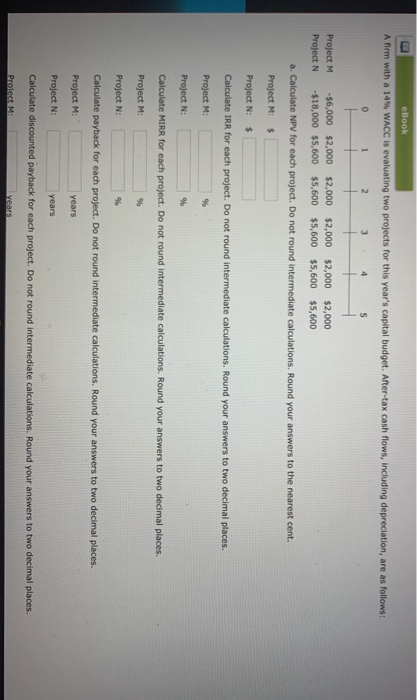
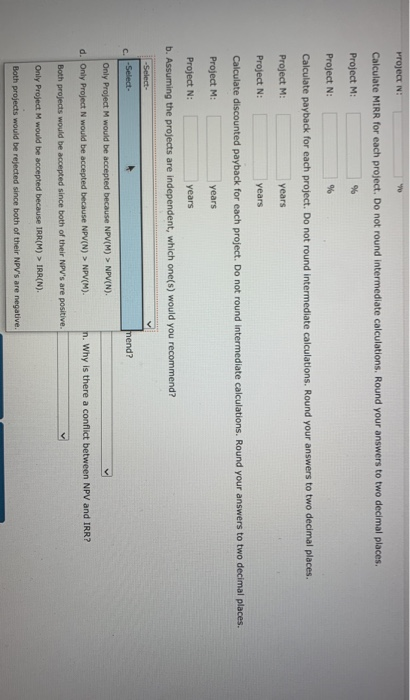
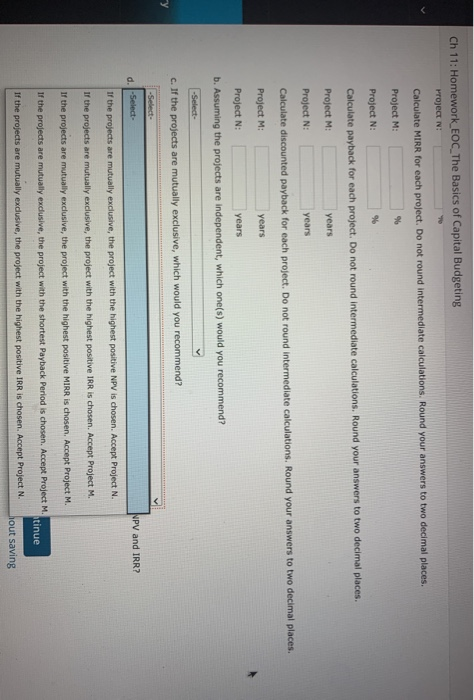
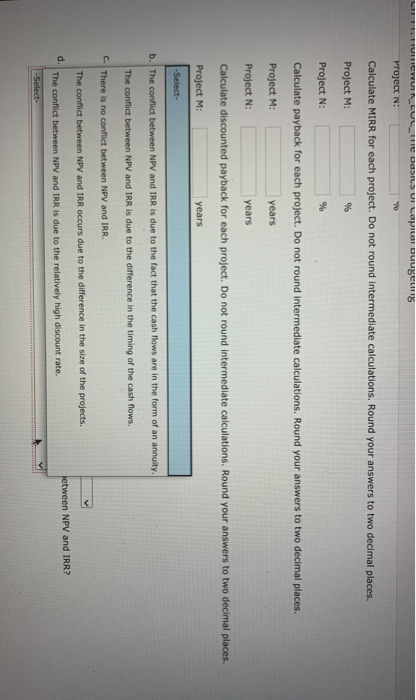
eBook A firm with a 14% WACC is evaluating two projects for this year's capital budget. After-tax cash flows, including depreciation, are as follows: 2 3 4 5 Project M Project N -$6,000 $2,000 $2,000 $2,000 $2,000 $2,000 -$18,000 $5,600 $5,600 $5,600 $5,600 $5,600 a. Calculate NPV for each project. Do not round Intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Project M: $ Project N: $ Calculate IRR for each project. Do not round Intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: % Project N: % Calculate MIRR for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: 9 Project N: 9 Calculate payback for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: years Project N: years Calculate discounted payback for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Protect Me years Project N: w Calculate MIRR for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: % Project N: % Calculate payback for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: years Project N: years Calculate discounted payback for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: years Project N: years b. Assuming the projects are independent, which one(s) would you recommend? -Select- c. -Select- mend? Only Project M would be accepted because NPV(M) > NPVN). d. Only Project N would be accepted because NPV(N) NPV(M). n. Why is there a conflict between NPV and IRR? Both projects would be accepted since both of their NPV's are positive. Only Project M would be accepted because IRR(M) > IRR(N). Both projects would be rejected since both of their NPV's are negative. Ch 11: Homework EOC_The Basics of Capital Budgeting Project N Calculate MIRR for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: % Project N: 96 Calculate payback for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places Project M years Project N: years Calculate discounted payback for each project. Do not round Intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: years Project N: years b. Assuming the projects are independent, which one(s) would you recommend? -Select- c. If the projects are mutually exclusive, which would you recommend? -Select- d. -Select- NPV and IRR? If the projects are mutually exclusive, the project with the highest positive NPV is chosen. Accept Project N. If the projects are mutually exclusive, the project with the highest positive IRR is chosen. Accept Project M. If the projects are mutually exclusive, the project with the highest positive MIRR is chosen. Accept Project M. If the projects are mutually exclusive, the project with the shortest Payback period is chosen. Accept Project M. atinue If the projects are mutually exclusive, the project with the highest positive IRR is chosen. Accept Project N. hout saving LIFIUTIVUINEUL DOILS UI Lapie buugeurs Project N Calculate MIRR for each project. Do not round Intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: % Project N: % Calculate payback for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Project M: years Project N: years Calculate discounted payback for each project. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places Project M: years -Select- b. The conflict between NPV and IRR is due to the fact that the cash flows are in the form of an annuity. The conflict between NPV and IRR is due to the difference in the timing of the cash flows. C. There is no conflict between NPV and IRR. The conflict between NPV and IRR occurs due to the difference in the size of the projects. d. etween NPV and IRR? The conflict between NPV and IRR is due to the relatively high discount rate. -Select