loop through the rows and columns of the matrices to add corresponding elements for (int i = 0; i
private void setMatrixVals(int[][] mVals) { // Initialize the matrix with given values matrix = new int[mVals.length][mVals[0].length]; // Loop through the rows and columns of the given values to copy them into the matrix for (int i = 0; i
public String toString() { // Create a string builder to hold the string representation of the matrix StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); // Loop through the rows and columns of the matrix to append each element to the string builder for (int i = 0; i
next code
import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner;
public class MatrixDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); // Get user input for matrix size and maxRand value System.out.print("Enter the number of rows: "); int rows = input.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter the number of columns: "); int columns = input.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter the maximum random value: "); int maxRand = input.nextInt(); // Create first matrix and display Matrix matrix1 = new Matrix(rows, columns, maxRand); System.out.println("Matrix 1:"); System.out.println(matrix1.toString()); // Transpose matrix1 and display Matrix matrix1Transposed = matrix1.transpose(); System.out.println("Matrix 1 Transposed:"); System.out.println(matrix1Transposed.toString()); // Multiply matrix1 by scalar and display System.out.print("Enter a scalar value to multiply Matrix 1: "); int scalar = input.nextInt(); Matrix matrix1Scalar = matrix1.scalarMultiply(scalar); System.out.println("Matrix 1 Scalar Multiplied by " + scalar + ":"); System.out.println(matrix1Scalar.toString()); // Create second matrix and display System.out.print("Enter the number of rows for Matrix 2: "); int rows2 = input.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter the number of columns for Matrix 2: "); int columns2 = input.nextInt(); Matrix matrix2 = new Matrix(rows2, columns2, maxRand); System.out.println("Matrix 2:"); System.out.println(matrix2.toString()); // Add matrix1 and matrix2 if they are the same size if (matrix1.isSameSize(matrix2)) { Matrix matrixSum = matrix1.add(matrix2); System.out.println("Matrix 1 + Matrix 2:"); System.out.println(matrixSum.toString()); } else { System.out.println("Matrix 1 and Matrix 2 cannot be added."); } } // Returns a 2D array of random int values with the specified number of rows, columns, and maxRand value public static int[][] getRandomArray(int rows, int columns, int maxRand) { Random rand = new Random(); int[][] array = new int[rows][columns]; for (int i = 0; i 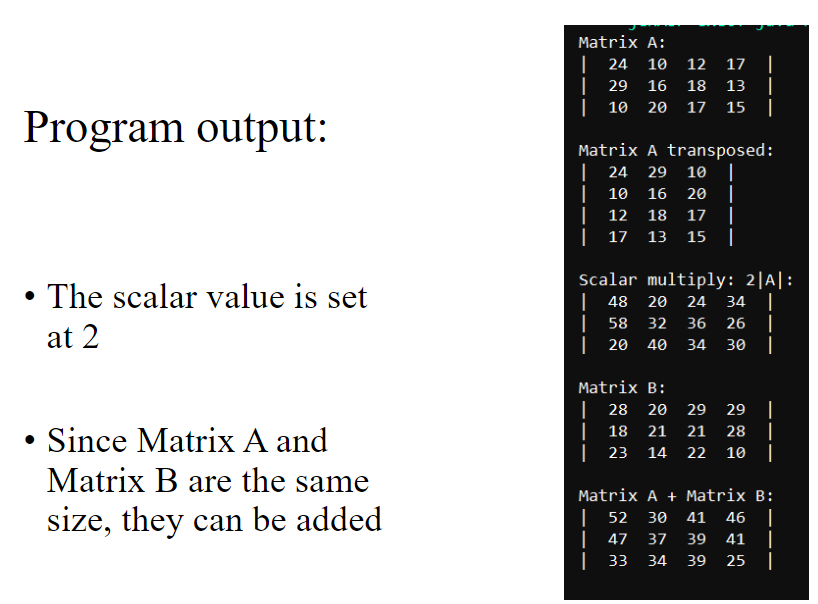
The private field is a two dimensional array of int values Since the size is not yet known, this can be set up as follows: The constructor calls the setMatrixVals(mVals) setter method to assign the correct information to the private field The setMatrixVals(mVals) setter method must make a copy of the parameter This copy becomes the private field The getMatrixVals( ) getter method must return a copy of the field 7
Program requirements (continued): Matrix class The sameSize(m2) method returns true if the this object and the parameter Matrix object (i.e. m2) have the same number of rows and columns Else returns false The transpose( ) method returns the this object transposed Therefore, the rows become the columns and the columns become the rows The scalarMult(scVal) method returns the Matrix object that is obtained by multiplying all elements of the this object by the scVal(data type int) value of the parameter The add(m2) method returns the Matrix object that results from adding the this object and the parameter Matrix object The toString( ) method returns a consistent representation of the two dimensional array (i.e. the private field) 8
Program requirements (continued): Matrix class The getMatrixVals( ) getter method must return a copy of the field Why is this important? If the method returns only the name of the array, it is actually returning the address in memory Therefore, any other method that has access to this address can potentially change the information stored at that address. Therefore, to protect the security of the data, we must return a copy and not the address The same concept applies to the setter method, which is why a copy of the parameter array must be made and assigned to the private field Note that this will necessitate implementing a nested for loop and copying each value in the correct place 9
Program requirements: MatrixDemo.java (i.e. the driver class) Implement a method to return a two dimensional array of random int values Parameters: the number of rows and columns and the maxRand val In the main method: Instantiate a Matrix object The size can be set up as constant values or obtained from the user Display the Matrix by calling the toString( ) method Transpose and display the transposed Matrix Scalar multiply and display the resultant Matrix (the scalar value can be set as a constant or obtained from the user) Instantiate a second Matrix object Display the second Matrix If the two are the same size, add the two Matrix objects and display resultant sum Else, display error message that they cannot be added 10
To solve Project6 do the following: Create a new folder and name it Project6 Create two new Java files, named as follows: Matrix.java MatrixDemo.java First understand the problem that needs to be solved To develop this understanding, include studying the grading rubric so that you will understand how your project will be graded Complete the Matrix.java class definition by following the UML, which is in slide 3 of this document Reminder: First identify pseudocode and enter as comments in the program Complete the MatrixDemo.java class, which is the driver class in which Matrix objects will be instantiated Reminder: First identify pseudocode and enter as comments in the program Verify that your program gives correct output by testing it.
Program output: - The scalar value is set at 2 - Since Matrix A and Matrix B are not the same size, they cannot Matrix A+ Matrix B : be added To add matrices, they must Program output: - The scalar value is set at 2 - Since Matrix A and Matrix B are the same size, they can be added
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


