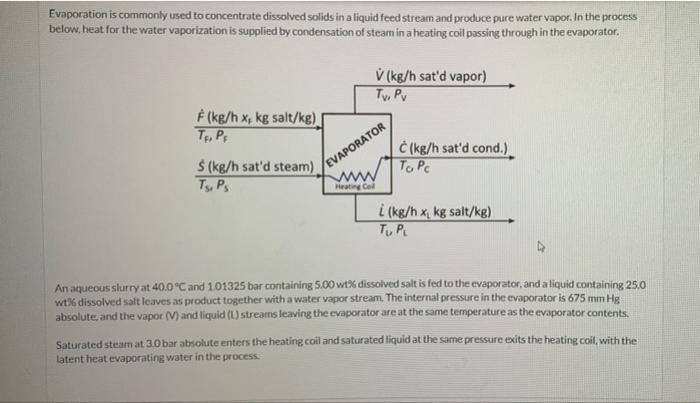
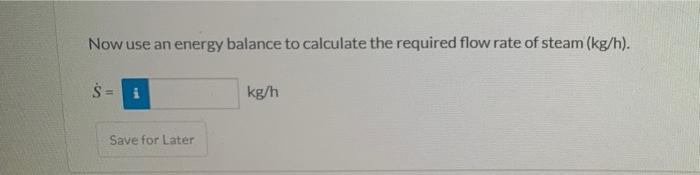
Evaporation is commonly used to concentrate dissolved solids in a liquid feed stream and produce pure water vapor. In the process below. beat for the water vaporization is supplied by condensation of steam in a heating coil passing through in the evaporator. V (kg/h sat'd vapor) Tv. Pv (kg/hx, kg salt/kg) TAP EVAPORATOR (kg/h sat'd cond.) To Pc $(kg/h sat'd steam) Tsips Heating i (kg/h xi kg salt/kg) TUPU An aqueous slurry at 40.0C and 101325 bar containing 5.00 wt% dissolved salt is fed to the evaporator, and a liquid containing 25.0 wt% dissolved salt leaves as product together with a water vapor stream. The internal pressure in the evaporator is 675 mmHg absolute, and the vapor (V) and liquid (L) streams leaving the evaporator are at the same temperature as the evaporator contents. Saturated steam at 3.0 bar absoluto enters the heating coil and saturated liquid at the same pressure exits the heating coil, with the latent heat evaporating water in the process. Now use an energy balance to calculate the required flow rate of steam (kg/h). S = kg/h Save for Later Evaporation is commonly used to concentrate dissolved solids in a liquid feed stream and produce pure water vapor. In the process below. beat for the water vaporization is supplied by condensation of steam in a heating coil passing through in the evaporator. V (kg/h sat'd vapor) Tv. Pv (kg/hx, kg salt/kg) TAP EVAPORATOR (kg/h sat'd cond.) To Pc $(kg/h sat'd steam) Tsips Heating i (kg/h xi kg salt/kg) TUPU An aqueous slurry at 40.0C and 101325 bar containing 5.00 wt% dissolved salt is fed to the evaporator, and a liquid containing 25.0 wt% dissolved salt leaves as product together with a water vapor stream. The internal pressure in the evaporator is 675 mmHg absolute, and the vapor (V) and liquid (L) streams leaving the evaporator are at the same temperature as the evaporator contents. Saturated steam at 3.0 bar absoluto enters the heating coil and saturated liquid at the same pressure exits the heating coil, with the latent heat evaporating water in the process. Now use an energy balance to calculate the required flow rate of steam (kg/h). S = kg/h Save for Later