Question
Emilia randomly assigns participants to taste samples of either Godiva chocolate or Hershey chocolate. After sampling, participants are asked to rate their enjoyment on a
- Emilia randomly assigns participants to taste samples of either Godiva chocolate or Hershey chocolate. After sampling, participants are asked to rate their enjoyment on a scale from 1 to 10 (1 = disgusting, 10 = heavenly). Emilia finds:
MGodiva-MHershey= 2.1, 95% CI [1.1, 3.1]
Which of these conclusions is best supported by her data?
Godiva chocolate is liked almost the same as Hershey. The CI indicates that any difference is quite small.
Godiva chocolate was liked a bit more in this sample, but the CI is so broad that no firm conclusions can be made.
Godiva chocolate is not liked as much as Hershey. The CI indicates at least a moderate preference for Hershey.
Godiva chocolate was liked more than Hershey chocolate was. The CI indicates at least a slight preference but possibly a large one.
2.
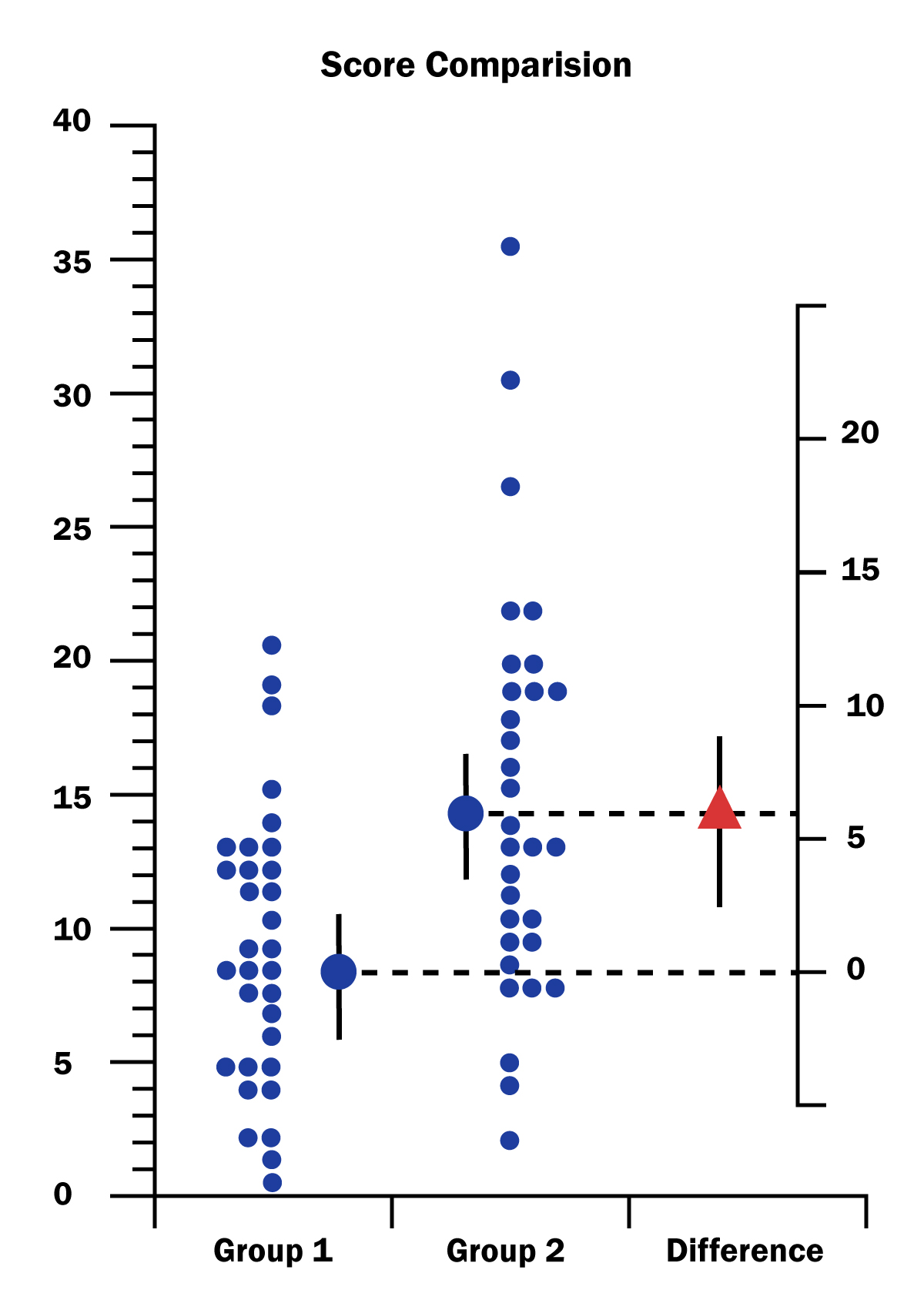
This figure compares exam scores from two different groups.
