Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
drop downs are favorabke or unfavorable is the prediction of what activity costs will be as activity output changes. Variance analysis within an activity framework
drop downs are favorabke or unfavorable 
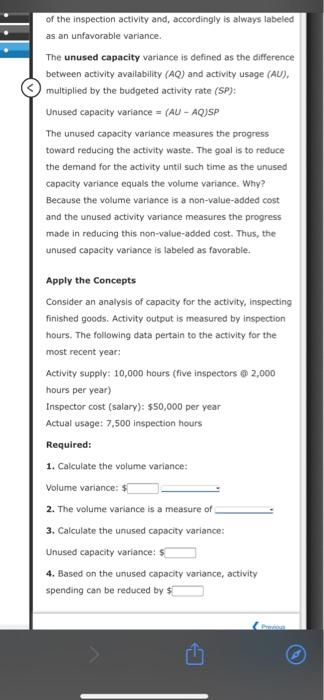
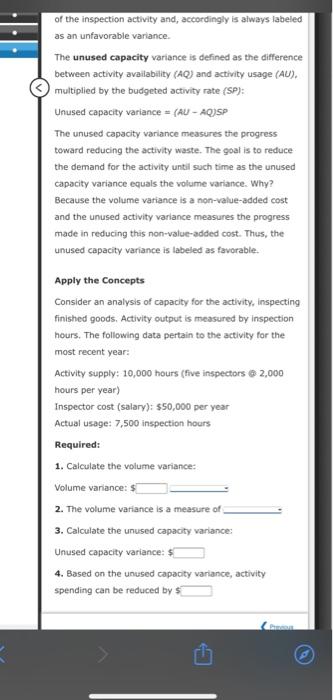
is the prediction of what activity costs will be as activity output changes. Variance analysis within an activity framework makes it possible to improve traditional budgetary performance reporting. It also enhances the ability to manage activities. In a unit-based approach, budgeted costs for the actual level of activity are obtained by assuming that a single unit-based driver (units of product or direct labor hours) drives all costs. A cost formula is developed for each cost item as a function of either units produced or direct labor hours. For example, assume that a firm has developed the following formula for budgeting total manufacturing costs: Total budgeted cost = $425,000 + $22[DLH). Thus, the total budgeted costs for 15,000 direct labor hours would be If, however, costs vary with respect to more than one driver and the drivers are not highly correlated with direct labor hours, then the predicted costs can be misleading The solution, of course, is to build flexible budget formulas for more than one driver. Cost estimation procedures (high-low method, the method of least squares, and so on) can be used to estimate and validate the cost formulas for each activity. This multiple cost-formula approach allows managers to predict more accurately what costs should be for different levels of activity usage, as measured by the activity output measure. For example, there may be a budget formula for inspections: Inspection cost = $80,000 + $2,100 (number of batches) and for purchasing: $200,000 + $2 (number of orders). Thus, instead of being treated as a fixed cost with respect to direct labor hours, the two overhead items will vary with batches and number of purchase orders, respectively. The total budgeted inspection cost for 10 batches would be $ and the total budgeted purchasing cost for processing 20,000 purchase orders would be $ - of the inspection activity and, accordingly is always labeled as an unfavorable variance The unused capacity variance is defined as the difference between activity availability (AQ) and activity usage (AU). multiplied by the budgeted activity rate (SP): Unused capacity variance = (AU - AQJSP The unused capacity variance measures the progress toward reducing the activity waste. The goal is to reduce the demand for the activity until such time as the unused capacity variance equals the volume variance. Why? Because the volume variance is a non-value-added cost and the unused activity variance measures the progress made in reducing this non-value-added cost. Thus, the unused capacity variance is labeled as favorable. Apply the Concepts Consider an analysis of capacity for the activity, inspecting finished goods. Activity output is measured by inspection hours. The following data pertain to the activity for the most recent year: Activity supply: 10,000 hours (five inspectors 2,000 hours per year) Inspector cost (salary): $50,000 per year Actual usage: 7,500 inspection hours Required: 1. Calculate the volume variance: Volume variance: $ 2. The volume variance is a measure of 3. Calculate the unused capacity variance: Unused capacity variance: $ 4. Based on the unused capacity variance, activity spending can be reduced by $ of the inspection activity and, accordingly is always labeled as an unfavorable variance The unused capacity variance is defined as the difference between activity availability (AQ) and activity usage (AU). multiplied by the budgeted activity rate (SP): Unused capacity variance = (AU-AQJSP The unused capacity variance measures the progress toward reducing the activity waste. The goal is to reduce the demand for the activity until such time as the unused capacity variance equals the volume variance. Why? Because the volume variance is a non-value-added cost and the unused activity variance measures the progress made in reducing this non-value-added cost. Thus, the unused capacity variance is labeled as favorable. Apply the concepts Consider an analysis of capacity for the activity, inspecting finished goods, Activity output is measured by inspection hours. The following data pertain to the activity for the most recent year: Activity supply: 10,000 hours (five inspectors @ 2,000 hours per year) Inspector cost (salary): $50,000 per year Actual usage: 7,500 inspection hours Required: 1. Calculate the volume variance: Volume variance: $ 2. The volume variance is a measure of 3. Calculate the unused capacity variance: Unused capacity variance: $ 4. Based on the unused capacity variance, activity spending can be reduced by 


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


