Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Ethylbenzene is converted to styrene in the catalytic dehydrogenation reaction: C 8 H 1 0 ( g ) C 8 H 8 ( g )
Ethylbenzene is converted to styrene in the catalytic dehydrogenation reaction:
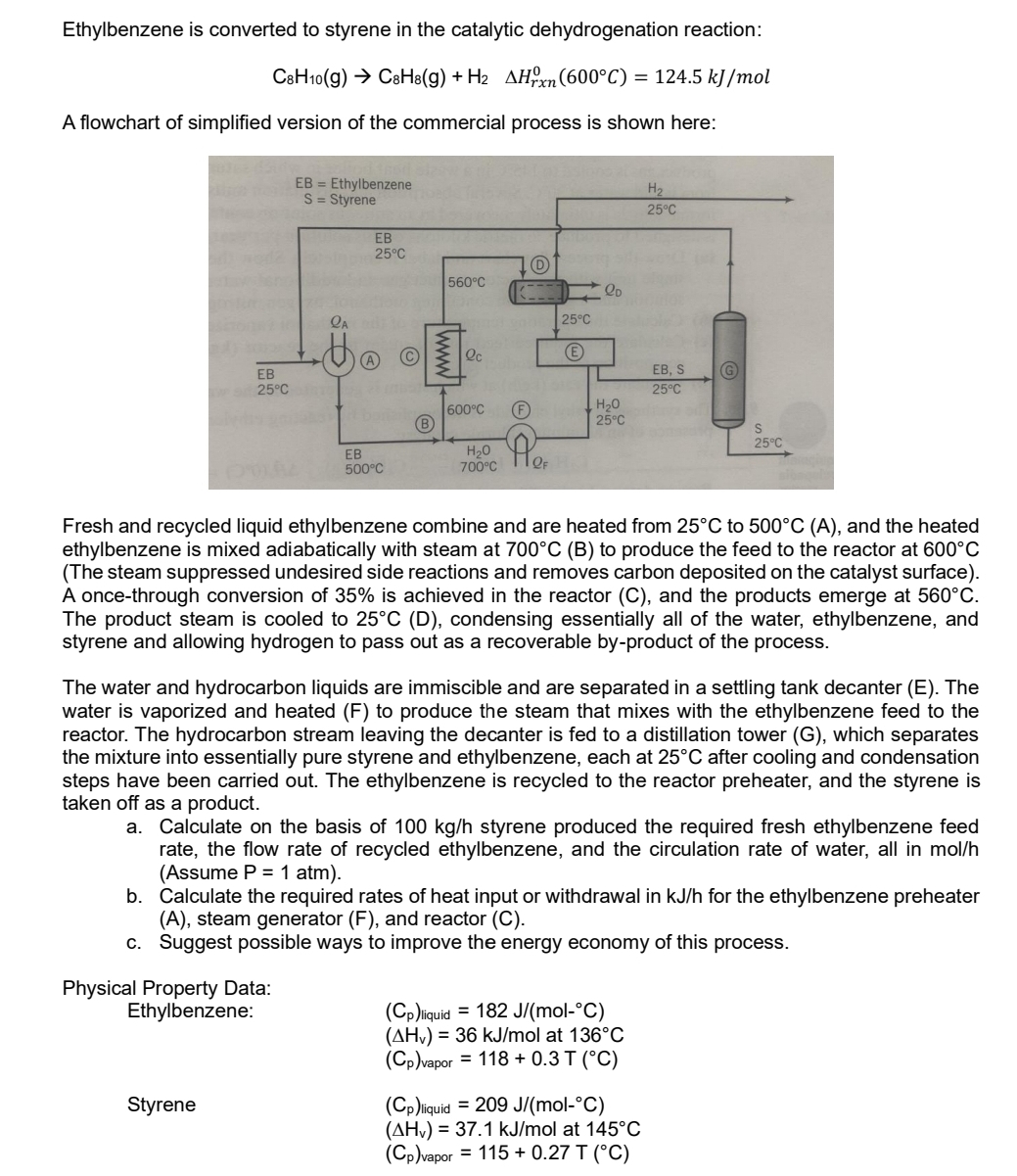
A flowchart of simplified version of the commercial process is shown here:
Fresh and recycled liquid ethylbenzene combine and are heated from to and the heated ethylbenzene is mixed adiabatically with steam at to produce the feed to the reactor at The steam suppressed undesired side reactions and removes carbon deposited on the catalyst surface A oncethrough conversion of is achieved in the reactor C and the products emerge at The product steam is cooled to D condensing essentially all of the water, ethylbenzene, and styrene and allowing hydrogen to pass out as a recoverable byproduct of the process.
The water and hydrocarbon liquids are immiscible and are separated in a settling tank decanter E The water is vaporized and heated to produce the steam that mixes with the ethylbenzene feed to the reactor. The hydrocarbon stream leaving the decanter is fed to a distillation tower G which separates the mixture into essentially pure styrene and ethylbenzene, each at after cooling and condensation steps have been carried out. The ethylbenzene is recycled to the reactor preheater, and the styrene is taken off as a product.
a Calculate on the basis of styrene produced the required fresh ethylbenzene feed rate, the flow rate of recycled ethylbenzene, and the circulation rate of water, all in Assume atm.
b Calculate the required rates of heat input or withdrawal in for the ethylbenzene preheater steam generator and reactor
c Suggest possible ways to improve the energy economy of this process.
Physical Property Data:
Ethylbenzene:
Styrene
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