see attached image.
What is best concluded from this figure?
The CI of the difference indicates anywhere from a moderate up to a large advantage for Group 1.
The CI of the difference indicates anywhere from a moderate up to a large advantage for Group 2.
The CI of the difference is small and centered around 0.
The CI of these data ranges from 3 to 6.
3.
At a treatment clinic, Desrae randomly assigns 12 depressed patients to either a new type of brain stimulation (Group 1?the treatment group) or the standard treatment (Group 2?the control group). After 1 week, participants completed a scale that measures depressive symptoms. The control group still has high depression (MControl= 15). The group that received brain stimulation has lower depression (MBrainstim= 9). Comparing the data from the two groups, she finds:MControl- MBrainstim= 6, 95% CI [2.54, 8.63]
What should she conclude?
The patients who received the new treatment improved as a result of expecting that the new treatment would make them less depressed.
The new treatment is clearly effective but only barely.
The new treatment clearly is not effective.
The results are promising because the CI rules out no difference, and the mean difference is above zero.
4.
Calculating the CI for the difference between two independent groups requires each of the followingexcept
a t component, based on the degrees of freedom and confidence level desired.
a variability component, reflecting the variation in scores in both groups.
a sample size component, reflecting the size of the sample.
an expectation component reflecting the expected CI's mean.
5.
Cohen'sdis
the same measure as the margin of error.
the lower bound of the CI.
a standardized way of expressing group differences that doesn't depend on the scale of the original measurement.
a test for homogeneity of variance.
6.
Each of the following assumptions is made when calculating a CI for the difference between two independent groupsexcept
the variances are approximately equal for both groups (homogeneity of variance).
scores are normally distributed for both groups.
both groups are random samples.
the groups were created simultaneously.
7.
When comparing two independent groups
the larger the sample sizes, the shorter the CI of the difference.
the more variation in the data, the shorter the CI of the difference.
the larger the mean of sample means, the shorter the CI of the difference.
the smaller the sample sizes, the shorter the CI of the difference.
8.
Researchers randomly assigned college students to drink either water or two cans of Red Bull. Immediately afterwards, all students completed the GRE. The researchers concluded that Red Bull had essentially no effect on GRE scores. Which result matches this conclusion?
dunbiased = 0.01, 95% CI [?0.02, 0.04]
dunbiased= 1.0, 95% CI [0.8, 1.2]
dunbiased= -1.0, 95% CI [?1.2, ?0.8]
dunbiased= 0.01, 95% CI [?2.0, 2.0]
9.
A researcher randomly assigns participants to either an exercise group or a sleep group before taking a motor-skills test. She uses the NHST approach, with a null hypothesis thatMsleep- Mexercise= 0 and an ? of 0.05. She reports:t(38) = 3.02,p= 0.004. Which of the following is the best answer?
This is a statistically significant finding.
The 95% CI for Msleep- Mexercisewill include 0.
The likelihood of Type I error is high.
The researcher will fail to reject the null hypothesis.
10.
For the same study described in the previous question, imagine that the researcher had not randomly assigned participants to sleep or exercise. Instead, imagine that she recruited participants and split them into two groups based on whether or not, in the hour before the study, they happened to have slept or exercised. What would be different about this approach?
Because sleep and exercise are measured differently, it would be necessary to use d.
Without random assignment, the NHST approach cannot be used.
Without random assignment, no confidence interval can be calculated.
Without random assignment, the researcher cannot draw causal conclusions.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


