Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1) (23 marks) In this question, you will undertake a welfare analysis of policies applied to a polluting industry. Make sure that you clearly

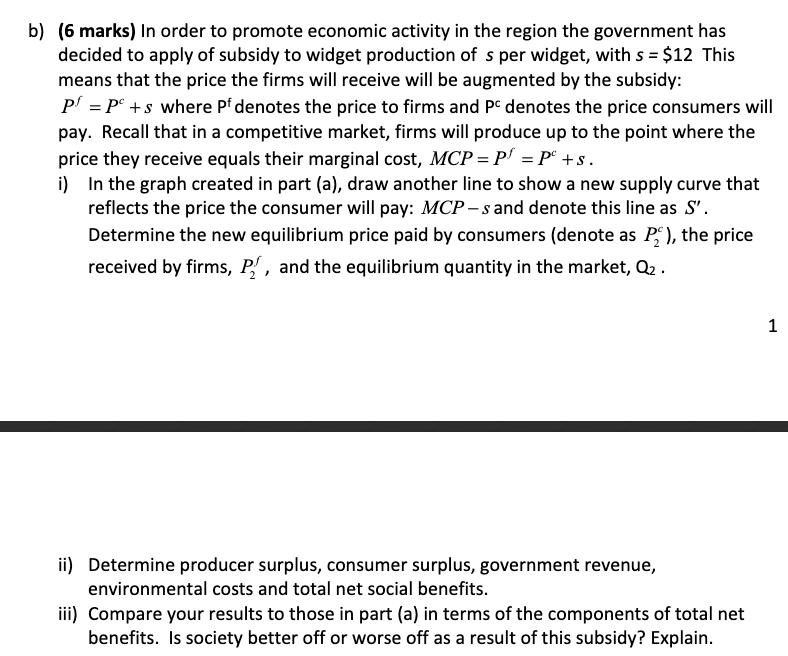

1) (23 marks) In this question, you will undertake a welfare analysis of policies applied to a polluting industry. Make sure that you clearly explain your answers. Suppose widgets are produced by a competitive industry. The demand equation for widgets has been estimated as: P=140-20, where Q denotes the quantity produced per month and P denotes the price. The private marginal cost of the widget industry is given as: MCP=20+20, where MCP denotes marginal private cost. It has been determined that every unit of production of widgets generates $20 of environmental damages. a) (6 marks) Suppose there is no government regulation in this market. i) Sketch the MPC and demand curves on a graph. State the equation for the marginal social cost curve, MCS, and add it to your graph. Determine the equilibrium price (P) and quantity (Q) in this market. ii) Determine total social benefits (TSB), total social costs (TSC), and total net social benefits (TNSB). iii) Determine producer surplus, consumer surplus, and environmental costs. b) (6 marks) In order to promote economic activity in the region the government has decided to apply of subsidy to widget production of s per widget, with s = $12 This means that the price the firms will receive will be augmented by the subsidy: P = P +s where Pf denotes the price to firms and Pc denotes the price consumers will pay. Recall that in a competitive market, firms will produce up to the point where the price they receive equals their marginal cost, MCP= P = P + s. i) In the graph created in part (a), draw another line to show a new supply curve that reflects the price the consumer will pay: MCP-s and denote this line as S'. Determine the new equilibrium price paid by consumers (denote as P), the price received by firms, P, and the equilibrium quantity in the market, Q. ii) Determine producer surplus, consumer surplus, government revenue, environmental costs and total net social benefits. iii) Compare your results to those in part (a) in terms of the components of total net benefits. Is society better off or worse off as a result of this subsidy? Explain. 1 c) (6 marks) As an economist advising the government, you recommend that instead of subsidizing widgets, a pollution tax should be applied. What level of pollution tax do you recommend? Redraw the graph created in part (a), but this time add include your recommended pollution tax. Determine the new equilibrium price paid by consumers (denote as P), the price received by firms, P, and the equilibrium quantity in the market, Q3. Undertake a welfare analysis indicating producer and consumer surplus, environmental costs, and government revenue. Compare the total net social benefits with those calculated in parts (a) and (b). d) (5 marks) Read the article: "Economist Schools Brief, Pigouvian taxes" The Economist, August 19 2017 edition. a. Briefly describe three theoretical objections that have been raised regarding a pollution tax. (3 marks) b. Two practical problems with a pollution tax are that (1) it is regressive, having a disproportionate effect on those with low incomes, and (2) it may encourage people to switch to imported goods from countries that do not impose a pollution tax. What are possible solutions to these problems? (2 marks)
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.52 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a i Sketching MPC and Demand curves and determining MCS The private marginal cost MCP curve is given as MCP 20 20 40 The demand equation is P 140 20Q To find the equation for the marginal social cost ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


