Question
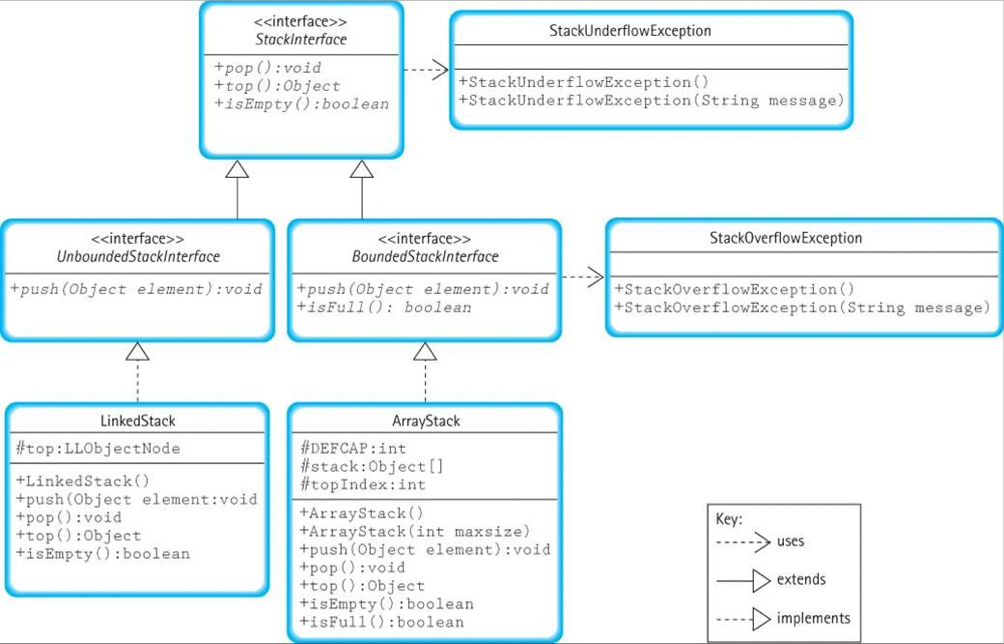
Draw the UML diagram of your VectorStack , place it in the correct spot in the UML Class Diagram given. Do not forget to draw
Draw the UML diagram of your VectorStack, place it in the correct spot in the UML Class Diagram given. Do not forget to draw the relations between your VectorStack and other classes (arrows).
StackInterface.java:
public interface StackInterface
public T pop() throws StackUnderflowException;
public T top();
public boolean isEmpty();
}
BoundedStackInterface.java:
public interface BoundedStackInterface
public void push(T element) throws StackOverflowException;
public boolean isFull();
}
UnboundedStackInterface.java:
public interface UnboundedStackInterface
public void push(T element);
}
ArrayStack.java:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class ArrayStack
protected final int DEFCAP = 100;
protected T[] stack;
protected int numElements = 0;
public ArrayStack() {
stack = (T[]) new Object[DEFCAP];
}
public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {
stack = (T[]) new Object[maxSize];
}
public void push(T element) throws StackOverflowException {
if (isFull())
throw new StackOverflowException("Enqueue attempted on a full stack.");
else {
stack[numElements] = element;
numElements = numElements + 1;
}
}
public T pop() throws StackUnderflowException {
if (isEmpty())
throw new StackUnderflowException(
"Dequeue attempted on empty stack.");
else {
numElements--;
T toReturn = stack[numElements];
return toReturn;
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (numElements == 0);
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (numElements == stack.length);
}
@Override
public T top() {
if (isEmpty())
return null;
else
return stack[numElements - 1];
}
}
LinkedStack.java:
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedStack
LinkedList
public LinkedStack() {
list = new LinkedList();
}
public void push(T s) {
// add at back
list.add(s);
}
public T pop() throws StackUnderflowException {
if (isEmpty())
throw new StackUnderflowException(
"Dequeue attempted on empty stack.");
// remove from end
return list.removeLast();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (list.size() == 0);
}
public boolean isFull() {
return false;
}
@Override
public T top() {
if(isEmpty())
return null;
else
return list.getLast();
}
}
StackUnderflowException.java:
public class StackUnderflowException extends Exception {
public StackUnderflowException(String string) {
super(string);
}
public StackUnderflowException() {
super();
}
}
StackOverflowException.java:
public class StackOverflowException extends Exception {
public StackOverflowException(String string) {
super(string);
}
public StackOverflowException() {
}
}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


