ECONOMICS MULTIPLE CHOICE
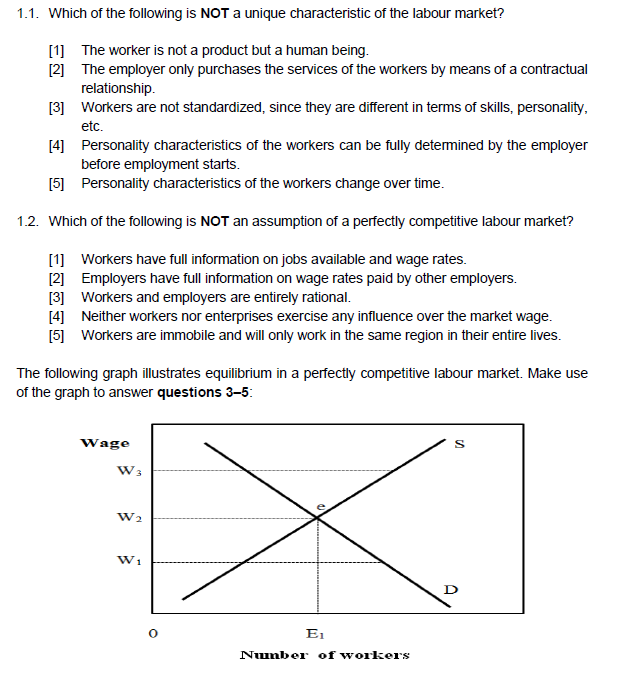
1.1. Which of the following is NOT a unique characteristic of the labour market? [1] The worker is not a product but a human being. [2] The employer only purchases the services of the workers by means of a contractual relationship. [3] Workers are not standardized, since they are different in terms of skills, personality, etc. [4] Personality characteristics of the workers can be fully determined by the employer before employment starts. [5] Personality characteristics of the workers change over time. 1.2. Which of the following is NOT an assumption of a perfectly competitive labour market? [1] Workers have full information on jobs available and wage rates. [2] Employers have full information on wage rates paid by other employers. [3] Workers and employers are entirely rational. [4] Neither workers nor enterprises exercise any influence over the market wage. [5] Workers are immobile and will only work in the same region in their entire lives. The following graph illustrates equilibrium in a perfectly competitive labour market. Make use of the graph to answer questions 3-5: Wage W 3 W 2 W1 D 0 E1 Number of workers1.3. Which of the following is NOT correct? [1] Equilibrium takes place at point e. [2] The equilibrium wage is W2. [3] The equilibrium wage is W1. [4] Number of workers employed at equilibrium is E1 [5] Equilibrium takes place where labour supply and demand curves intersect 1.4. When the labour demand curve shifts rightwards, at the new equilibrium, there is no change in wage. [2] the wage decreases. [3] the wage increases. [4] the labour supply curve also shifts rightwards. [5] the labour supply curve shifts leftwards. 1.5. When the wage rate equals W1, this wage is below the equilibrium wage. [2] there is an excess demand for labour. [3] number of employed decreases compared to what happens at equilibrium. [4] unemployment does not take place. [5] the number of employed remains unchanged at E1. 1.6 Which of the following factors does NOT result in an increase of labour participation of women? [1] The rising relative wages for women due to reduced discrimination [2] The rising levels of education among women [3] Increasing coverage of various social grants [4] Declining birth rates [5] Declining productivity in the household 1.7. Use the information in the following Table to calculate the total labour force (TLF) of a hypothetical country in 2019Employees 7 500 000 Employers 1 000 000 Self-employed 1 500 000 Unemployed 5 000 000 Inactive 8 000 000 [1] TLF= 2 500 000 [2] TLF= 9 000 000 [3] L = 10 000 000 [4] TLF= 15 000 000 [5] TLF= 23 000 000 1.8. Use the information in the following Table to calculate the labour force participation rate (LFPR) of a hypothetical country in 2019. Round off the answer to 2 decimal place. Full population (all ages) 3 000 000 Working-age population 2 500 000 Labour force 2 000 000 [1] LFPR = 66.67% [2] LFPR = 80.00% [3] LFPR = 83.33% [4] LFPR = 90.00% [5] LFPR = 100.00% 1.9. Which of the following is CORRECT regarding the first stage of demographic transition? [1] high birth rates and high mortality rates [2] high birth rates and declining mortality rates [3] declining zero birth rates and zero mortality rates [4] declining birth rates and low mortality rates 151 low birth rates and low mortality rates