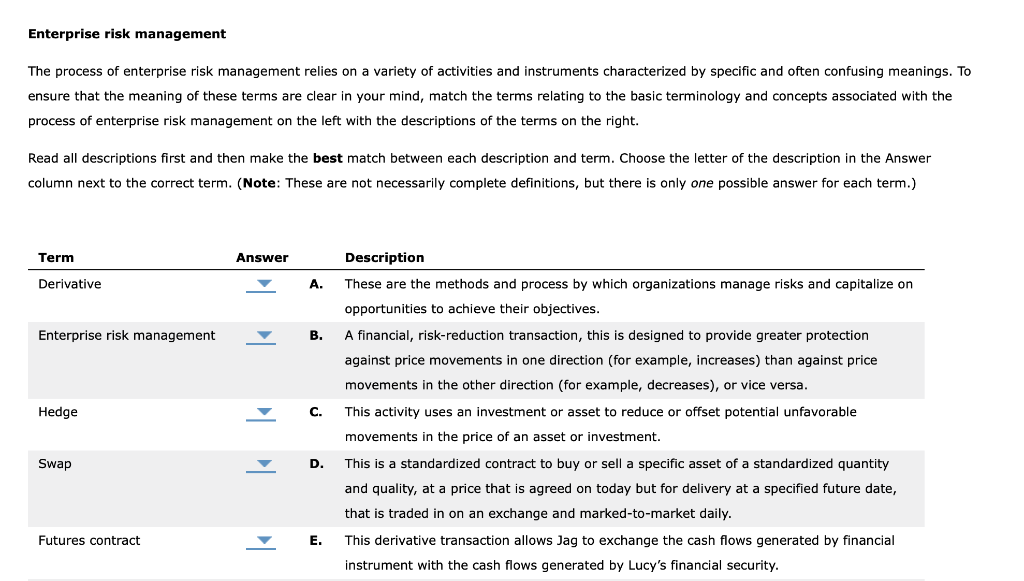

Enterprise risk management The process of enterprise risk management relies on a variety of activities and instruments characterized by specific and often confusing meanings. To ensure that the meaning of these terms are clear in your mind, match the terms relating to the basic terminology and concepts associated with the process of enterprise risk management on the left with the descriptions of the terms on the right. Read all descriptions first and then make the best match between each description and term. Choose the letter of the description in the Answer column next to the correct term. (Note: These are not necessarily complete definitions, but there is only one possible answer for each term.) Term Answer Derivative A. Enterprise risk management B. Hedge C. Description These are the methods and process by which organizations manage risks and capitalize on opportunities to achieve their objectives. A financial, risk-reduction transaction, this is designed to provide greater protection against price movements in one direction (for example, increases) than against price movements in the other direction (for example, decreases), or vice versa. This activity uses an investment or asset to reduce or offset potential unfavorable movements in the price of an asset or investment. This is a standardized contract to buy or sell a specific asset of a standardized quantity and quality, at a price that is agreed on today but for delivery at a specified future date, that is traded in on an exchange and marked-to-market daily. This derivative transaction allows Jag to exchange the cash flows generated by financial instrument with the cash flows generated by Lucy's financial security. Swap D. Futures contract E. Perfect hedge F. In this transaction, a futures contract-and the underlying asset-is purchased to protect the hedger against potential price increases on either physical commodities or financial assets. The hedger may elect to take future physical delivery of the underlying asset on the delivery date specified in the futures contract. Natural hedge G. The value of this security depends on the market price or interest rate of another security or asset. Asymmetric hedge o H. This nonstandardized financial contract allows a business or individual to purchase or sell an asset today at a price agreed on today but with the physical delivery of the asset occurring at some agreed-on date in the future. Long hedge I. In this transaction, a business or individual invests in two different assets or cash flow- generating activities, and the cash flows produced by the assets are mirror images of one another. As a result of this transaction, the risk associated with one asset can be reduced or exactly offset by the second asset. Forward contract J. This financial transaction uses a second, different financial instrument to exactly cancel out, or offset, the risk of an unhedged financial instrument or transaction. Enterprise risk management The process of enterprise risk management relies on a variety of activities and instruments characterized by specific and often confusing meanings. To ensure that the meaning of these terms are clear in your mind, match the terms relating to the basic terminology and concepts associated with the process of enterprise risk management on the left with the descriptions of the terms on the right. Read all descriptions first and then make the best match between each description and term. Choose the letter of the description in the Answer column next to the correct term. (Note: These are not necessarily complete definitions, but there is only one possible answer for each term.) Term Answer Derivative A. Enterprise risk management B. Hedge C. Description These are the methods and process by which organizations manage risks and capitalize on opportunities to achieve their objectives. A financial, risk-reduction transaction, this is designed to provide greater protection against price movements in one direction (for example, increases) than against price movements in the other direction (for example, decreases), or vice versa. This activity uses an investment or asset to reduce or offset potential unfavorable movements in the price of an asset or investment. This is a standardized contract to buy or sell a specific asset of a standardized quantity and quality, at a price that is agreed on today but for delivery at a specified future date, that is traded in on an exchange and marked-to-market daily. This derivative transaction allows Jag to exchange the cash flows generated by financial instrument with the cash flows generated by Lucy's financial security. Swap D. Futures contract E. Perfect hedge F. In this transaction, a futures contract-and the underlying asset-is purchased to protect the hedger against potential price increases on either physical commodities or financial assets. The hedger may elect to take future physical delivery of the underlying asset on the delivery date specified in the futures contract. Natural hedge G. The value of this security depends on the market price or interest rate of another security or asset. Asymmetric hedge o H. This nonstandardized financial contract allows a business or individual to purchase or sell an asset today at a price agreed on today but with the physical delivery of the asset occurring at some agreed-on date in the future. Long hedge I. In this transaction, a business or individual invests in two different assets or cash flow- generating activities, and the cash flows produced by the assets are mirror images of one another. As a result of this transaction, the risk associated with one asset can be reduced or exactly offset by the second asset. Forward contract J. This financial transaction uses a second, different financial instrument to exactly cancel out, or offset, the risk of an unhedged financial instrument or transaction








