Question
E7-5 (Algo) Calculating Ending Inventory and Cost of Goods Sold Under FIFO, LIFO, and Average Cost LO7-2 Nittany Company uses a periodic inventory system. At
E7-5 (Algo) Calculating Ending Inventory and Cost of Goods Sold Under FIFO, LIFO, and Average Cost LO7-2
Nittany Company uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31 of the current year, the accounting records provided the following information for product 1:
Units Unit Cost Inventory, December 31, prior year 1,890 $ 4 For the current year: Purchase, March 21 5,080 6 Purchase, August 1 2,820 7 Inventory, December 31, current year 4,150
Part 1 required:
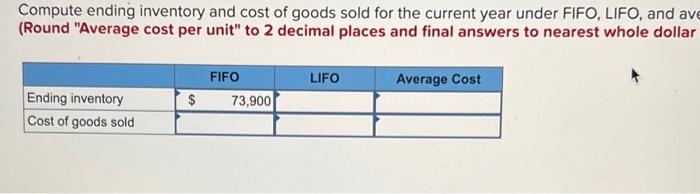
Compute ending inventory and cost of goods sold for the current year under FIFO, LIFO, and average cost inventory costing methods. (Round "Average cost per unit" to 2 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar amount.)
Nittany Company uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31 of the current year, the accounting records provided the following information for product 1:
| Units | Unit Cost | |||||
| Inventory, December 31, prior year | 1,890 | $ | 4 | |||
| For the current year: | ||||||
| Purchase, March 21 | 5,080 | 6 | ||||
| Purchase, August 1 | 2,820 | 7 | ||||
| Inventory, December 31, current year | 4,150 | |||||
Part 1 required:
Compute ending inventory and cost of goods sold for the current year under FIFO, LIFO, and average cost inventory costing methods. (Round "Average cost per unit" to 2 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar amount.)
Givoly Inc. uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31 of the current year, the accounting records provided the following information for product 2:
Units Unit Cost Inventory, December 31, prior year 6,700 $ 9 For the current year: Purchase, March 5 18,700 7 Purchase, September 19 9,700 3 Sale ($26 each) 8,100 Sale ($28 each) 15,700 Operating expenses (excluding income tax expense) $ 397,000
Givoly Inc. uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31 of the current year, the accounting records provided the following information for product 2:
| Units | Unit Cost | ||||||||
| Inventory, December 31, prior year | 6,700 | $ | 9 | ||||||
| For the current year: | |||||||||
| Purchase, March 5 | 18,700 | 7 | |||||||
| Purchase, September 19 | 9,700 | 3 | |||||||
| Sale ($26 each) | 8,100 | ||||||||
| Sale ($28 each) | 15,700 | ||||||||
| Operating expenses (excluding income tax expense) | $ | 397,000 | |||||||
E7-8 Part 1
Part 2 Required:
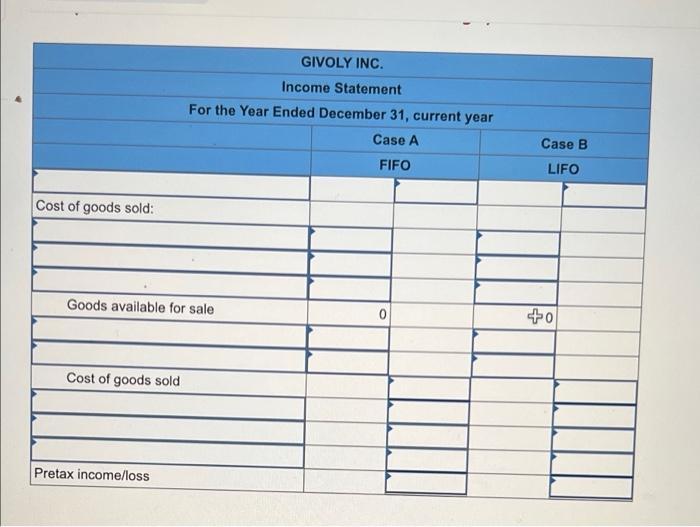
Prepare a separate income statement through pretax income that details cost of goods sold for (a) Case A: FIFO and (b) Case B: LIFO. (Loss amounts should be indicated with a minus sign.)
Part 3: Compute the difference between the pretax income and the ending inventory amounts for the two cases.
Part 2 Required:
Prepare a separate income statement through pretax income that details cost of goods sold for (a) Case A: FIFO and (b) Case B: LIFO. (Loss amounts should be indicated with a minus sign.)
Part 3: Compute the difference between the pretax income and the ending inventory amounts for the two cases.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


