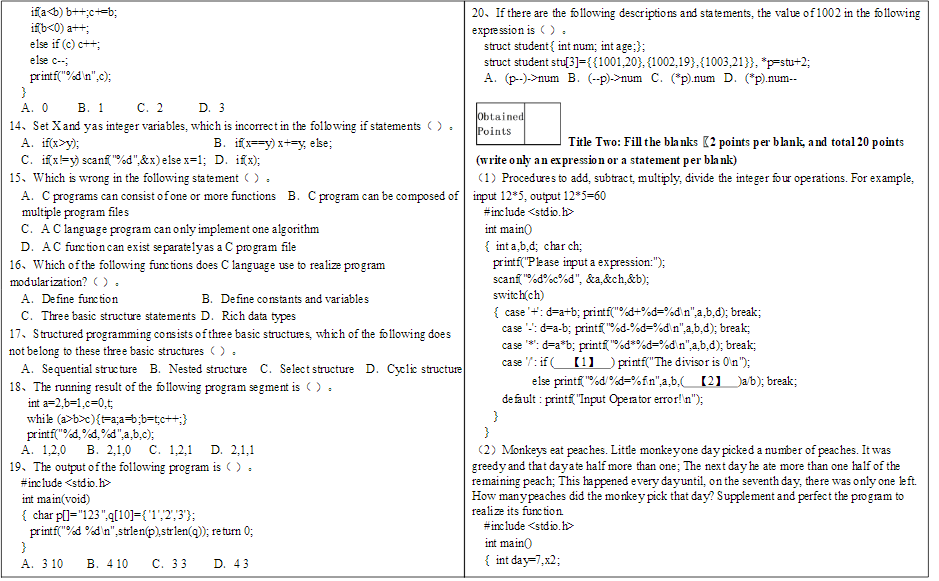
else - ifa) b++;ct=b; 20. If there are the following descriptions and statements, the value of 1002 in the following ifbnum B. (--)->num C. (*p).num D. (*p).num-- } A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3 Obtained 14. Set Xand yas integer variables, which is incorrect in the following if statements(). Points A. if(x>y): B. if(x==y) x+=y, ele; Title Two: Fill the blanks K2 points per blank, and total 20 points c. if(x=y) scanf("%d",&x) else x=1; D. if(x); (write only an expression or a statement per blank) 15. Which is wrong in the following statement(). (1) Procedures to add, subtract, multiply, divide the integer four operations. For example, A. C programs can consist of one or more functions B. C program can be composed of input 1285, output 12*5=60 multiple program files #include
C. AC language program can only implement one algorithm int maino D. AC function can exist separatelyas a C program file { int a,b,d; char ch; 16. Which of the following functions does C language use to realize program printf("Please input a expression:"); modularization?) scanf("%d%c%d", &a,&ch,&b): A. Define function B. Define constants and variables switch(ch) C. Three basic structure statements D. Rich data types { case'+: d=a+b; printf("%d+%d=%d n".a.b.d); break; 17. Structured programming consists of three basic structures, which of the following does case': d=a-b; printf("%d-%d=%d n".a.b.d); break; not belong to these three basic structures (). case '*: d=a*b; printf"%d*%d=%d n".a.b.d); break; A. Sequential structure B. Nested structure C. Select structure D. Cyclic structure case ': if (1) printf("The divisor is 'n"); 18. The running result of the following program segment is). else printf("%d%d=%n".a.b. (2) Jab); break; int a=2,b=1,c=0,5; default: printf "Input Operator error!'n"); while (a>b>c){t=a;a=b;b=t;c++;} } printf("%d%d%d".a.b.c); } A. 1,2,0 B. 2,1,0 c. 1,2,1 D. 2,1,1 (2) Monkeys eat peaches. Little monkeyone day picked a number of peaches. It was 19. The output of the following program is (). greedy and that dayate half more than one: The next day he ate more than one half of the #include remaining peach; This happened every dayuntil, on the seventh day, there was only one left int main(void) How many peaches did the monkey pick that day? Supplement and perfect the program to { char p[="123".q[10]={'1,23'); realize its function printf("%dd n", strlen(p), strlen(q)); return 0; #include } int maino A. 3 10 B 4 10 C. 33 D. 43 { int day=7.x2







